 W
WMetamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock types, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The original rock (protolith) is subjected to heat and pressure, causing profound physical or chemical change. The protolith may be a sedimentary, igneous, or existing metamorphic rock.
 W
WAmphibolite is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase.
 W
WAnthracite, also known as hard coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highest ranking of coals.
 W
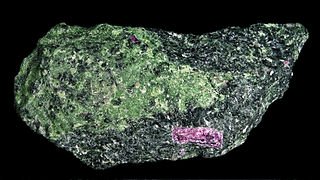
WAlthough anyolite is advertised as a variety of the mineral zoisite from Kenya and the Arusha Region of Tanzania, anyolite is actually a metamorphic rock composed of intergrown green zoisite, black/dark green pargasite, and ruby. The term anyolite is however not an officially accepted term for a metamorphic rock. It is said to be named after the Maasai word anyoli, meaning "green." Anyolite is also referred to as ruby in zoisite, ruby zoisite, ruby-zoisite or Tanganyika artstone.
 W
WBoudinage is a geological term for structures formed by extension, where a rigid tabular body such as hornfels, is stretched and deformed amidst less competent surroundings. The competent bed begins to break up, forming sausage-shaped boudins. Boudinage is common and can occur at any scale, from microscopic to lithospheric, and can be found in all terranes. In lithospheric-scale tectonics, boudinage of strong layers can signify large-scale creep transfer of rock matter. The study of boudinage can, also, help provide insight to the forces involved in tectonic deformation of rocks and their strength.
 W
WCataclasite is a cohesive granular fault rock. Comminution, also known as cataclasis, is an important process in forming cataclasites. They fall into the category of cataclastic rocks which are formed through faulting or fracturing in the upper crust. Cataclasites are distinguished from fault gouge, which is incohesive, and fault breccia, which contains coarser fragments.
 W
WCharnockite is applied to any orthopyroxene-bearing quartz-feldspar rock, formed at high temperature and pressure, commonly found in granulite facies metamorphic regions, as an end-member of the charnockite series.
 W
WClastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.
 W
WThe Dalradian Supergroup is a stratigraphic unit in the lithostratigraphy of the Grampian Highlands of Scotland and in the north and west of Ireland. The diverse assemblage of rocks which constitute the supergroup extend across Scotland from Islay in the west to Fraserburgh in the east and are confined by the Great Glen Fault to the northwest and the Highland Boundary Fault to the southeast. Much of Shetland east of the Walls Boundary Fault is also formed from Dalradian rocks. Dalradian rocks extend across the north of Ireland from County Antrim in the north east to Clifden on the Atlantic coast, although obscured by later Palaeogene lavas and tuffs or Carboniferous rocks in large sections.
 W
WEclogite is a metamorphic rock formed when mafic igneous rock is subjected to high pressure. Eclogite forms at pressures greater than those typical of the crust of the Earth. An unusually dense rock, eclogite can play an important role in driving convection within the solid Earth.
 W
WEozoön canadense is a pseudofossil.
 W
WEpidosite is a highly altered epidote and quartz bearing rock. It is the result of slow hydrothermal alteration or metasomatism of the basaltic sheeted dike complex and associated plagiogranites that occurs below the massive sulfide ore deposits which occur in ophiolites. Most epidosites represent the zone of intense metal leaching below and lateral to the sulfide deposits which is the result of convection of heated ocean water through the fractured basalts of the sheeted dikes.
 W
WFoliation in geology refers to repetitive layering in metamorphic rocks. Each layer can be as thin as a sheet of paper, or over a meter in thickness. The word comes from the Latin folium, meaning "leaf", and refers to the sheet-like planar structure. It is caused by shearing forces, or differential pressure. The layers form parallel to the direction of the shear, or perpendicular to the direction of higher pressure. Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are typically formed in the absence of significant differential pressure or shear. Foliation is common in rocks affected by the regional metamorphic compression typical of areas of mountain belt formation.
 W
WFruchtschiefer is a local variety of contact metamorphic rock that is derived from argillite.
 W
WFulgurites are natural tubes, clumps, or masses of sintered, vitrified, and/or fused soil, sand, rock, organic debris and other sediments that sometimes form when lightning discharges into ground. Fulgurites are classified as a variety of the mineraloid lechatelierite. When ordinary negative polarity cloud-ground lightning discharges into a grounding substrate, greater than 100 million volts of potential difference may be bridged. Such current may propagate into silica-rich quartzose sand, mixed soil, clay, or other sediments, rapidly vaporizing and melting resistant materials within such a common dissipation regime. This results in the formation of generally hollow and/or vesicular, branching assemblages of glassy tubes, crusts, and clumped masses. Fulgurites have no fixed composition because their chemical composition is determined by the physical and chemical properties of whatever material is being struck by lightning.
