 W
WBhitarkanika Mangroves is a mangrove wetland in Odisha, India, covering an area of 650 km (400 mi) in the Brahmani and Baitarani river deltas.
 W
WThe Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of Northeastern India and southern Bhutan.
 W
WBugyals are alpine pasture lands, or meadows, in higher elevation range between 3,300 metres (10,800 ft) and 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) of the Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, where they are called "nature’s own gardens". The topography of the terrain is either flat or sloped. The surface of these bugyals is covered with natural green grass and seasonal flowers. They are used by tribal herdsmen to graze their cattle. During the winter season the alpine meadows remain snow-covered. During summer months, the Bugyals present a riot of beautiful flowers and grass. As bugyals constitute very fragile ecosystems, particular attention needs to be given for their conservation.
 W
WThe Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests in Western and Southern India, containing large protected areas of natural tiger habitat.
 W
WThe Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Odisha, West Bengal and Chhattisgarh. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi River lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).
 W
WThe Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Odisha, West Bengal and Chhattisgarh. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi River lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).
 W
WThe Deccan thorn scrub forests are a xeric shrubland ecoregion of south India and northern Sri Lanka. Historically this area was covered by tropical dry deciduous forest, but this only remains in isolated fragments. The vegetation now consists of mainly of southern tropical thorn scrub type forests. These consist of open woodland with thorny trees with short trunks and low, branching crowns; spiny and xerophytic shrubs; and dry grassland. This is the habitat of the great Indian bustard and blackbuck, though these and other animals are declining in numbers; this area was at one time home to large numbers of elephants and tigers. Almost 350 species of bird have been recorded here. The remaining natural habitat is threatened by overgrazing and invasive weeds, but there are a number of small protected areas which provide a haven for the wildlife. Trees in these forests have adapted to not require much water.
 W
WThe East Deccan dry evergreen forests is an ecoregion of southeastern India. The ecoregion includes the coastal region behind the Coromandel Coast on the Bay of Bengal, between the Eastern Ghats and the sea. It covers eastern Tamil Nadu, part of Puducherry and south eastern Andhra Pradesh.
 W
WThe Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, or East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of 341,100 square kilometers (131,700 sq mi), extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states.
 W
WThe Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, and Nepal, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the eastern portion of the Himalaya Range.
 W
WThe Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests is a temperate broadleaf forest ecoregion found in the middle elevations of the eastern Himalayas, including parts of Nepal, India, and Bhutan. These forests have an outstanding richness of wildlife.
 W
WThe Eastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion which is found in the middle and upper elevations of the eastern Middle Himalayas, in western Nepal, Bhutan and northern Indian states including Arunachal Pradesh.
 W
WThe Godavari-Krishna mangroves are a mangrove ecoregion of India's eastern coast.
 W
WThe Himalayan subtropical broadleaf forests is an ecoregion that extends from the middle hills of central Nepal through Darjeeling into Bhutan and also into the Indian States of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. It represents the east-west-directed band of subtropical broadleaf forest at an altitude of between 500 to 1,000 m along the Outer Himalayan Range, and includes several forest types traversing an east to west moisture gradient.
 W
WThe Himalayan subtropical pine forests are a large subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion covering portions of Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Pakistan.
 W
WThe Indus River Delta-Arabian Sea mangroves are a large mangrove ecoregion on the Arabian Sea coast of Sindh Province, Pakistan. The Indus River Delta forms a vast alluvial fan composed of mud flats interspersed with channels and fringed with mangrove forests. Much of the forested area has been destroyed and the remaining parts are threatened.
 W
WThe Karakoram-West Tibetan Plateau alpine steppe is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion found in parts of Pakistan, China, Afghanistan, and India.
 W
WThe Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests is a mostly arid ecoregion in northwestern India that stretches over 103,100 sq mi (267,000 km2) across Gujarat, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. The dry deciduous forests in the region are dominated by teak, and thorny trees and scrub in drier areas.
