 W
WAetokremnos is a rock shelter near Limassol on the southern coast of Cyprus. It is situated on a steep cliff site c. 40 m (131.23 ft) above the Mediterranean sea. The name means "Cliff of the eagles" in Greek. Around 40 m2 (430.56 sq ft) have been excavated and out of the four layers documented, the third is sterile.
 W
WNahal Amud, also known as the Wadi al-Amud, is a stream in the Upper Galilee region of Israel that flows into the Sea of Galilee.
 W
WThe Argiles d'Octeville is a geological formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic. It is equivalent to the Kimmeridge Clay in England and predominantly consists of claystone, with some limestone. It is well exposed in cliff section at Cap de la Hève
 W
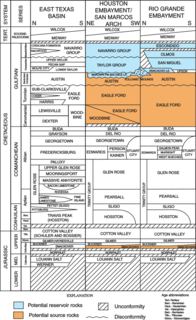
WThe Buda Limestone is a geological formation in the High Plains and Trans-Pecos regions of West Texas and in southern New Mexico, whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Pterosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WCave of Los Aviones, located at sea level near Cartagena in southeastern Spain, is a paleontology site dating back to the Middle Paleolithic era. It is famous for having yielded in 2010 several perforated and painted seashell beads thought to have been crafted as jewelry by Neanderthals.
 W
WCerro de los Batallones is a hill at Torrejón de Velasco, Madrid, Spain where a number of fossil sites from the Upper Miocene (MN10) have been found. Nine sites have been discovered with predominately vertebrate fossils, invertebrates and plants being less represented. The first deposits were discovered accidentally in July 1991.
 W
WThe Clarkia fossil beds is a Miocene lagerstätte near Clarkia, Idaho.
 W
WThe Cromer Forest Bed is a geological formation in Norfolk, England. It consists of river gravels, estuary and floodplain sediments predominantly clays and muds as well as sands along the coast of northern Norfolk. It is the type locality for the Cromerian Stage of the Pleistocene between 0.8 and 0.5 million years ago., The deposit itself range varies in age from about 2 to 0.5 million years ago. It is about 6 metres thick and is exposed in cliff section near the town of West Runton. For over a century the bed, named after the local town of Cromer, has been famous for its assemblage of fossil mammal remains, containing the diverse remains of numerous taxa, including deer, carnivorans and birds. Although most of the forest bed is now obscured by coastal defence, the Cromer Forest Bed continues to be eroded and is rich in fossils including the skeletal remains of the West Runton Mammoth which was discovered in 1990. The oldest human footprints outside Africa, the Happisburgh footprints as well as handaxes and bison bones with cut marks were also found in layers considered to belong to this deposit near the town of Happisburgh.
 W
WThe Dalangshan Formation, also referred to as the Dalangshan Group is a geological formation in the Sanshui District of Guangdong Province, China, the strata of which date back to the Late Cretaceous period.
 W
WDob's Linn is a small steep valley in Dumfries and Galloway, just north of the A708 road between Moffat and Selkirk, in Scotland. It is part of the Grey Mare's Tail Nature Reserve which is owned by the National Trust for Scotland. According to tradition, Dob's Linn is named for a covenanter, Halbert Dobson, who took refuge there from Government troops during The Killing Time in the late 17th century.
 W
WThe Fig Tree Formation, also called Fig Tree Group, is a stromatolite-containing geological formation in South Africa. The rock contains fossils of microscopic life forms of about 3.26 billion years old. Identified organisms include the bacterium Eobacterium isolatus and the algae-like Archaeosphaeroides barbertonensis. The fossils in the Fig Tree Formation are considered some of the oldest known organisms on Earth, and provide evidence that life may have existed much earlier than previously thought. The formation is composed of shales, turbiditic greywackes, volcaniclastic sandstones, chert, turbiditic siltstone, conglomerate, breccias, mudstones, and iron-rich shales.
