 W
WAnza-Borrego Desert State Park (ABDSP) is a California State Park located within the Colorado Desert of southern California, United States. The park takes its name from 18th century Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza and borrego, a Spanish word for sheep. With 585,930 acres (237,120 ha) that includes one-fifth of San Diego County, it is the largest state park in California.
 W
WThe Arica Mountains are a small mountain range in northern Riverside County, California. The range lies along the south edge of Rice Valley 6.2 miles (10.0 km) southwest of the old Rice townsite on California State Route 62. They lie 6 miles (9.7 km) north of the Little Maria Mountains and 9 miles (14 km) southwest of the Turtle Mountains. The Granite Mountains lie about 8 miles to the west. They are in the Colorado Desert, in the Lower Colorado River Valley region. They are north the Palen Mountains and Big Maria Mountains; and northwest of Blythe, California.
 W
WThe Big Maria Mountains are located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of California, near the Colorado River and Arizona. The range lies between Blythe and Vidal, and west of U.S. Route 95 in California and east of Midland. The mountains are home to the Eagle Nest Mine and reach an elevation of 1,030 meters, (3,379 ft). A power line that runs from Parker Dam to Yuma, Arizona runs through the range. A smaller range, the Little Maria Mountains, lie to the west of the Big Marias.
 W
WThe Big Morongo Canyon Preserve is a 31,000-acres native plants habitat and wildlife preserve located in the Little San Bernardino Mountains of the Transverse Ranges, in the transition zone between the higher Mojave Desert and lower elevation Colorado Desert section of the Sonoran Desert. Due to its location within this transition zone, the area is especially high in natural diversity. The natural spring fed desert oasis found here is one of the 10 largest Cottonwood and Willow riparian habitats in California. It is also identified by the Audubon Society as one of the most important avian habitat areas in California.
 W
WThe Chocolate Mountains of California are located in Imperial and Riverside counties in the Colorado Desert of Southern California. The mountains stretch more than 60 miles (100 km) in a northwest to southeast direction, and are located east of the Salton Sea and south and west of the Chuckwalla Mountains and the Colorado River. To the northwest lie the Orocopia Mountains.
 W
WThe Chuckwalla Mountains are a mountain range in the transition zone between the Colorado Desert—Sonoran Desert and the Mojave Desert, climatically and vegetationally, in Riverside County of southern California.
 W
WCibola National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge in the floodplain of the lower Colorado River between Arizona and California and surrounded by a fringe of desert ridges and washes. The refuge encompasses both the historic Colorado River channel as well as a channelized portion constructed in the late 1960s. Along with these main waterbodies, several important backwaters are home to many wildlife species that reside in this Yuma Desert portion of the Sonoran Desert. Because of the river's life-sustaining water, wildlife here survive in an environment that reaches 120 °F (49 °C) in the summer and receives an average of only 2 inches (5.1 cm) of rain per year.
Coachella Valley National Wildlife Refuge is a 3,709-acre (15.01 km2) protected area in the Coachella Valley, located east of Palm Springs near Palm Desert, California. The refuge contains the majority of critical habitat for the Coachella Valley Fringe-toed Lizard within the Coachella Valley Preserve and Indio Hills Palms State Reserve.
 W
WThe Fish Creek Mountains Wilderness is located about 25 miles west of Brawley, California, and southeast of the Vallecito Mountains in the United States. The wilderness is located in the Fish Creek Mountains region in the northern part of the Carrizo Impact Area, which is closed to the public.
 W
WHavasu National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California. It preserves habitat for desert bighorn sheep to the endangered southwestern willow flycatcher, birds and other animals. The refuge protects 30 river miles - 300 miles (480 km) of shoreline - from Needles, California, to Lake Havasu City, Arizona. One of the last remaining natural stretches of the lower Colorado River flows through the 20-mile-long (32 km) Topock Gorge.
