 W
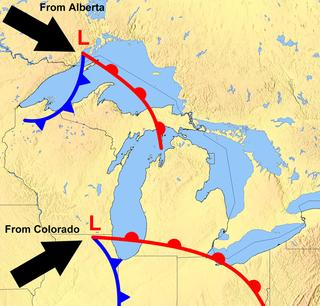
WAn Alberta clipper, also known as a Canadian clipper, is a fast moving low pressure area weather system which generally affects the central provinces of Canada and parts of the Upper Midwest, Great Lakes, and New England, precipitating a sudden temperature drop and sharp winds. Alberta clippers take their name from Alberta, the province from which they appear to descend, and from clipper ships of the 19th century, one of the fastest ships of that time.
 W
WA nor'easter is a macro-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. The original use of the term in North America is associated with storms that impact the upper north Atlantic coast of the United States and the Atlantic Provinces of Canada.
 W
WThe Great Lakes Storm of 1913, historically referred to as the "Big Blow," the "Freshwater Fury," or the "White Hurricane," was a blizzard with hurricane-force winds that devastated the Great Lakes Basin in the Midwestern United States and Ontario, Canada from November 7 through November 10, 1913. The storm was most powerful on November 9, battering and overturning ships on four of the five Great Lakes, particularly Lake Huron. Deceptive lulls in the storm and the slow pace of weather reports contributed to the storm's destructiveness.
 W
WThe blizzard of 1977 hit western New York as well as southern Ontario from January 28 to February 1. Daily peak wind gusts ranging from 46 to 69 mph were recorded by the National Weather Service in Buffalo, with snowfall as high as 100 in (254 cm) recorded in areas, and the high winds blew this into drifts of 30 to 40 ft. There were 23 total storm-related deaths in western New York, with five more in northern New York.
 W
WThe December 2009 North American Blizzard was a powerful nor'easter that formed over the Gulf of Mexico in December 2009, and became a major snowstorm that affected the East Coast of the United States and Canadian Atlantic provinces. The snowstorm brought record-breaking December snowfall totals to Washington, D.C., Baltimore, and Philadelphia.
 W
WThe February 5–6, 2010 North American blizzard, commonly referred to as Snowmageddon, was a paralyzing and crippling blizzard that had major and widespread impact in the Northeastern United States. The storm's center tracked from Baja California Sur on February 2nd, 2010 to the East coast on February 6, 2010, before heading east out into the Atlantic. Effects were felt to the north and west of this track in northern Mexico, California, and the Southwestern, Midwestern, Southeastern, and most notably Mid-Atlantic States. Severe weather, including extensive flooding and landslides in Mexico, and historic snowfall totals in every one of the Mid-Atlantic states, brought deaths to Mexico, New Mexico, Virginia, Pennsylvania and Maryland.
 W
WThe January 31 – February 2, 2011 North American winter storm, also called the 2011 Groundhog Day Blizzard, was a powerful and historic winter storm, situated around the United States and Canada on Groundhog Day. During the initial stages of the storm, some meteorologists predicted that the system would affect over 100 million people in the United States. The storm brought cold air, heavy snowfall, blowing snow, and mixed precipitation on a path from New Mexico and northern Texas to New England and Eastern Canada. The Chicago area saw 21.2 inches (54 cm) of snow and blizzard conditions, with winds of over 60 mph (100 km/h). With such continuous winds, the Blizzard continued to the north and affected Eastern and Atlantic Canada. The most notable area affected in Canada was Toronto and the Greater Toronto Area. Blizzard conditions affected many other large cities along the storm's path, including Tulsa, Oklahoma City, Kansas City, St. Louis, Springfield, El Paso, Las Cruces, Des Moines, Milwaukee, Detroit, Indianapolis, Dayton, Cleveland, New York City, New York's Capital District, and Boston. Many other areas not normally used to extreme winter conditions, including Albuquerque, Dallas and Houston, experienced significant snowfall or ice accumulation. The central Illinois National Weather Service in Lincoln, Illinois issued only their fourth Blizzard Warning in the forecast office's 16-year history. Snowfall amounts of 20 to 28 inches were forecast for much of Northern and Western Illinois.
