 W
WThe Aleutian Islands, also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying an area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about 1,200 mi (1,900 km) westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and mark a dividing line between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude and the easternmost by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line. While nearly all the archipelago is part of Alaska and is usually considered as being in the "Alaskan Bush", at the extreme western end, the small, geologically related Commander Islands belong to Russia.
 W
WArakamchechen Island is an island in the Bering Sea.
 W
WBering Island is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea.
 W
WBesboro Island is a small island in the Norton Sound, Bering Sea, off the shores of Alaska. It is located 11 miles (18 km) west of the mainland and 38 miles (61 km) southwest of Christmas Mountain, Nulato Hills.
 W
WBig Diomede Island is the western island of the two Diomede Islands in the middle of the Bering Strait. The island is a part of the Chukotsky District of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug of Russia. The border separating Russia and the United States runs north-south between the Diomede Islands.
 W
WThe Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands are a group of treeless, sparsely populated islands in the Bering Sea located about 175 kilometres (109 mi) east of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East. The islands consist of Bering Island, Medny Island and fifteen smaller ones, the largest of which are Tufted Puffin Rock , 15 hectares, and Kamen Ariy, which are between 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) and 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) west of the only settlement, Nikolskoye. Administratively, they compose Aleutsky District of Kamchatka Krai in Russia.
 W
WThe Diomede Islands, also known in Russia as Gvozdev Islands, consist of two rocky, mesa-like islands:The Russian island of Big Diomede, also known as Imaqliq, Inaliq, Nunarbuk or Ratmanov Island The U.S. island of Little Diomede or Ignaluk, also known as Krusenstern Island
 W
WFairway Rock is a small islet in the Bering Strait, located southeast of the Diomede Islands and west of Alaska's Cape Prince of Wales. It has an area of 0.3 km2 (0.12 mi2). Known to Eskimo natives of the Bering Strait region in prehistory, Fairway was documented by James Cook in 1778 and named by Frederick Beechey in 1826. Although uninhabited, the island is a nesting site for seabirds — most notably the least and crested auklet — which prompt egg-collecting visits from local indigenous peoples. The United States Navy placed radioisotope thermoelectric generator-powered environmental monitoring equipment on the island from the 1960s through the 1990s.
 W
WHagemeister Island is an island in the U.S. state of Alaska, located on the north shore of Bristol Bay at the entrance to Togiak Bay.
 W
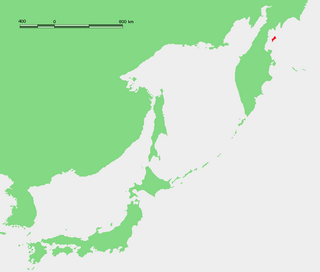
WHall Island is a small island located 3.5 miles (5.6 km) to the northwest of St. Matthew Island in the Bering Sea in Alaska, United States. It serves as a haulout site for Pacific walrus. It is 5 miles (8.0 km) in length and has a land area of 6.1758 square miles (15.995 km2). The highest point is 1,610 feet (490 m). Hall Island is uninhabited. It is part of the Bering Sea unit of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. It is one of three hall islands.
 W
WKaraginsky Island or Karaginskiy Island is an island in the Karaginsky Gulf of the Bering Sea. The 40 km (25 mi)-wide strait between the Kamchatka Peninsula and this island is called Litke Strait. Karaginsky Island is a Ramsar site.
 W
WKing Island is an island in the Bering Sea, west of Alaska. It is about 40 miles (64 km) west of Cape Douglas and is south of Wales, Alaska.
 W
WLittle Diomede Island or “Yesterday Isle” is an island of Alaska, United States. It is the smaller of the two Diomede Islands located in the middle of the Bering Strait between the Alaska mainland and Siberia.
 W
WMedny Island, also spelled Mednyy or Mednyi, sometimes called Copper Island in English, is the smaller of the two main islands in the Commander Islands in the North Pacific Ocean, east of Kamchatka, Russia. These islands belong to the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation.
