 W
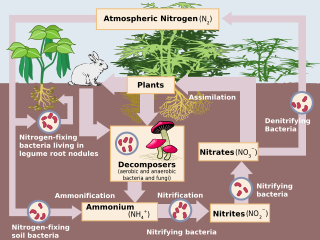
WThe nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmosphere nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems.
 W
WAmino acids are organic compounds that contain amine (–NH2) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of certain amino acids. About 500 naturally occurring amino acids are known (though only 20 appear in the genetic code) and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to polarity, pH level, and side chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid residues form the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.
 W
WAmmonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent smell. It is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water.
 W
WAmmonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline solid consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017.
 W
WAnammox, an abbreviation for anaerobic ammonium oxidation, is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle that takes place in many natural environments. The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1999, and were a great surprise for the scientific community. In the anammox reaction, nitrite and ammonium ions are converted directly into Diatomic Nitrogen and water.
 W
WMartinus Willem Beijerinck was a Dutch microbiologist and botanist who was one of the founders of virology and environmental microbiology.
 W
WBlood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a medical test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen found in blood. The liver produces urea in the urea cycle as a waste product of the digestion of protein. Normal human adult blood should contain 6 to 20 mg/dL of urea nitrogen. Individual laboratories will have different reference ranges as the assay used can vary between laboratories. The test is used to detect renal problems. It is not considered as reliable as creatinine or BUN/creatinine ratio blood studies.
 W
WCyanamide is an organic compound with the formula CN2H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug in Canada, Europe, and Japan. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2).
 W
WDenitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitrification as a type of respiration that reduces oxidized forms of nitrogen in response to the oxidation of an electron donor such as organic matter. The preferred nitrogen electron acceptors in order of most to least thermodynamically favorable include nitrate (NO3−), nitrite (NO2−), nitric oxide (NO), nitrous oxide (N2O) finally resulting in the production of dinitrogen (N2) completing the nitrogen cycle. Denitrifying microbes require a very low oxygen concentration of less than 10%, as well as organic C for energy. Since denitrification can remove NO3−, reducing its leaching to groundwater, it can be strategically used to treat sewage or animal residues of high nitrogen content. Denitrification can leak N2O, which is an ozone-depleting substance and a greenhouse gas that can have a considerable influence on global warming.
 W
WThe Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, are a large and economically important family of flowering plants. It includes trees, shrubs, and perennial or annual herbaceous plants, which are easily recognized by their fruit (legume) and their compound, stipulate leaves. Many legumes have characteristic flowers and fruits. The family is widely distributed, and is the third-largest land plant family in number of species, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with about 751 genera and about 19,000 known species. The five largest of the genera are Astragalus, Acacia, Indigofera, Crotalaria, and Mimosa, which constitute about a quarter of all legume species. The ca. 19,000 known legume species amount to about 7% of flowering plant species. Fabaceae is the most common family found in tropical rainforests and in dry forests in the Americas and Africa.
 W
WA glucogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis. This is in contrast to the ketogenic amino acids, which are converted into ketone bodies.
 W
WGuano is the accumulated excrement of seabirds and bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to its exceptionally high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium: key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a lesser extent, sought for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials.
 W
WHalf Sphere exposure (HSE) is a protein solvent exposure measure that was first introduced by Hamelryck (2005). Like all solvent exposure measures it measures how buried amino acid residues are in a protein. It is found by counting the number of amino acid neighbors within two half spheres of chosen radius around the amino acid. The calculation of HSE is found by dividing a contact number (CN) sphere in two halves by the plane perpendicular to the Cβ-Cα vector. This simple division of the CN sphere results in two strikingly different measures, HSE-up and HSE-down. HSE-up is defined as the number of Cα atoms in the upper half and analogously HSE-down is defined as the number of Cα atoms in the opposite sphere.
 W
WA ketogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies and "myelin, especially during early development, when brain myelin synthesis is extremely high” according to the National institute of Health. This is in contrast to the glucogenic amino acids, which are converted into glucose. Ketogenic amino acids are unable to be converted to glucose as both carbon atoms in the ketone body are ultimately degraded to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle.
 W
WLeghemoglobin is an oxygen-carrying phytoglobin found in the nitrogen-fixing root nodules of leguminous plants. It is produced by these plants in response to the roots being colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria, termed rhizobia, as part of the symbiotic interaction between plant and bacterium: roots not colonized by Rhizobium do not synthesise leghemoglobin. Leghemoglobin has close chemical and structural similarities to hemoglobin, and, like hemoglobin, is red in colour. It was originally thought that the heme prosthetic group for plant leghemoglobin was provided by the bacterial symbiont within symbiotic root nodules. However, subsequent work shows that the plant host strongly expresses heme biosynthesis genes within nodules, and that activation of those genes correlates with leghemoglobin gene expression in developing nodules.