 W
WThe Early February 2013 North American blizzard was a powerful blizzard that developed from the combination of two areas of low pressure, primarily affecting the Northeastern United States and parts of Canada, causing heavy snowfall and hurricane-force winds. The storm crossed the Atlantic Ocean, affecting Ireland and the United Kingdom. The nor'easter's effects in the United States received a Category 3 rank on the Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale, classifying it as a "Major" Winter Storm.
 W
WThe January 2015 North American blizzard was a powerful and severe blizzard that dumped up to 3 feet (910 mm) of snowfall in parts of New England. Originating from a disturbance just off the coast of the Northwestern United States on January 23, it initially produced a light swath of snow as it traveled southeastwards into the Midwest as an Alberta clipper on January 24–25. It gradually weakened as it moved eastwards towards the Atlantic Ocean, however, a new dominant low formed off the East Coast of the United States late on January 26, and rapidly deepened as it moved northeastwards towards southeastern New England, producing pronounced blizzard conditions. The nor’easter then gradually weakened as it moved away into Canada. The storm was also given unofficial names, such as Blizzard of 2015, and Winter Storm Juno.
 W
WThe January 2016 United States Blizzard was a crippling and historic nor'easter blizzard that produced up to 3 ft of snow in parts of the Mid-Atlantic and Northeast United States from January 22 to January 24, 2016. Evolving from a shortwave trough that formed in the Pacific Northwest on January 19, the system consolidated into a defined low-pressure area on January 21 over Texas. Regarding it as a "potentially historic blizzard", meteorologists indicated the storm could produce more than 2 ft (61 cm) of snow across a wide swath of the Mid-Atlantic region and could "paralyze the eastern third of the nation". Winter weather expert Paul Kocin described the blizzard as "kind of a top-10 snowstorm".
 W
WThe Mid-December 2007 North American winter storms were a series of winter storms that affected much of central and eastern North America, from December 8 to December 18, 2007. The systems affected areas from Oklahoma to Newfoundland and Labrador with freezing rain, thunderstorms, sleet, snow, damaging winds, and blizzard-like conditions in various areas. The first two storms produced copious amounts of ice across the Midwestern United States and Great Plains from December 8 to December 11, knocking out power to approximately 1.5 million customers from Oklahoma north to Iowa. The second storm moved northeast, producing heavy snow across New York and New England. A third storm was responsible for a major winter storm from Kansas to the Canadian Maritimes, bringing locally record-breaking snowfalls to Ontario, an icestorm across the Appalachians, and thunderstorms and tornadoes to the Southeastern United States.
 W
WNear the end of 2012, a massive storm complex developed that produced both a tornado outbreak and a blizzard across the southern and eastern United States. On Christmas Day 2012, a tornado outbreak occurred across Southern United States. This severe weather/tornado event affected the United States Gulf Coast and southern East Coast over a two-day span. It occurred in conjunction with a much larger winter storm event that brought blizzard conditions to much of the interior United States. In total, 31 tornadoes were confirmed by the National Weather Service in five states from Texas to North Carolina. All but one of the tornadoes that occurred during the outbreak touched down on December 25, with the other occurring the following day in North Carolina. Two of the tornadoes were destructive enough to be rated EF3 on the Enhanced Fujita Scale. At least 16 people died as a result of the related blizzard, and thousands were without power.
 W
WA historic snowstorm struck the Ohio Valley of the United States, as well as Ontario in Canada, on December 22 and December 23 and is not the same storm that led to snow in Texas on Christmas Eve. It lasted roughly 30 hours, and brought snowfall amounts up to 29 inches (74 cm) to portions of the Midwestern United States. Damages from the storm totaled US$900 million (2004 dollars). A total of 18 died during the storm, one from Canada, mainly due to car accidents.
 W
WThe December 2010 North American blizzard was a major nor'easter and historic blizzard affecting the Contiguous United States and portions of Canada from December 5–29, 2010. From January 4–15, the system was known as Windstorm Benjamin in Europe. It was the first significant winter storm of the 2010–11 North American winter storm season and the fifth North American blizzard of 2010. The storm system affected the northeast megalopolis, which includes major cities such as Norfolk, Philadelphia, Newark, New York City, Hartford, Providence, and Boston. The storm brought between 12 and 32 inches of snow in many of these areas.