 W
WNelson Island is an island in the Bethel Census Area of southwestern Alaska. It is 42 miles (68 km) long and 20–35 miles (32–56 km) wide. With an area of 843 square miles (2,183 km²), it is the 15th largest island in the United States. It is separated from the Alaska mainland to its north by the Ningaluk River, to its east by the Kolavinarak River and from Nunivak Island to its southwest by the Etolin Strait.
 W
WNunivak Island is a permafrost-covered volcanic island lying about 30 miles (48 km) offshore from the delta of the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers in the US state of Alaska, at a latitude of about 60° N. The island is 1,631.97 square miles (4,226.8 km2) in area, making it the second-largest island in the Bering Sea and eighth-largest island in the United States. It is 76.2 kilometers (47.3 mi) long and 106 kilometers (66 mi) wide. It has a population of 191 persons as of the 2010 census, down from 210 in 2000. The island's entire population lived in the north coast city of Mekoryuk.
 W
WThe Pribilof Islands are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about 200 miles (320 km) north of Unalaska and 200 miles (320 km) southwest of Cape Newenham. The Siberian coast is roughly 500 miles (800 km) northwest. About 77 square miles (200 km2) in total area, they are mostly rocky and are covered with tundra, with a population of 572 as of the 2010 census.
 W
WThe Punuk Islands are a chain of three small islets in the Bering Sea off the eastern end of St. Lawrence Island. They are located 8.5 km to the southeast of Cape Apavawook and 18 km to the southwest of Niyghapak Point.
 W
WSt. George Island is one of the Pribilof Islands of the state of Alaska, United States, in the Bering Sea off the western coast of the state. The island has a land area of 90 km² and a population of about 100 people, all living in its only community, the city of St. George, which encompasses the entire island.
 W
WSaint Paul Island is the largest of the Pribilof Islands, a group of four Alaskan volcanic islands located in the Bering Sea between the United States and Russia. The village of St. Paul is the only residential area on the island. The three nearest islands to Saint Paul Island are Otter Island to the southwest, Saint George slightly to the south, and Walrus Island to the east.
 W
WThe Seal Islands are a group of 12/+ islands in the Bering Sea, trending northeast 7 miles (11 km), close to the shores of Bristol Bay, Alaska, 33 miles (53 km) southwest of Port Heiden, Alaska Airfield; Bristol Bay Low.
 W
WSledge Island, or Ayak Island, is a small island in the Bering Sea. It is located 5.3 mi (8.5 km) from the southwestern shore of the Seward Peninsula, off the shores of Alaska.
 W
WSt. Matthew Island is a remote island in the Bering Sea in Alaska, 183 miles (295 km) west-northwest of Nunivak Island. The entire island's natural scenery and wildlife is protected as it is part of the Bering Sea unit of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge.
 W
WSt. Michael Island is an island on the southeast side of the Norton Sound in Alaska. The island is about 9.3 miles (15.0 km) long and 6.2 miles (10.0 km) wide.
 W
WStuart Island is an island on the southeast side of the Norton Sound of Alaska. The island is about 9.3 miles (15.0 km) long and 6.2 miles (10.0 km) wide with a land area of 52.195 square miles (135.18 km2) and had no resident population at the 2000 census. The name "Stuart's Island" was given during the third voyage of James Cook in September 1778.
 W
WWalrus Island is a small islet located 15 km east of Saint Paul Island, Alaska in the Bering Sea. It is part of the Pribilof Islands group. Its length is 2,130 feet (650 m) and its area is 50.3 acres (0.2036 km²). There is no resident population.
 W
WThe Walrus Islands are a group of craggy coastal islands in the Bering Sea, close to the northern shores of Bristol Bay, Alaska at the entrance to Togiak Bay. They are located 18 km to the east of Hagemeister Island, and are protected as the Walrus Islands State Game Sanctuary by the state. A part of the island group is also of archaeological importance, with numerous deeply stratified sites covering 6,000 years of human use. For this reason, Crooked Island, Summit Island and Round Island were designated the Walrus Islands Archeological District, a National Historic Landmark District comprising 14 historical sites, in December 2016.
 W
WYttygran Island is an island in the Bering Sea 24 kilometres northwest of Cape Chaplino, close to the coast of Chukotka.