 W
WThe Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula with its mouth of the Bay at the south end located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states and all of Washington, D.C. / District of Columbia.
 W
WLake Accotink is a reservoir in North Springfield in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Lake Accotink is formed by the damming of Accotink Creek. The lake is surrounded by Lake Accotink Park.
 W
WAllen Pond Park is an 85-acre (340,000 m2) multi-use park, located in and managed by the City of Bowie in Prince George's County, Maryland. The park includes an Ice Arena, Amphitheater, boat rentals, Skate Park, 10-acre (40,000 m2) stocked pond, six lighted ballfields, picnic areas and pavilions, walking and biking trails, a lighted basketball court, fitness station and several playground areas. It is also the home of Opportunity Park, which offers 100% accessible experiences at its tot lot, school-aged playground, fitness cluster and fishing. The park has a 39% total wood coverage, with the pond occupying 12% of the park. The parking lot that services the park can be accessed from 3404 Mitchellville Road, across from the Mitchellville Road Soccer Fields, and from the main 3330 Northview Drive entrance.
 W
WLake Anne is a reservoir in the unincorporated suburban community of Reston in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. The lake is part of the Difficult Run drainage area of the county.
 W
WLake Artemesia is a man-made lake in Prince George's County, Maryland, located within the Lake Artemesia Natural Area in College Park and Berwyn Heights. The lake covers an area of 38 acres (150,000 m2), and the surrounding natural area is administered by Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission and includes aquatic gardens, fishing piers, and hiker-biker trails.
 W
WLake Braddock is a reservoir in the community of Burke in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Lake Braddock is created by an impoundment on a tributary stream of Pohick Creek, itself a tributary of the Potomac River.
 W
WBreckenridge Reservoir is a small reservoir on Chopawamsic Creek in Prince William and Stafford counties, Virginia. The reservoir's western shore is the Marine Corps Base Quantico and the eastern shore is a part of Prince William Forest Park, which is a unit of the National Park Service. The reservoir is open to fishing along with a Virginia fishing license and Marine Corps Base Quantico permit. Primitive campsites and a hiking trail are on the Prince William Forest Park side of the reservoir. Reservoir storage volume is approximately 22,500,000 cubic feet with a surface area of about 1,820,000 square feet.
 W
WBrushy Fork Lake is an 18-acre (7 ha) impoundment on the South Branch South Fork Potomac River located three miles (5 km) south of Sugar Grove in southeastern Pendleton County, West Virginia, United States. Brushy Fork Lake lies in the Dry River District of the George Washington National Forest.
 W
WCanadarago Lake is a 1,917-acre (7.76 km2) lake located in Otsego County, New York and is the source of Oaks Creek. The Village of Richfield Springs is located at the lake's northern end. It is the second largest lake in Otsego County, lying to the west of and parallel to the larger Otsego Lake. The lake's name is also spelled "Candajarago Lake" or "Caniadaraga Lake".
 W
WCarpenter Point is a point of land on the Wicomico River in Charles County, Maryland. It is located on the northern shore of Cobb Neck on the tidal part of the Wicomico River, which was called the West Wicomico River in early colonial records to differentiate it from the Wicomico River on the Eastern Shore of Maryland. The land was originally part of or very near the western border of Captain James Neale's "Wollaston Manor" estate. Cooksey's Point is the next point to the west, and McReynolds Point the next point to the east.
 W
WThe Chesapeake & Delaware Canal is a 14-mile (22.5 km)-long, 450-foot (137.2 m)-wide and 35-foot (10.7 m)-deep ship canal that connects the Delaware River with the Chesapeake Bay in the states of Delaware and Maryland in the United States. The C&D Canal is owned and operated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Philadelphia District. The project office in Chesapeake City, Maryland, is also the site of the C&D Canal Museum and Bethel Bridge Lighthouse. The canal saves approximately 300 miles on the route between Wilmington and Baltimore, and similar for Philadelphia to Baltimore, whereas otherwise ships would have to go around the lower peninsula of Delaware.
