 W
WAlbula is a genus of fish belonging to the bonefish family Albulidae.
 W
WBananogmius is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in what is today Kansas during the Late Cretaceous. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway, which split North America in two during the Late Cretaceous.
 W
WCimolichthys is an extinct genus of 1.5- to 2.0-meter-long nektonic predatory aulopiformid fish.
 W
WCretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the Late Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, Carcharocles angustidens, and Carcharocles megalodon.
 W
WCretoxyrhina is an extinct genus of large mackerel shark that lived about 107 to 73 million years ago during the late Albian to late Campanian of the Late Cretaceous period. The type species, C. mantelli, is more commonly referred to as the Ginsu shark, first popularized in reference to the Ginsu knife, as its theoretical feeding mechanism is often compared with the "slicing and dicing" when one uses the knife. Cretoxyrhina is traditionally classified as the likely sole member of the family Cretoxyrhinidae but other taxonomic placements have been proposed, such as within the Alopiidae and Lamnidae.
 W
WEnchodus is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of Enchodus flourished during the Late Cretaceous, and survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, persisting into the late Eocene.
 W
WEotrachodon orientalis is a species of hadrosaurid that was described in 2016. The holotype was found in the Mooreville Chalk Formation in Alabama in 2007 and includes a well-preserved skull and partial skeleton, making it a rare find among dinosaurs of Appalachia. Another primitive hadrosaur, Lophorhothon, is also known from the same formation, although Eotrachodon lived a few million years prior. A phylogenetic study has found Eotrachodon to be the sister taxon to the hadrosaurid subfamilies Lambeosaurinae and Saurolophinae. This, along with the other Appalachian hadrosaur Hadrosaurus and possibly Lophorhothon, Claosaurus and both species of Hypsibema, suggests that Appalachia was the ancestral area of Hadrosauridae.
 W
WGlobidens is an extinct genus of mosasaur lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily.
 W
WIchthyodectes is an extinct genus of Ichthyodectidae fish which lived during the Late Cretaceous. Fossils of the species included have been found from Canada to Texas.
 W
WIchthyornis is an extinct genus of toothed seabird-like ornithuran from the late Cretaceous period of North America. Its fossil remains are known from the chalks of Alberta, Alabama, Kansas, New Mexico, Saskatchewan, and Texas, in strata that were laid down in the Western Interior Seaway during the Turonian through Campanian ages, about 95–83.5 million years ago. Ichthyornis is a common component of the Niobrara Formation fauna, and numerous specimens have been found.
 W
WIschyodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fish belonging to the subclass Holocephali, which includes the modern-day chimaeras. Fossils are known from Europe, North America, and New Zealand.
 W
WLophorhothon is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, the first genus of dinosaur discovered in Alabama, in the United States.
 W
WMosasaurus is the type genus of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The earliest fossils known to science were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 1700s, which were initially thought to have been the bones of crocodiles or whales. One particular skull discovered at around 1780, and which was seized during the French Revolutionary Wars for its scientific value and transported to Paris, was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any animal known today. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. However, Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the new animal; this task was completed by William Daniel Conybeare in 1822 when he named it Mosasaurus in reference to its origin in fossil deposits near the Meuse River; the name is accordingly a portmanteau derived from the words Mosa and saurus. The relationships between Mosasaurus and modern reptiles are controversial and scientists continue to debate whether its closest living relatives are monitor lizards or snakes.
 W
WOdontaspis is a genus of sand shark with two extant species.
 W
WPachyrhizodus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous in the Western Interior Seaway in North America and in Colombia, South America. The type species is P. basalis. The species P. etayoi, described in 1997 by María Páramo from the La Frontera Formation in Colombia, was named honouring Colombian geologist and paleontologist Fernando Etayo.
 W
WPrognathodon is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like Mosasaurus and Clidastes. Prognathodon has been recovered from deposits ranging in age from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian in the Middle East, Europe and North America.
 W
WProtostega is an extinct genus of sea turtle containing a single species, Protostega gigas. Its fossil remains have been found in the Smoky Hill Chalk formation of western Kansas and time-equivalent beds of the Mooreville Chalk Formation of Alabama. Fossil specimens of this species were first collected in 1871, and named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1872. With a length of 3 metres (9.8 ft), it is the second-largest sea turtle that ever lived, second only to the giant Archelon, and the third-largest turtle of all time behind Archelon and Stupendemys.
 W
WPseudocorax is an extinct genus of shark with two species. It is known from the Cretaceous of Egypt, parts of Eurasia, and the United States. Its name stands for "false raven", due to the similarity of its teeth to those of Squalicorax. While originally considered to be a member of the family Anacoracidae, a study in 2012 moved it and Galeocorax into the new family Pseudocoracidae, making it only distantly related to Squalicorax.
 W
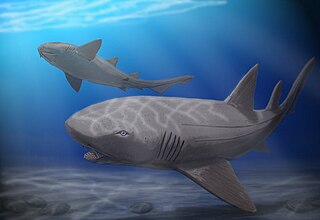
WPtychodus is a genus of extinct hybodontiform sharks. As well as a genus of durophagous (shell-crushing) sharks from the Late Cretaceous. Fossils of Ptychodus teeth are found in many Late Cretaceous marine sediments. There are many species among the Ptychodus that have been uncovered on all the continents around the globe. Such species are Ptychodus mortoni, P. decurrens, P. marginalis, P. mammillaris, P. rugosus and P. latissimus to name a few. They died out approximately 85 million years ago in the Western Interior Sea, where a majority of them were found. A recent publication found that Ptychodus are classified as neoselachian versus hybodont or batoid.
 W
WSaurodon is an extinct genus of Ichthyodectid fish from the Cretaceous.
 W
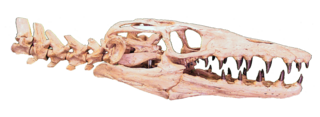
WScapanorhynchus is an extinct genus of shark that lived from the early Cretaceous until possibly the Miocene if S. subulatus is a mitsukurinid and not a sand shark. Their extreme similarities to the living goblin shark, Mitsukurina owstoni, lead some experts to consider reclassifying it as Scapanorhynchus owstoni. However, most shark specialists regard the goblin shark to be distinct enough from its prehistoric relatives to merit placement in its own genus.
 W
WSelmasaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Plioplatecarpinae subfamily alongside genera like Angolasaurus and Platecarpus. Two species are known, S. russelli and S. johnsoni, both are exclusively known from Santonian deposits in the United States.
 W
WSerratolamna is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks belonging to the family Cretoxyrhinidae.
 W
WSqualicorax is a genus of extinct lamniform shark known to have lived during the Cretaceous period.
 W
WToxochelys is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas.
 W
WXiphactinus is an extinct genus of large predatory marine bony fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous. When alive, the fish would have resembled a gargantuan, fanged tarpon. The species Portheus molossus described by Cope is a junior synonym of X. audax. Skeletal remains of Xiphactinus have come from the Carlile Shale and Greenhorn Limestone of Kansas, and Cretaceous formations all over the East Coast in the United States, as well as Europe, Australia, the Kanguk and Ashville Formations of Canada,, La Luna Formation of Venezuela and the Salamanca Formation in Argentina.