 W
WGneiss is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. Gneiss is formed by high temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Orthogneiss is gneiss derived from igneous rock. Paragneiss is gneiss derived from sedimentary rock. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures and pressures than schist. Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct foliation.
 W
WGranulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated with quartz and anhydrous ferromagnesian minerals, with granoblastic texture and gneissose to massive structure. They are of particular interest to geologists because many granulites represent samples of the deep continental crust. Some granulites experienced decompression from deep in the Earth to shallower crustal levels at high temperature; others cooled while remaining at depth in the Earth.
 W
WHälleflinta, a white, grey, yellow, greenish or pink, fine-grained rock consisting of an intimate mixture of quartz and feldspar.
 W
WHornfels is the group name for a set of contact metamorphic rocks that have been baked and hardened by the heat of intrusive igneous masses and have been rendered massive, hard, splintery, and in some cases exceedingly tough and durable. These properties are due to fine grained non-aligned crystals with platy or prismatic habits, characteristic of metamorphism at high temperature but without accompanying deformation. The term is derived from the German word Hornfels, meaning "hornstone", because of its exceptional toughness and texture both reminiscent of animal horns. These rocks were referred to by miners in northern England as whetstones.
 W
WImpactite is rock created or modified by one or more impacts of a meteorite. Impactites are considered metamorphic rock, because their source materials were modified by the heat and pressure of the impact. On Earth, impactites are made primarily of modified terrestrial material, sometimes with pieces of the original meteorite.
 W
WJadeitite is a metamorphic rock found in blueschist-grade metamorphic terranes. It is found in isolated metasomatically altered rock units within serpentinite associated with subduction zone environments. Jadeitite consists almost entirely of the pyroxene mineral jadeite and is typically mined as a source of the ornamental rock or gemstone, jade. Occurrences include Myanmar, Guatemala, Japan, Kazakhstan and in the Coast Ranges of western North America.
 W
WKhondalite is a foliated metamorphic rock. In India, it is also called Bezwada Gneiss and Kailasa Gneiss. It was named after the Khond tribe of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh because well-formed examples of the rock were found in the inhabited hills of these regions of eastern India.
 W
WKnotenschiefer is a variety of spotted slate characterized by conspicuous subspherical or polyhedral clots that are often individual minerals such as cordierite, biotite, chlorite, andalusite and others.
 W
WKomatiite is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava with ≥ 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite was named for its type locality along the Komati River in South Africa, and frequently displays spinifex texture composed of large dendritic plates of olivine and pyroxene.
 W
WListwanite (also sometimes spelled listvenite, listvanite, or listwaenite) is an unusual rock type that forms when the groundmass of ultramafic rocks, most commonly mantle peridotites, is partially altered to carbonate minerals and cut by ubiquitous carbonate veins containing one or more of magnesite, calcite, dolomite, ankerite, and/or siderite. Original Pyroxene and olivine in the peridotite are commonly altered to Mg- or Ca-carbonate and hydrous Mg-silicates, such as serpentine and talc. Complete carbonation of peridotite means that every single atom of magnesium and calcium as well as some of the iron atoms have combined with CO2 to form secondary carbonate minerals such a magnesite, calcite, and siderite, while the remaining silica atoms, formerly found in pyroxene and olivine (prior to alteration), are found in quartz, serpentine, and talc. Thus, in terms of bulk mineralogy, listwanites consist primarily of quartz (often of a rusty red colour), carbonate, serpentine, talc, ± mariposite/fuchsite (i.e., Cr-muscovite) ± gold.
 W
WIn geology, metavolcanic rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first produced by a volcano, either as lava or tephra. Then, the rock was buried underneath subsequent rock and was subjected to high pressures and temperatures, causing the rock to recrystallize. Metavolcanic rock is commonly found in greenstone belts.
 W
WMigmatite is a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments. It consists of two or more constituents often layered repetitively; one layer was formerly paleosome, a metamorphic rock that was reconstituted subsequently by partial melting; the alternate layer has a pegmatitic, aplitic, granitic or generally plutonic appearance. Commonly, migmatites occur below deformed metamorphic rocks that represent the base of eroded mountain chains, commonly within Precambrian cratonic blocks,
 W
WMylonite is a fine-grained, compact metamorphic rock produced by dynamic recrystallization of the constituent minerals resulting in a reduction of the grain size of the rock. Mylonites can have many different mineralogical compositions; it is a classification based on the textural appearance of the rock.
 W
WNuummite is a rare metamorphic rock that consists of the amphibole minerals gedrite and anthophyllite. It is named after the area of Nuuk in Greenland, where it was found.
 W
WOakley stone is the trade name of a building stone that occurs in the mountains of southern Idaho in the western United States. It is more properly known as Rocky Mountain quartzite or Idaho quartzite, a metamorphic rock. The stone is quarried south of the city of Oakley in Cassia County, northeast of the three-state border with Nevada & Utah. The quarries are located on the west slope of Middle Mountain in the Albion Mountains, northwest of the City of Rocks National Reserve.