 W
WThe December 17–22, 2012 North American blizzard was a winter storm that affected the Midwestern and Eastern United States. Forming on December 17, the winter storm moved across the midwest, forcing schools to close throughout the region. Numerous warnings and advisories had been posted by the National Weather Service for many states, including Iowa, Nebraska, Illinois, and Wisconsin. Both O'Hare International Airport and Midway International Airport in Chicago, Illinois canceled most departures and arrivals. According to flight tracking website FlightStats.com, more than 1,000 flights were canceled across the region. More than 130,000 customers were without power across the west and midwest.
 W
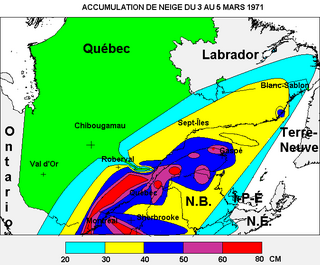
WThe Eastern Canadian blizzard of March 1971 was a severe winter storm that struck portions of eastern Canada from March 3 to March 5, 1971. The storm was also nicknamed the "Storm of the Century" in Quebec. The event included the worst 24-hour snowfall on record in the city of Montreal with 43 centimeters of snow falling on March 4, for a total of 47 centimeters, until the one-day record was broken again on December 27, 2012. Higher terrain in eastern Quebec received as much as 80 centimeters. Heavy snowfall was also recorded in eastern Ontario and northern New Brunswick as well as parts of the Northeastern United States. The storm itself was responsible for the deaths of 17 people in Montreal along with numerous other injuries directly and indirectly attributed to the blizzard.
 W
WThe February 2007 North American blizzard was a massive winter storm that affected most of the eastern half of North America, starting on February 12, 2007 and peaking on Valentine's Day, February 14. The storm produced heavy snowfalls across the midwestern United States from Nebraska to Ohio and produced similar conditions across parts of the northeastern United States, and into Canada in Ontario, Quebec and New Brunswick. Significant sleet and freezing rain fell across the southern Ohio Valley and affected portions of the east coast of the United States, including the cities of Boston, Baltimore, Washington, D.C., New York City and Philadelphia.
 W
WThe February 25–27, 2010 North American blizzard was a winter storm and severe weather event that occurred in the Mid-Atlantic and New England regions of the United States between February 24–26, 2010. The storm dropped its heaviest snow of 12 to 24 inches across a wide area of interior New England, New York, and Pennsylvania. The storm also brought flooding rains to coastal sections of New England, with some areas experiencing as much as 4 inches (10 cm). Aside from precipitation, the Nor'easter brought hurricane-force sustained winds to coastal New England.
 W
WThe Great Appalachian Storm of November 1950 was a large extratropical cyclone which moved through the Eastern United States, causing significant winds, heavy rainfall east of the Appalachian Mountains, and blizzard conditions along the western slopes of the mountains. Hurricane-force winds, peaking at 110 miles per hour (180 km/h) in Concord, New Hampshire, and 160 miles per hour (260 km/h) in the highlands of New England, disrupted power to 1 million customers during the event.
 W
WThe Great Blizzard of 1978 was a historic winter storm that struck the Ohio Valley and Great Lakes regions from Wednesday, January 25 through Friday, January 27, 1978. It is often cited as one of the most severe blizzards in US history. The third lowest non-tropical atmospheric pressure ever recorded in the mainland United States occurred as the storm passed over Mount Clemens, Michigan, where the barometer fell to 956.0 mb (28.23 inHg) on January 26.
 W
WThe Groundhog Day gale was a severe winter storm that hit the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada on February 2, 1976.
 W
WThe October 2006 Buffalo storm was an unusual early-season lake effect snow storm that hit the Buffalo, New York area and other surrounding areas of the United States and Canada, from the afternoon of Thursday, October 12 through the morning of Friday, October 13, 2006. It was called Lake Storm "Aphid" by the National Weather Service office in Buffalo in accordance with their naming scheme of lake effect snow storms for that year, which related to insects, though locals never used that terminology and have simply referred to it as the October Surprise or the October Storm or Arborgeddon.