 W
WThe Imperial National Wildlife Refuge protects wildlife habitat along 30 miles (50 km) of the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California, including the last un-channeled section before the river enters Mexico. The Imperial Refuge Wilderness, a federally designated, 15,056-acre (60.93 km2), wilderness area is protected within the refuge. It also surrounds the Picacho State Recreation Area. This section of the Colorado River is popular for boating, hiking, fishing, camping, exploring old mining camps and wildlife watching.
 W
WThe Indian Pass Wilderness is 32,418-acre (13,119 ha) wilderness area under the administered by the Bureau of Land Management. The reserve is located in the very southeastern part of the Chocolate Mountains, in the southeastern part of California, just to the west of the Colorado River in the Lower Colorado River Valley. It adjoins the Picacho Peak Wilderness to the south, and the Imperial National Wildlife Refuge to the east.
 W
WJoshua Tree National Park is an American national park in southeastern California, east of Los Angeles and San Bernardino, near Palm Springs. It is named for the Joshua trees native to the Mojave Desert. Originally declared a national monument in 1936, Joshua Tree was redesignated as a national park in 1994 when the U.S. Congress passed the California Desert Protection Act. Encompassing a total of 790,636 acres – slightly larger than the state of Rhode Island – the park includes 429,690 acres of designated wilderness. Straddling San Bernardino and Riverside Counties, the park includes parts of two deserts, each an ecosystem whose characteristics are determined primarily by elevation: the higher Mojave Desert and the lower Colorado Desert. The Little San Bernardino Mountains traverse the southwest edge of the park.
 W
WThe Little Maria Mountains are located in southeastern California in the United States. The range lies in a northwest-southeasterly direction east of the Palen Mountains and west of the Big Maria Mountains. The mountain range is approximately 15 miles long and is located about 12.6 miles north of Interstate 10, and 12 miles southwest of the abandoned Rice Army Airfield near State Route 62. The Victor Mine is found at the southeastern end of the range near Midland.
 W
WThe Little Picacho Wilderness is a 38,214-acre (15,465 ha) wilderness area under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Land Management. The wilderness is found in a southeast extension of the Chocolate Mountains adjacent to the Colorado River, in the southeastern part of California. It should not be confused with the Picacho Peak Wilderness which is located to the northeast.
 W
WThe Little San Bernardino Mountains are a short mountain range of the Transverse Ranges, located in southern California in the United States. They extend for approximately 40 mi (64 km) southeast from the San Bernardino Mountains through San Bernardino and Riverside Counties to near the northeast edge of the Salton Sink and Salton Sea.
 W
WThe McCoy Mountains are located in southeastern California in the United States. The southeast terminus of the range lies adjacent the western edge of the Parker Valley in a southern stretch of the Lower Colorado River Valley corridor.
 W
WThe Mecca Hills are a low mountain range located in Riverside County, southern California, in the United States.
 W
WThe Mopah Range is a desert mountain range, in the Lower Colorado River Valley region, in southeastern San Bernardino County, California.
 W
WThe Ogilby Hills are a mountain range in Imperial County, California.
 W
WThe Orocopia Mountains are located in Riverside County in southern California, United States, east of the Coachella Valley, west of the Chuckwalla Mountains, and south of Interstate 10 in the Colorado Desert. The range lies in an east-west direction, and is approximately 18 miles long. The Orocopia Mountains are north of and overlooking the Salton Sea and south of Joshua Tree National Park, with the Chocolate Mountains to the southeast and the scenic Mecca Hills just northwest.
 W
WThe Palen Mountains are located in the southern Mojave Desert – northern Colorado Desert in eastern Riverside County, California, USA. The range lies southeast of the Coxcomb Mountains, and northeast of the Chuckwalla Mountains near Interstate 10. The mountains lie in a southwest-northeasterly direction, and are approximately 15 miles long and nine miles wide at their widest point.
 W
WThe Philip L. Boyd Deep Canyon Desert Research Center is one of the original seven of the total 39 sites in the University of California Natural Reserve System. It contains lands originally donated to the University by regent Philip L. Boyd in 1958. The Research Center is contained within UNESCO's Mojave and Colorado Deserts Biosphere Reserve.