 W
WThe Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the "Grand Old Ditch," operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River from Washington, D.C., to Cumberland, Maryland. The canal's principal cargo was coal from the Allegheny Mountains.
 W
WChesapeake Bay Interpretive Buoy System (CBIBS) is a network of observational buoys that are deployed throughout the Chesapeake Bay to observe the estuary's changing conditions and to serve as way points along the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail. They are maintained by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). These "smart buoys" observe and record meteorological, oceanographic and water quality data which can be obtained in real-time by calling 1-877-BUOY-BAY or by logging on to http://buoybay.noaa.gov/. CBIBS is an operational buoy system in the Chesapeake Bay dedicated to maintaining a broad range of measurements necessary to track Bay restoration progress.
 W
WThe Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland.
 W
WThe Chesapeake Bay Commission is an advisory body that consults with the legislatures of Maryland, Virginia and Pennsylvania about environmental, economic and social issues related to the Chesapeake Bay. The commission was established in 1980 by the states of Maryland and Virginia. Pennsylvania joined the commission in 1985.
 W
WDalecarlia Reservoir is the primary storage basin for drinking water in Washington, D.C., fed by an underground aqueduct in turn fed by low dams which divert portions of the Potomac River near Great Falls and Little Falls. The reservoir is located between Spring Valley and the Palisades, two neighborhoods in Northwest Washington, and Brookmont, a neighborhood in Montgomery County, Maryland.
 W
WThe Eastern Bay is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay located between Queen Anne's County, Maryland and Talbot County, Maryland on the Eastern Shore. Its main tributaries include the Miles River and the Wye River. It is located south of the Chester River and north of the Choptank River and is connected to the Chester River via Kent Narrows.
 W
WThe Georgetown Reservoir is a reservoir that is part of the water supply and treatment infrastructure for the District of Columbia. It is located in the Palisades neighborhood of Washington, D.C., approximately two miles downstream from the Maryland–D.C. boundary.
 W
WHill Top, Maryland, is a rural community in Charles County, 2.4 km (1.5 mi) west-northwest of Welcome and 3.2 km (2 mi) east-southeast of Ironsides, on Hilltop Road, a loop off of Maryland Route 6, and about 7 miles west of Port Tobacco. Hill Top existed as a community as early as 1850, in which year it is shown in the U.S. Federal Census as a census district. Hilltop is the seat of a Roman Catholic parish founded in 1851, whose first church building, St. Ignatius Church, was constructed in 1859.
 W
WJennings Randolph Lake is a reservoir of 952 acres (3.85 km2) located on the North Branch Potomac River in Garrett County, Maryland and Mineral County, West Virginia. It is approximately eight miles upstream of Bloomington, Maryland, and approximately five miles north of Elk Garden, West Virginia.
 W
WKingman Lake is a 110-acre (0.45 km2) artificial lake located in the Anacostia River in Washington, D.C., in the United States. The lake was created in 1920 when the United States Army Corps of Engineers used material dredged from the Anacostia River to create Kingman Island. The Corps of Engineers largely blocked the flow of the Anacostia River to the west of Kingman Island, creating the lake. Kingman Lake is currently managed by the National Park Service.
 W
WLake Holiday is a 249-acre (101 ha) artificial lake located northwest of Winchester in Frederick County, Virginia, United States. The lake flows into Isaacs Creek, an east-flowing tributary of Back Creek, which flows north through West Virginia to the Potomac River. The main creeks feeding the lake are Isaacs Creek and Yeiders Run/Miller Run.
 W
WLiberty Reservoir is a reservoir west of Baltimore, Maryland; about a mile north of Patapsco Valley State Park's McKeldin area. It is owned by the City of Baltimore Department of Public Works, but is located outside the city, and it divides Baltimore and Carroll Counties.
 W
WLittle Seneca Lake is a reservoir located near the Boyds community in Montgomery County, Maryland.
 W
WThe Loch Raven Reservoir is a reservoir that provides drinking water for the City of Baltimore and most of Baltimore County, Maryland. It is fed by the Big Gunpowder Falls river, and has a capacity of 23 billion US gallons (87,000,000 m3) of water.