 W
WNitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NO−3. Salts containing this anion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all nitrates are soluble in water. A common example of an inorganic nitrate salt is potassium nitrate. Removal of one electron yields the nitrate radical, also called nitrogen trioxide NO3.
 W
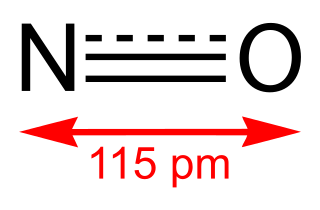
WNitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical, i.e., it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a historic class that drew researches which spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.
 W
WNitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite followed by the oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate. The transformation of ammonia to nitrite is usually the rate limiting step of nitrification. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Nitrification is an aerobic process performed by small groups of autotrophic bacteria and archaea. This process was discovered by the Russian microbiologist Sergei Winogradsky.
 W
WThe nitrite ion, which has the chemical formula NO−2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite can also refer to organic compounds with the -ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.
 W
WAll plants require sufficient supplies of macronutrients for healthy growth, and nitrogen (N) is a nutrient that is commonly in limited supply. Nitrogen deficiency in plants can occur when organic matter with high carbon content, such as sawdust, is added to soil. Soil organisms use any nitrogen to break down carbon sources, making N unavailable to plants. This is known as "robbing" the soil of nitrogen. All vegetables apart from nitrogen fixing legumes are prone to this disorder.
 W
WNitrogenases are enzymes (EC 1.18.6.1EC 1.19.6.1) that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria). These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase.
 W
WNitrosamines are organic compounds of the chemical structure R2N−N=O, where R is usually an alkyl group. They feature a nitroso group (NO+) bonded to a deprotonated amine. Most nitrosamines are carcinogenic.
 W
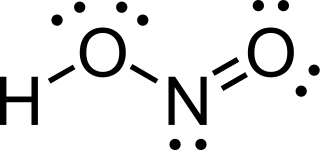
WNitrosyl-O-hydroxide is an isomer of nitrous acid, which has been experimentally observed in the gas phase. HOON contains the longest oxygen-oxygen bond thus far observed in any known molecule, measured to be 1.9149 angstroms. There had been speculation about the existence of this molecule, and ab initio calculations have suggested that it might have a stable chemically bonded structure.
 W
WNitrosylation is the general term for covalent incorporation of a nitric oxide "nitrosyl" moiety into another molecule. There are multiple chemical mechanisms by which this can be achieved; including biological enzymes and industrial processes. The biological functions of nitrosylation are particularly important as S-nitrosylation, the conjugation of NO to cysteine thiols in proteins, is an important part of cell signalling. Coordination of NO to transition metals to give metal nitrosyl complexes, is also referred to as nitrosylation.
 W
WNitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase and in the form of nitrite salts. Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.
 W
WNitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. It is soluble in water.
 W
WProteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
 W
WReactive nitrogen ("Nr") is a term used for a variety of nitrogen compounds that support growth directly or indirectly. Representative species include the gases nitrogen oxides (NOx), ammonia (NH3), nitrous oxide (N2O), as well as the anion nitrate (NO3−). Most of these species are the result of intensive farming, especially the (mis)use of fertilizers. Although required for life, nitrogen is stored in the biosphere in an unreactive ("unfixed") form N2, which supports only a few life forms. Reactive nitrogen is however "fixed" and is readily converted into protein, which supports life, leading to depletion of oxygen in fresh waters by eutrophication. Nr is removed from the biosphere via Denitrification.
 W
WRhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. In general, they are gram negative, motile, non-sporulating rods.
 W
WRoot nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans.
 W
WSodium phenylbutyrate is a salt of an aromatic fatty acid, 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA) or 4-phenylbutyric acid. The compound is used to treat urea cycle disorders, because its metabolites offer an alternative pathway to the urea cycle to allow excretion of excess nitrogen. It is an orphan drug, marketed by Ucyclyd Pharma under the trade name Buphenyl, by Swedish Orphan International (Sweden) as Ammonaps, and by Fyrlklövern Scandinavia as triButyrate.
 W
WThe transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. This is in contrast to the direct sulfurylation pathways for the synthesis of cysteine or homocysteine via the replacement of the acetyl/succinyl group with free sulfide. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
 W
WUric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones.
 W
WVanadium nitrogenase is a key enzyme for nitrogen fixation found in nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and is used as an alternative to molybdenum nitrogenase when molybdenum is unavailable. Vanadium nitrogenases are an important biological use of vanadium, which is uncommonly used by life. An important component of the nitrogen cycle, vanadium nitrogenase converts nitrogen gas to ammonia, thereby making otherwise inaccessible nitrogen available to plants. Unlike molybdenum nitrogenase, vanadium nitrogenase can also reduce carbon monoxide to ethylene, ethane and propane but both enzymes can reduce protons to hydrogen gas and acetylene to ethylene.
 W
WSergei Nikolaievich Winogradsky was a Russian microbiologist, ecologist and soil scientist who pioneered the cycle-of-life concept.