 W
WLandscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. Concisely, landscape ecology can be described as the science of landscape diversity as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity.
 W
WConservation biology is the management of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions. It is an interdisciplinary subject drawing on natural and social sciences, and the practice of natural resource management.
 W
WMonarch Watch is a volunteer-based citizen science organization that tracks the fall migration of the monarch butterfly. It is self-described as "a nonprofit education, conservation, and research program based at the University of Kansas that focuses on the monarch butterfly, its habitat, and its spectacular fall migration."
 W
WBiogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms.
 W
WCross-boundary subsidies are caused by organisms or materials that cross or traverse habitat patch boundaries, subsidizing the resident populations. The transferred organisms and materials may provide additional predators, prey, or nutrients to resident species, which can affect community and food web structure. Cross-boundary subsidies of materials and organisms occur in landscapes composed of different habitat patch types, and so depend on characteristics of those patches and on the boundaries in between them. Human alteration of the landscape, primarily through fragmentation, has the potential to alter important cross-boundary subsidies to increasingly isolated habitat patches. Understanding how processes that occur outside of habitat patches can affect populations within them may be important to habitat management.
 W
WIn ecology, a disturbance is a temporary change in environmental conditions that causes a pronounced change in an ecosystem. Disturbances often act quickly and with great effect, to alter the physical structure or arrangement of biotic and abiotic elements. A disturbance can also occur over a long period of time and can impact the biodiversity within an ecosystem.
 W
WIn ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors and how it in turn alters those same factors. "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".
 W
WThe ecology of fear is a conceptual framework describing the psychological impact that predator-induced stress experienced by animals has on populations and ecosystems. Within ecology, the impact of predation has been traditionally viewed as limited to the animals that they directly kill, while the ecology of fear advances evidence that predators may have a far more substantial impact on the individuals that they predate, reducing fecundity, survival and population sizes. To avoid being killed, animals that are preyed upon will employ anti-predator defenses which aid survival but may carry substantial costs.
 W
WAn ecosystem engineer is any animal that creates, significantly modifies, maintains or destroys a ecosystem (ecology)|habitat]]. These organisms can have a large impact on species richness and landscape-level heterogeneity of an area. As a result, ecosystem engineers are important for maintaining the health and stability of the environment they are living in. Since all organisms impact the environment they live in in one way or another, it has been proposed that the term "ecosystem engineers" be used only for keystone species whose behavior very strongly affects other organisms.
 W
WAn ecotone is a transition area between two biological communities, where two communities meet and integrate. It may be narrow or wide, and it may be local or regional. An ecotone may appear on the ground as a gradual blending of the two communities across a broad area, or it may manifest itself as a sharp boundary line.
 W
WIn evolutionary ecology, an ecotype, sometimes called ecospecies, describes a genetically distinct geographic variety, population or race within a species, which is genotypically adapted to specific environmental conditions.
 W
WIn ecology, edge effects are changes in population or community structures that occur at the boundary of two or more habitats. Areas with small habitat fragments exhibit especially pronounced edge effects that may extend throughout the range. As the edge effects increase, the boundary habitat allows for greater biodiversity.
 W
WIn ecology, habitat identifies is the array of resources, physical and biotic factors, present in an area that allow the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation its ecological niche. Thus, habitat is a specie-specific therm, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the therm habitat-type is more appropriate.
 W
WThe intermediate disturbance hypothesis (IDH) suggests that local species diversity is maximized when ecological disturbance is neither too rare nor too frequent. At low levels of disturbance, more competitive organisms will push subordinate species to extinction and dominate the ecosystem. At high levels of disturbance, due to frequent forest fires or human impacts like deforestation, all species are at risk of going extinct. According to IDH theory, at intermediate levels of disturbance, diversity is thus maximized because species that thrive at both early and late successional stages can coexist. IDH is a nonequilibrium model used to describe the relationship between disturbance and species diversity. IDH is based on the following premises: First, ecological disturbances have major effects on species richness within the area of disturbance. Second, interspecific competition results from one species driving a competitor to extinction and becoming dominant in the ecosystem. Third, moderate ecological scale disturbances prevent interspecific competition.
 W
WLandscape and Urban Planning is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Elsevier. It covers landscape science, urban and regional planning, landscape and ecological engineering, landscape and urban ecology, and other practice-oriented fields. The editors-in-chief are Joan I. Nassauer and Peter H. Verburg.
 W
WLandscape genetics is the scientific discipline that combines population genetics and landscape ecology. It broadly encompasses any study that analyses plant or animal population genetic data in conjunction with data on the landscape features and matrix quality where the sampled population lives. This allows for the analysis of microevolutionary processes affecting the species in light of landscape spatial patterns, providing a more realistic view of how populations interact with their environments. Landscape genetics attempts to determine which landscape features are barriers to dispersal and gene flow, how human-induced landscape changes affect the evolution of populations, the source-sink dynamics of a given population, and how diseases or invasive species spread across landscapes.
