 W
WThe Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands is an uninhabited external territory of Australia consisting of four low-lying tropical islands in two separate reefs, and the 12-nautical-mile territorial sea generated by the islands. The territory is located in the Indian Ocean situated on the edge of the continental shelf, about 320 km (199 mi) off the northwest coast of Australia and 144 km (89 mi) south of the Indonesian island of Rote.
 W
WThe Bonin Islands, also known as the Ogasawara Islands , or, Yslas del Arzobispo, are an archipelago of over 30 subtropical and tropical islands, some 1,000 kilometres directly south of Tokyo, Japan. The name "Bonin Islands" comes from the Japanese word bunin, meaning "no people" or "uninhabited". The only inhabited islands of the group are Chichijima (父島), the seat of the municipal government, and Hahajima (母島).
 W
WThe Bounty Islands are a small group of 13 uninhabited granite islets and numerous rocks, with a combined area of 135 ha, in the South Pacific Ocean. Territorially part of New Zealand, they lie about 670 km (416 mi) east-south-east of New Zealand's South Island, 530 km (329 mi) south-west of the Chatham Islands, and 215 km (134 mi) north of the Antipodes Islands. The group is a World Heritage Site.
 W
WCampbell Island / Motu Ihupuku is an uninhabited subantarctic island of New Zealand, and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers 112.68 square kilometres (43.51 sq mi) of the group's 113.31 km2 (43.75 sq mi), and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island, Isle de Jeanette-Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the southernmost extremity of New Zealand. The island is mountainous, rising to over 500 metres (1,640 ft) in the south. A long fjord, Perseverance Harbour, nearly bisects it, opening out to sea on the east coast.
 W
WThe Chatham Islands, are a part of New Zealand, and form an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 kilometres (500 mi) east of the South Island. The archipelago consists of about ten islands within an approximate 60-kilometre (37 mi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. They include New Zealand's easternmost point, the Forty-Fours. Some of the islands, formerly cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.
 W
WThe Duke of York Islands are a group of islands located in East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea. They are found in St George's Channel between New Britain and New Ireland islands and form part of the Bismarck Archipelago. The Duke of York Islands were named in 1767 by Philip Carteret to honour Prince Edward, son of Frederick, Prince of Wales and younger brother of George III of the United Kingdom.
 W
WEaster Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. Easter Island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.
 W
WThe German–Spanish Treaty of 1899, signed by the German Empire and the Kingdom of Spain, involved Spain selling the vast majority of its remaining Pacific Ocean islands to Germany for 25 million pesetas.
 W
WGuam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States. The capital city of Guam is Hagåtña, and the most populous city is Dededo. Guam has been a member of the Pacific Community since 1983. The inhabitants of Guam are American citizens by birth. The indigenous Guamanians are the Chamorros, who are related to other Austronesian peoples of Indonesia, the Philippines, Taiwan, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
 W
WThe Happy Isles of Oceania is a travel book written by writer Paul Theroux and published in 1992. It is an account of a trip taken through the Pacific Islands shortly after the break-up of his first marriage. Starting in New Zealand, he travels to Australia and Papua New Guinea and then follows the clusters of islands throughout the Pacific Ocean, passing through Easter Island and finishing his trip in Hawaii.
 W
WHawaii is a state of the United States of America in the Pacific Ocean. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only island state, and the only state in the tropics.
 W
WJohnston Atoll, also known as Kalama Atoll to Native Hawaiians, is an unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and is closed to public entry. Limited access for management needs is only by Letter of Authorization from the U.S. Air Force and a Special Use Permit from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
 W
WThe Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands are a chain of atolls and coral islands. Kingman Reef is largely submerged and Filippo Reef is shown on some maps, although its existence is doubted. The islands were formed by volcanic activity and are located in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. The 11 islands stretch for 2,350 kilometres in a northwest–southeast direction, making it one of the longest island chains of the world. Eight of the islands form part of Kiribati, while the remaining three are United States territories grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands. Only Kiritimati and Tabuaeran atolls and Teraina Island have a permanent population.
 W
WManono is an island of Samoa, situated in the Apolima Strait between the main islands of Savai'i and Upolu, 3.4 km west-northwest off Lefatu Cape, the westernmost point of Upolu.
 W
WManus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth-largest island in Papua New Guinea, with an area of 2,100 km2 (810 sq mi), measuring around 100 km × 30 km. Manus Island is covered in rugged jungles which can be broadly described as lowland tropical rain forest. The highest point on Manus Island is Mt. Dremsel, 718 metres (2,356 ft) above sea level at the centre of the south coast. Manus Island is volcanic in origin and probably broke through the ocean's surface in the late Miocene, 8 to 10 million years ago. The substrate of the island is either directly volcanic or from uplifted coral limestone.
 W
WMelanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from New Guinea island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Tonga.
 W
WMicronesia is a subregion of Oceania, composed of thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south; as well as with the wider Austronesian peoples.
 W
WMinami-Tori-shima , also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some 1,848 kilometers (1,148 mi) southeast of Tokyo and 1,267 km (787 mi) east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line between mainland Tokyo and Wake Island, 1,415 km (879 mi) further to the east-southeast. The closest island to Minami-Tori-shima is East Island in the Mariana Islands, which is 1,015 km (631 mi) to the west-southwest.
 W
WNew Britain is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern.