 W
WThe Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion of Bangladesh and India. The ecoregion covers an area of 254,100 square kilometres (98,100 sq mi), comprising most of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Bihar and Tripura, and extending into adjacent states of Odisha, Uttar Pradesh and a tiny part of Assam.
 W
WThe Malabar Coast moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern India.
 W
WThe Maldives-Lakshadweep-Chagos Archipelago tropical moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in South Asia. It spans a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean, including Lakshadweep, a union territory of India; the Maldives, an independent country; and the British Indian Ocean Territory, an overseas territory of the United Kingdom.
 W
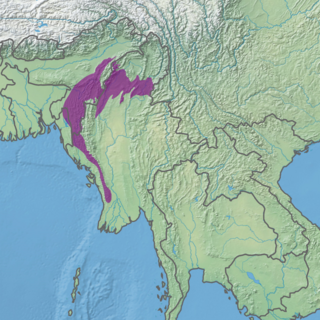
WThe Meghalaya subtropical forests is an ecoregion of Northeast India. The ecoregion covers an area of 41,700 square kilometers (16,100 sq mi), and despite its name, comprise not only the state of Meghalaya, but also parts of southern Assam, and a tiny bit of Nagaland around Dimapur. It also contains many other habitats than subtropical forests, but the montane subtropical forests found in Meghalaya is an important biome, and was once much more widespread in the region, and for these reasons chosen as the most suitable name. The scientific designation is IM0126.
 W
WThe Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion which occupies the lower hillsides of the mountainous border region joining India, Bangladesh, and Burma (Myanmar). The ecoregion covers an area of 135,600 square kilometres (52,400 sq mi). Located where the biotas of the Indian Subcontinent and Indochina meet, and in the transition between subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, the Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests are home to great biodiversity. The WWF rates the ecoregion as "Globally Outstanding" in biological distinctiveness.
 W
WThe Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion of central India. The ecoregion lies mostly in Madhya Pradesh state, but extends into portions of Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh states.
 W
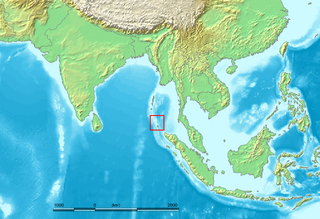
WThe Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 km north of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 km southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they form part of the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.
 W
WThe North Western Ghats moist deciduous forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern India.
 W
WThe North Western Ghats montane rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern India. It covers an area of 30,900 square kilometers (11,900 sq mi), extending down the spine of the Western Ghats range, from southernmost Gujarat through Maharashtra, Goa, and Karnataka. The montane rain forests are found above 1000 meters elevation, and are surrounded at lower elevations by the North Western Ghats moist deciduous forests.
 W
WThe Northeast India-Myanmar pine forests is a montane subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion in the mountains of Northeastern India and adjacent portions of Myanmar.
 W
WThe Northeastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forests are a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the middle to upper elevations of the eastern Himalayas and southeast Tibetan Plateau. The ecoregion occurs in southeastern Tibet Autonomous Region, China, in northern and eastern Arunachal Pradesh, India, and extreme eastern Bhutan.
 W
WThe Northern dry deciduous forests, also known as the North Deccan dry deciduous forests, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of east-central India.
 W
WThe Northwestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of the elevations of the northwestern Himalaya of China, India, and Pakistan.
 W
WThe Northwestern thorn scrub forests is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of Pakistan and Northern India, stretching along the border lowlands and hills between the two countries. Once covered in deciduous forest, this ecoregion has been degraded through agriculture and the extraction of timber so that it currently has a scanty covering of thorny scrub dominated by such trees as Acacia senegal, Acacia leucophloea and Prosopis cineraria. Where the soils are particularly saline, there are patches of semi-desert. A number of mammals are found in this habitat and about four hundred species of bird. Some small areas are protected but the collection of firewood and the conversion of the land to subsistence farming continues.
 W
WThe Odisha semi-evergreen forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of eastern India. The ecoregion covers an area of 8,600 square kilometers (3,300 sq mi) on the coastal plain of Odisha state, bounded by the Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests west and north-west, transitioning from the huge ecoregion Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests along the north coastand, and surrounding the smaller ecoregion Godavari-Krishna mangroves along a stretch of the south-east coast by the Bay of Bengal.