 W
WQuail Mountain, at 5,816 feet (1,773 m), is the highest mountain in Joshua Tree National Park and the highest point in the Little San Bernardino Mountains of the very southern reach of the Mojave Desert. It is one of the southernmost peaks in the Transverse Ranges, with the Peninsular Ranges just across the Colorado Desert and Coachella Valley.
 W
WThe Riverside Mountains are a mountain range in Riverside County, California. The town of Vidal, California is located in the West Riverside Mountains.
 W
WLocated on the northeastern side of the Salton Sea, the Salton Sea State Recreation Area offers hunting, fishing, swimming, and camping to visitors.
 W
WSand to Snow National Monument is a U.S. National Monument located in San Bernardino County and into northern Riverside County, Southern California.
 W
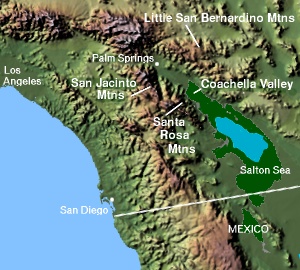
WThe Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument is a National Monument in southern California. It includes portions of the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto mountain ranges, the northernmost ones of the Peninsular Ranges system. The national monument covers portions of Riverside County, west of the Coachella Valley, approximately 100 miles (160 km) southeast of downtown Los Angeles.
 W
WThe Santa Rosa Mountains are a short mountain range in the Peninsular Ranges system, located east of the Los Angeles Basin and northeast of the San Diego metropolitan area of southern California, in the southwestern United States.
 W
WThe Santa Rosa Wilderness is a 72,259-acre (292.42 km2) wilderness area in Southern California, in the Santa Rosa Mountains of Riverside and San Diego counties, California. It is in the Colorado Desert section of the Sonoran Desert, above the Coachella Valley and Lower Colorado River Valley regions in a Peninsular Range, between La Quinta to the north and Anza Borrego Desert State Park to the south. The United States Congress established the wilderness in 1984 with the passage of the California Wilderness Act, managed by the both US Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. In 2009, the Omnibus Public Land Management Act was signed into law which added more than 2,000 acres (8.1 km2). Most of the Santa Rosa Wilderness is within the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument.
 W
WThe Sawtooth Mountains Wilderness is a federal wilderness area of 32,136 acres (130.0 km2) located in the Sawtooth Mountains in eastern San Diego County, California. It is located in the Colorado Desert, 35 miles (56 km) south of Borrego Springs, near Anza Borrego Desert State Park.
 W
WThe Sonny Bono Salton Sea National Wildlife Refuge is located 40 miles (64 km) north of the Mexican border at the southern end of the Salton Sea in California's Imperial Valley. Situated along the Pacific Flyway, the Refuge is the only one of its kind, located 227 feet (69 m) below sea level. Because of its southern latitude, elevation and location in the Colorado Desert, the Refuge experiences some of the highest temperatures in the nation. Daily temperatures from May to October generally exceed 100 °F with temperatures of 116°–120 °F recorded yearly.
 W
WThe Turtle Mountains, are located in northeastern San Bernardino County, in the southeastern part of California. The colorful Turtle Mountains vary from deep reds, browns, tans and grays, to black. The area has numerous springs and seeps. The Turtle Mountains are also a National Natural Landmark, with two mountain sections of entirely different composition.
 W
WThe Whipple Mountains are located in eastern San Bernardino County, California. They are directly west of the Colorado River, Parker Dam, and Lake Havasu; south of Needles, California; north of Parker, Arizona and Vidal, California; and northeast of Vidal Junction, California.
 W
WThe Whipple Mountains Wilderness is a 76,122-acre (30,805 ha) wilderness administered by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Most of the Whipple Mountains are within the wilderness area. It is located in the northeastern Colorado Desert near the Colorado River. Lake Havasu and Lake Havasu City are 25 miles (40 km) to the North. Earp, California and Parker, Arizona are 20 miles (32 km) to the South. The Parker Dam is 8 miles (13 km) due east.