 W
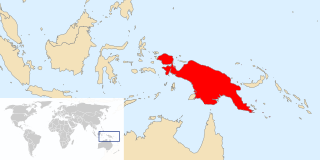
WNew Guinea is the world's second-largest island and, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island wholly or partly within the Southern Hemisphere and Oceania. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait from the Australian continent. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
 W
WNew Ireland or Latangai, is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately 7,404 km2 (2,859 sq mi) in area with c. 120,000 people. It is named after the island of Ireland. It is the largest island of New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by Saint George's Channel. The administrative centre of the island and of New Ireland province is the town of Kavieng located at the northern end of the island. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neumecklenburg.
 W
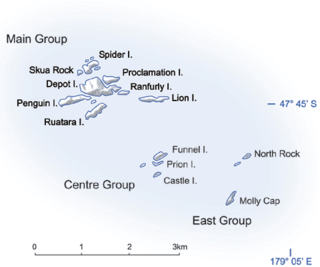
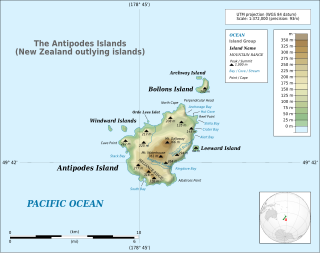
WThe New Zealand outlying islands comprise nine island groups, located in the subtropics and Subantarctic, which are part of New Zealand but lie outside of the New Zealand continental shelf. Although considered as integral parts of New Zealand, seven of the nine island groups are not part of any region or district, but are instead designated as Area Outside Territorial Authority. The two exceptions are the Chatham Islands, which form a special territorial authority themselves, and the Solander Islands, which are part of the Southland Region and Southland District.
 W
WThe Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, is an insular area and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 14 islands in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The CNMI includes the 14 northernmost islands in the Mariana Archipelago; the southernmost island, Guam, is a separate U.S. territory. The CNMI and Guam are the westernmost territories of the United States.
 W
WOkinotorishima is a coral reef with two rocks enlarged with tetrapod-cement structures. It is administered by Japan with a total shoal area of 8,482 m2 and land area 9.44 square metres (101.6 sq ft). Its dry land area is mostly made up by three concrete encasings and there is a 100 by 50 m stilt platform in the lagoon housing a research station. There is a third complete artificial tetrapod-cement islet. It is located on the Palau–Kyushu Ridge in the Philippine Sea, 534 km (332 mi) southeast of Okidaitōjima and 567 km (352 mi) west-southwest of South Iwo Jima in the Bonin Islands or 1,740 km (1,080 mi) south of Tokyo, Japan. The atoll is the southernmost part of Japan and the only Japanese territory in the tropics.
 W
WOneeke is the smaller of the two islands which form Kuria in the North Gilbert Islands. It is separated from Buariki, the larger island, by a narrow channel. A fringing reef extends from the island.
 W
WPalau, officially the Republic of Palau and historically Belau, Palaos or Pelew, is an island country located in the western Pacific Ocean. The country contains approximately 340 islands, and together with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia, forms the western chain of the Caroline Islands. Its area is 466 square kilometers (180 sq mi). The most populous island is Koror. The capital Ngerulmud is located on the nearby island of Babeldaob, in Melekeok State. Palau shares maritime boundaries with international waters to the north, Micronesia to the east, Indonesia to the south, and the Philippines to the west.
 W
WPoll Islet,, is an Australian island in the center of the Torres Strait Islands. It lies in the southern part of The Three Sisters island group and is located 5.2 kilometres (3.2 mi) south off Sue Island, the middle and only inhabited island in The Three Sisters. It is within the Guijar Islet locality in the Torres Strait Island Region local government area.
 W
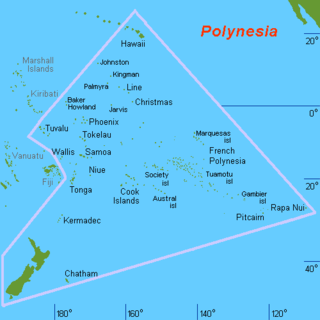
WPolynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians, sharing many similar traits including language family, culture, and beliefs. Historically, they had a strong tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand.
 W
WTasmania is an island state of Australia. It is located 240 km (150 mi) to the south of the Australian mainland, separated by Bass Strait. The state encompasses the main island of Tasmania, the 26th-largest island in the world, and the surrounding 334 islands. The state has a population of about 540,000 people as of March 2020. The state capital and largest city is Hobart, with around 40 percent of the population living in the Greater Hobart area.
 W
WTuvalu is an island country in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania, surrounded by the Pacific Ocean and situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. The country lies east-northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands, northeast of Vanuatu, southeast of Nauru, south of Kiribati, west of Tokelau, northwest of Samoa and Wallis and Futuna, and north of Fiji. It is composed of three reef islands and six atolls spread out between the latitude of 5° to 10° south and longitude of 176° to 180°, west of the International Date Line. Tuvalu has a population of 10,507. The total land area of the islands of Tuvalu is 26 square kilometres (10 sq mi).
 W
WThe Volcano Islands or Iwo Islands are a group of three Japanese islands south of the Ogasawara Islands that belong to the municipality of Ogasawara, Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. The islands are all active volcanoes lying atop an island arc that stretches south to the Marianas. They have an area of 32.55 square kilometres (12.57 sq mi), and a population of 380. The island of Iwo Jima in the Volcano Islands lies about 1,240 kilometres (770 mi) southeast of Miyazaki.
 W
WWake Island is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, 1,501 miles east of Guam, 2,298 miles west of Honolulu, 1,991 miles southeast of Tokyo, and 898 miles north of Majuro. The island is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States that is also claimed by the Republic of the Marshall Islands. Wake Island is one of the most isolated islands in the world and the nearest inhabited island is Utirik Atoll in the Marshall Islands, 592 miles to the southeast.