 W
WLandscape-scale conservation is a holistic approach to landscape management, aiming to reconcile the competing objectives of nature conservation and economic activities across a given landscape. Landscape-scale conservation may sometimes be attempted because of climate change. It can be seen as an alternative to site based conservation.
 W
WA metapopulation consists of a group of spatially separated populations of the same species which interact at some level. The term metapopulation was coined by Richard Levins in 1969 to describe a model of population dynamics of insect pests in agricultural fields, but the idea has been most broadly applied to species in naturally or artificially fragmented habitats. In Levins' own words, it consists of "a population of populations".
 W
WAlbert Morris, was a highly acclaimed amateur Australian botanist, landscaper, ecologist, conservationist and pioneer developer of the re-vegetation technique natural regeneration, who also utilised restoration principles that are today known as ecological restoration.
 W
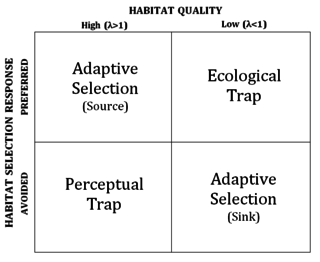
WA perceptual trap is an ecological scenario in which environmental change, typically anthropogenic, leads an organism to avoid an otherwise high-quality habitat. The concept is related to that of an ecological trap, in which environmental change causes preference towards a low-quality habitat.
 W
WRestoration ecology is the scientific study supporting the practice of ecological restoration, which is the practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human intervention and action. Effective restoration requires an explicit goal or policy, preferably an unambiguous one that is articulated, accepted, and codified. Restoration goals reflect societal choices from among competing policy priorities, but extracting such goals is typically contentious and politically challenging.
 W
WThe barrier effect of roads and highways is a phenomenon usually associated with landscape ecology, referring to the barrier that linear infrastructure like roads c or railways place on the movement of animals. Largely viewed as a negative process, the barrier effect has also been found to have several positive effects, particularly with smaller species. To reduce a road or railway's barrier effect, wildlife crossings are regarded as one of the best mitigation options, ideally in combination with wildlife fencing. The barrier effect is closely linked to habitat fragmentation and road ecology.
 W
WA shade tree is a large tree whose primary role is to provide shade in the surrounding environment due to its spreading canopy and crown, where it may give shelter from sunlight in the heat of the summer for people who seek recreational needs in urban parks and house yards, and thus, also protecting them from the sun's harmful UV rays and sunburns. Therefore, some shade trees may be grown specifically for the comfort of the population due to their convenient shelter.
 W
WSpecies distribution modelling (SDM), also known as environmental (or ecological) niche modelling (ENM), habitat modelling, predictive habitat distribution modelling, and range mapping uses computer algorithms to predict the distribution of a species across geographic space and time using environmental data. The environmental data are most often climate data, but can include other variables such as soil type, water depth, and land cover. SDMs are used in several research areas in conservation biology, ecology and evolution. These models can be used to understand how environmental conditions influence the occurrence or abundance of a species, and for predictive purposes. Predictions from an SDM may be of a species’ future distribution under climate change, a species’ past distribution in order to assess evolutionary relationships, or the potential future distribution of an invasive species. Predictions of current and/or future habitat suitability can be useful for management applications.
 W
WA stone stripe, also called a lava stringer, is an elongated concentration of mostly talus-like basalt rock found along a hillside or the base of a cliff. Many stringers occur without cliffs. A stringer is identified by its lack of vegetative cover. They typically occur in north central Oregon and develop at 900 to 1,100 meter elevations. Lengths can range from only a few meters to over 150 meters, and widths measure from .3 to 3 meters. Depths of the stringers range from 20-65 centimeters.
 W
WCarl Troll, was a German geographer, brother of botanist Wilhelm Troll. From 1919 until 1922 Troll studied biology, chemistry, geology, geography and physics at the Universität in München. In 1921 he obtained his doctorate in botany and in 1925 his habilitation in geography. Between 1922 and 1927 he worked as an assistant at the Geography Institute in Munich. Troll was engaged in research in the ecology and geography of mountainous lands: between 1926 and 1929 went on a research journey throughout South American Andean countries where he visited northern Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Panama. In 1933 and 1934 his research interests took him to East and South Africa; in 1937 Troll was in Ethiopia; and in 1954 he visited Mexico.
 W
WA windbreak (shelterbelt) is a planting usually made up of one or more rows of trees or shrubs planted in such a manner as to provide shelter from the wind and to protect soil from erosion. They are commonly planted in hedgerows around the edges of fields on farms. If designed properly, windbreaks around a home can reduce the cost of heating and cooling and save energy. Windbreaks are also planted to help keep snow from drifting onto roadways or yards. Farmers sometimes use windbreaks to keep snow drifts on farm land that will provide water when the snow melts in the spring. Other benefits include contributing to a microclimate around crops, providing habitat for wildlife, and, in some regions, providing wood if the trees are harvested.