 W
WThe March 2017 North American Blizzard was a major late-season blizzard that affected the Northeastern United States, New England and Canada, dumping up to 3 feet of snow in the hardest hit areas, mainly New York, Vermont, New Hampshire and Southern Quebec. Forming out of an extratropical cyclone near the Northwest, the storm system dived into the northern portions of the United States, dropping light to moderate snow across the Great Lakes, Upper Midwest on March 11–12 before reaching the Ohio Valley the next day. It later coalesced into a powerful nor'easter off the East Coast, producing a swath of heavy snowfall across a large portion of the Northeast. The storm was given various unofficial names, such as Winter Storm Stella, Blizzard Eugene, and Blizzard of 2017.
 W
WThe Blizzard of 2003, also known as the Presidents' Day Storm II or simply PDII, was an historic and record-breaking snowstorm on the East Coast of the United States and Canada, which lasted from February 14 to February 19, 2003. It spread heavy snow across the major cities of the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states, making it the defining snowstorm of the very snowy winter of 2002-2003.
 W
WThe North American blizzard of 2006 was a nor'easter that began on the evening of February 11, 2006. It dumped heavy snow across the Mid-Atlantic and New England states, from Virginia to Maine through the early evening of February 12, and ended in Atlantic Canada on February 13. The major cities from Baltimore to Boston received at least a foot of snow, with a second-highest amount of 26.9 inches (68.3 cm) in New York City, the most since at least 1869, the start of record keeping, only broken by the January 2016 United States blizzard nearly 10 years later.
 W
WThe North American blizzard of 2008 was a winter storm that struck most of southern and eastern North America from March 6 to March 10, 2008. The storm was most notable for a major winter storm event from Arkansas to Quebec. It also produced severe weather across the east coast of the United States with heavy rain, damaging winds and tornadoes, causing locally significant damage. The hardest hit areas by the wintry weather were from the Ohio Valley to southern Quebec where up to a half a meter of snow fell locally including the major cities of Columbus, Ohio, Cleveland, Ohio, and Ottawa, Ontario. For many areas across portions of the central United States, Ontario and Quebec, it was the worst winter storm in the past several years. The blizzard and its aftermath caused at least 17 deaths across four US states and three Canadian provinces, while hundreds others were injured mostly in weather-related accidents and tornadoes.
 W
WThe 2009 North American Christmas blizzard was a powerful winter storm and severe weather event that affected the Midwestern United States, Great Plains, Southeastern United States, the Eastern Seaboard, and parts of Ontario. The storm began to develop on December 22 before intensifying to produce extreme winds and precipitation by the morning of December 24. The storm's rapid development made it difficult for forecasters to predict. The blizzard was reported to have claimed at least 21 lives, and disrupted air travel during the Christmas travel season. In the Southeastern and Central United States, there were 27 reported tornadoes on December 23–24. The storm, a Category 5 "Extreme" one on the Regional Snowfall Index, was the first winter weather event to rank as such since the Blizzard of '96.
 W
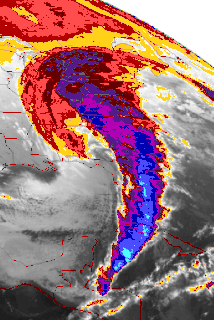
WThe Saskatchewan Blizzard of 2007 was a winter storm that struck northeastern British Columbia, central Alberta and central Saskatchewan on Wednesday, January 10, 2007. The storm hit the city of Saskatoon severely and is considered to be one of the worst storms in Saskatchewan's history. It brought motor vehicle traffic to a standstill, stranded people and shut down many public services. There were two fatalities from the storm.
 W
WThe 1993 Storm of the Century was a large cyclonic storm that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on March 12, 1993. The storm was unique and notable for its intensity, massive size, and wide-reaching effects; at its height, the storm stretched from Canada to Honduras. The cyclone moved through the Gulf of Mexico and then through the eastern United States before moving on to eastern Canada. The storm eventually dissipated in the North Atlantic Ocean on March 15.
 W
WWhite Juan is the unofficial name given to the hurricane-strength nor'easter blizzard of February 2004 that affected most of Atlantic Canada and the Eastern United States between February 17 and 20, 2004—five months after Hurricane Juan devastated Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island.