 W
WHuangnitang is a village of Zhoutang village (周塘村), Tianma Subdistrict (天马街道), Changshan County, Quzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. It is the location of the Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP), whic1ãßßà, Gawande crescenth marks the boundary between the Third and Darriwilian Stages of the Middle Ordovician. The GSSP was ratified by the International Union of Geological Sciences in 1997.
 W
WThe Kanguk Formation is a geological formation in the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, Canada whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Lake Ngapakaldi to Lake Palankarinna Fossil Area is a group of fossil sites located in the Australian state of South Australia within the Tirari Desert in the north-eastern part of the state's Far North region. The group has an overall area of 35 square kilometres (14 sq mi) and is located about 70 kilometres (43 mi) east of Lake Eyre and about 100 kilometres (62 mi) north-north-east of Marree, off the Birdsville Track near Etadunna Station.
 W
WLong Mile Cave, sometimes known locally as Pick'ny Mama Cave or Hell's Gate Cave, is a palaeontological and palaeoanthropological site in the Cockpit Country of north-western Jamaica.
 W
WMammoth Cave is a large limestone cave 21 km (13 mi) south of the town of Margaret River in south-western Western Australia, and about 300 km (190 mi) south of Perth. It lies within the Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park and is surrounded by Karri and Marri forest. It has also had extinct animal fossils found in Mammoth Cave.
 W
WMelbourne Bone Bed is a paleontological site located at Crane Creek in Melbourne, in the U.S. state of Florida. This site contains fossils from the Late Pleistocene period 20,000 to 10,000 years before present. The fossils include extinct animals such as varieties of camels, giant armadillos, giant beavers, giant bison, giant ground sloths, mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed cats and tapirs.
 W
WThe Moodies Group is a geological formation in South Africa and Eswatini. It has the oldest well-preserved siliciclastic tidal deposits on Earth, where microbial mats flourished.
 W
WThe Moreno Hill Formation is a geological formation in western New Mexico whose strata were deposited in the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Paluxy Formation is a geological formation found in Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas, Mississippi and Oklahoma, whose strata date back to the Early Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Paw Paw Formation is a geological formation in Texas whose strata date back to the late Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Petrified Forest 30 km south of Sarmiento, Argentina is a provincial natural monument.
 W
WThe Point Loma Formation is a sedimentary geological formation in Southern California. The strata date back to the Late Cretaceous epochs of the Cretaceous period, during the Mesozoic Era.
 W
WRed Gulch Dinosaur Tracksite is an assemblage of fossil dinosaur footprints on public land near Shell, in Big Horn County, Wyoming.
 W
WThe Ryugase Group is a geological formation on Sakhalin Island in far eastern Russia whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous.
 W
WThe San Carlos Formation is a geological formation in west Texas whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Sanga do Cabral Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
 W
WThe Selma Group is a geological formation in North America, within the U.S. states of Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennessee. The strata date from the Santonian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The group is composed of, in ascending order, the Mooreville Chalk Formation, Demopolis Chalk Formation, Ripley Formation, and Prairie Bluff Chalk Formation. Dinosaur and mosasaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the Selma Group.
 W
WSuntar-Khayata Range is a granite mountain range rising along border of Sakha Republic in the north with Amur Oblast and Khabarovsk Krai in the south.
 W
WSwansea Cave is a cave and palaeontological site in the Saint Catherine Parish of south-eastern Jamaica.
 W
WThe Talbragar fossil site is a paleontological site of Late Jurassic (Tithonian) age in the central west of New South Wales, Australia. It lies about 30 kilometres (19 mi) north-east of the town of Gulgong, and 300 kilometres (190 mi) north-west of Sydney. The site has been known for over a century during which it has been extensively excavated to the point of near exhaustion. It is now registered as a Crown Land Reserve for the preservation of fossils; access is by permit, and the collection of rocks and fossil specimens is prohibited. The 4-hectare (9.9-acre) reserve is listed on the Register of the National Estate.