 W
WPhyllite is a type of foliated metamorphic rock created from slate that is further metamorphosed so that very fine grained white mica achieves a preferred orientation. It is primarily composed of quartz, sericite mica, and chlorite.
 W
WPorcellanite or porcelanite, is a hard, dense rock somewhat similar in appearance to unglazed porcelain. It is often an impure variety of chert containing clay and calcareous matter. Porcellanite has been found, for example, in Northern Ireland, Poland and the Czech Republic.
 W
WRajlich's hypothesis is a physical hypothesis with a significance for geology. There exist macroscopic white lamellae inside quartz and other minerals in the Bohemian Massif and even at another places in whole of the world like wavefronts generated by a meteorite impact according to the hypothesis. The hypothetical wavefronts are composed of many microcavities. Their origin is seen in a physical phenomenon of ultrasonic cavitation, which is well known from the technical practice.
 W
WRodingite is a metasomatic rock composed of grossular-andradite garnet and calcic pyroxene; vesuvianite, epidote and scapolite. Rodingites are common where mafic rocks are in proximity to serpentinized ultramafic rocks. The mafic rocks are altered by high pH, Ca2+ and OH- fluids, which are a byproduct of the serpentinization process, and become rodingites. The mineral content of rodingites is highly variable, their high calcium, low silicon and environment of formation being their defining characteristic. Rodingites are common in ophiolites, serpentinite mélanges, ocean floor peridotites and eclogite massifs. Rodingite was first named from outcrops of the Dun Mountain Ophiolite Belt in the Roding River, Nelson, New Zealand.
 W
WSchist is a medium-grade metamorphic rock formed from mudstone or shale. Schist has medium to large, flat, sheet-like grains in a preferred orientation. It is defined by having more than 50% platy and elongated minerals, often finely interleaved with quartz and feldspar. These lamellar minerals include micas, chlorite, talc, hornblende, graphite, and others. Quartz often occurs in drawn-out grains to such an extent that a particular form called quartz schist is produced. Schist is often garnetiferous. Schist forms at a higher temperature and has larger grains than phyllite. Geological foliation with medium to large grained flakes in a preferred sheetlike orientation is called schistosity.
 W
WSerpentinite is a rock composed of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Minerals in this group, which are rich in magnesium and water, light to dark green, greasy looking and slippery feeling, are formed by serpentinization, a hydration and metamorphic transformation of ultramafic rock from the Earth's mantle. The mineral alteration is particularly important at the sea floor at tectonic plate boundaries.
 W
WSkarns or tactites are hard, coarse-grained metamorphic rocks that form by a process called metasomatism. Skarns tend to be rich in calcium-magnesium-iron-manganese-aluminium silicate minerals, which are also referred to as calc-silicate minerals. These minerals form as a result of alteration which occurs when hydrothermal fluids interact with a protolith of either igneous or sedimentary origin. In many cases, skarns are associated with the intrusion of a granitic pluton found in and around faults or shear zones that intrude into a carbonate layer composed of either dolomite or limestone. Skarns can form by regional, or contact metamorphism and therefore form in relatively high temperature environments. The hydrothermal fluids associated with the metasomatic processes can originate from either magmatic, metamorphic, meteoric, marine, or even a mix of these. The resulting skarn may consist of a variety of different minerals which are highly dependent on the original composition of both the hydrothermal fluid and the original composition of the protolith.
 W
WSoapstone is a talc-schist, which is a type of metamorphic rock. It is composed largely of the magnesium rich mineral talc. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occur in the zones where tectonic plates are subducted, changing rocks by heat and pressure, with influx of fluids, but without melting. It has been a medium for carving for thousands of years.
 W
WTectonites are metamorphic or tectonically deformed rocks whose fabric reflects the history of their deformation, or rocks with fabric that clearly displays coordinated geometric features that indicate continuous solid (ductile) flow during formation. Planar foliation results from a parallel orientation of platey mineral phases such as the phyllosilicates or graphite. Slender prismatic crystals such as amphibole produce a lineation in which these prisms or columnar crystals become aligned. Tectonites are rocks with minerals that have been affected by natural forces of the earth, which allowed their orientations to change. This usually includes recrystallization of minerals, and the foliation formation. Tectonites are studied through structural analysis and allows for the determination of two things:The orientation of shearing and compressive stresses during (dynamic) metamorphism The later stages of metamorphism
 W
WUltramafic rocks are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content, generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed of usually greater than 90% mafic minerals. The Earth's mantle is composed of ultramafic rocks. Ultrabasic is a more inclusive term that includes igneous rocks with low silica content that may not be extremely enriched in Fe and Mg, such as carbonatites and ultrapotassic igneous rocks.