 W
WThe Rann of Kutch is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between Pakistan and India. It is located mostly in Gujarat, India and in some parts of Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into the Great Rann and Little Rann.
 W
WSholas are the local name for patches of stunted tropical montane forest found in valleys amid rolling grassland in the higher montane regions of South India, largely in Kerala. These patches of shola forest are found mainly in the valleys and are usually separated from one another by undulating montane grassland. The shola and grassland together form the shola-grassland complex or mosaic. The word 'Shola' is probably derived from the Tamil language word cÕlai (சோலை) meaning grove.
 W
WThe South Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests is a tropical dry forest ecoregion in southern India. The ecoregion lies in the southernmost portion of the Deccan Plateau, and includes the southernmost portion of the Eastern Ghats.
 W
WThe South Western Ghats moist deciduous forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southern India. It covers the southern portion of the Western Ghats range and the Nilgiri Hills between 250 and 1000 meters elevation in Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu states.
 W
WThe South Western Ghats montane rain forests are an ecoregion of southern India, covering the southern portion of the Western Ghats range in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, at elevations over 1000 meters. They are cooler and wetter than the lower-elevation South Western Ghats moist deciduous forests, which surround the montane rain forests.
 W
WThe Southeast Tibet shrub and meadows are a montane grassland ecoregion that cover the southeast and eastern parts of the Tibetan Plateau in China. The meadows in this region of Tibet are in the path of the monsoon rains and are wetter than the other upland areas of the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese provinces covered by the Southeast Tibet shrub and meadows include the alpine parts of eastern Tibet Autonomous Region, the alpine parts of western and northern Sichuan, extreme southern and eastern Qinghai, and the montane areas of southern Gansu. Many mountain ranges support the Southeast Tibet meadows, stretching from the Nyainqêntanglha Mountains in the southwest to the Qilian Mountains in the northeast.
 W
WThe Sundarbans is a mangrove area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna Rivers in the Bay of Bengal. It spans from the Hooghly River in India's state of West Bengal to the Baleswar River in Bangladesh. It comprises closed and open mangrove forests, agriculturally used land, mudflats and barren land, and is intersected by multiple tidal streams and channels. Four protected areas in the Sundarbans are enlisted as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, viz. Sundarbans National Park, Sundarbans West, Sundarbans South and Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuaries. Despite these protections, the Indian Sundarbans were considered endangered in a 2020 assessment under the IUCN Red List of Ecosystems framework.
 W
WThe Sundarbans is a mangrove area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna Rivers in the Bay of Bengal. It spans from the Hooghly River in India's state of West Bengal to the Baleswar River in Bangladesh. It comprises closed and open mangrove forests, agriculturally used land, mudflats and barren land, and is intersected by multiple tidal streams and channels. Four protected areas in the Sundarbans are enlisted as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, viz. Sundarbans National Park, Sundarbans West, Sundarbans South and Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuaries. Despite these protections, the Indian Sundarbans were considered endangered in a 2020 assessment under the IUCN Red List of Ecosystems framework.
 W
WThe Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands is a narrow lowland ecoregion at the base of the Himalayas, about 25 km (16 mi) wide, and a continuation of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in India, Nepal and Bhutan. It is colloquially called Terai in the Ganges Basin east to Nepal, then Dooars in West Bengal, Bhutan and Assam east to the Brahmaputra River. It harbours the world's tallest grasslands, which are the most threatened and rare worldwide.
 W
WThe Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is a large arid region in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of 200,000 km2 (77,000 sq mi) and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 17th largest desert, and the world's 9th largest hot subtropical desert.
 W
WThe Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion of northern India.
 W
WThe Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Nepal, India, and Tibet, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the western portion of the Himalaya Range.
 W
WThe Western Himalayan broadleaf forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion which is found in the middle elevations of the western Himalayas, including parts of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
 W
WThe Western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the middle and upper elevations of the western Middle Himalayas of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.