 W
WLong Island was an island located in Chesapeake Bay, northwest of another former island, Holland Island. The island was shown on maps up until near 1934, when erosion of nearby islands combined with the rising sea levels caused it to be submerged.
 W
WThe McMillan Reservoir is a reservoir in Washington, D.C. that supplies the majority of the city's municipal water. It was originally called the Howard University Reservoir or the Washington City Reservoir, and was completed in 1902 by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The reservoir was built on the site of Smith Spring, one of the springs previously used for drinking water. Washington's earliest residents relied on natural springs but this came to be inadequate as the city's population grew. In 1850, Congress determined that the Potomac River should be the city's principal source of water.
 W
WMount Storm Lake – also known as New Stony River Reservoir – is a 1,200 acres (4.9 km2) reservoir created in 1965 on the Stony River in Grant County, West Virginia. It serves as a cooling pond for the Dominion 1.6 gigawatt Mount Storm Power Station, which provides electricity to more than two million customers in Northern Virginia. The reservoir stands at an altitude of 3,244 feet (989 m).
 W
WLake Needwood is a 75-acre (300,000 m2) reservoir in Derwood, Maryland, United States. Located east of Rockville, in the eastern part of Montgomery County, it is situated on Rock Creek. The lake was created by damming Rock Creek in 1965 with the goal of providing flood control and reducing soil erosion. Lake Needwood also protects the water quality of the creek by functioning as a retention basin to trap sediment from storm-water runoff.
 W
WOtsego Lake is a 4,046-acre (16.37 km2) lake located in Otsego County in the U.S. state of New York. It is the source of the Susquehanna River and largest lake in Otsego County. The Village of Cooperstown is located at the lake's southern end. Glimmerglass State Park is located on the lake's northeastern shore, and includes Hyde Hall, a large mansion constructed in 1817, that overlooks the lake. The Glimmerglass Opera, opened in June 1987, is located on the western shore.
 W
WParker Pond is a pond in Wicomico County, Maryland formed by a widening of Beaverdam Creek.
 W
WThe Patowmack Canal is a series of five inoperative canals located in Maryland and Virginia, United States, that was designed to bypass rapids in the Potomac River upstream of the present Washington, D.C. area. The most well known of them is the Great Falls skirting canal, whose remains are managed by the National Park Service as it is within Great Falls Park Virginia, an integral part of the George Washington Memorial Parkway.
 W
WPlummers Island is a 12-acre Potomac River island in Montgomery County, Maryland, about nine miles upriver from Washington, D.C., which holds the distinction of being the most scientifically studied island in North America. It is visible from the American Legion Memorial Bridge of the Capital Beltway, just downriver (east) of the bridge.
 W
WPocomoke Sound is a bay of the Chesapeake Bay that forms part of the boundary between the Eastern Shores of Maryland and Virginia. The Pocomoke River is the largest stream feeding into the Sound, which is bounded by Somerset County, Maryland on the north, Worcester County, Maryland, Accomack County, Virginia, and Beasley Bay on the east, the Chesapeake Bay on the south, and Tangier Sound on the west. Its southwesternmost point may be considered to be Watts Island, Virginia.
 W
WThe Potomac Company was created in 1785 to make improvements to the Potomac River and improve its navigability for commerce. The project is perhaps the first conceptual seed planted in the minds of the new American capitalists in what became a flurry of transportation infrastructure projects, most privately funded, that drove wagon road turnpikes, navigations, and canals, and then as the technology developed, investment funds for railroads across the rough country of the Appalachian Mountains. In a few decades, the eastern seaboard was crisscrossed by private turnpikes and canals were being built from Massachusetts to Illinois ushering in the brief seven decades of the American Canal Age. The Potomac Company's achievement was not just to be an early example, but of being significant also in size and scope of the project, which involved taming a mountain stream fed river with icing conditions and unpredictable freshets (floods).
 W
WPrettyboy Reservoir is a 206.5 km2 (79.7 sq mi) reservoir in northern Baltimore County, Maryland, also known as the Hereford Zone. Even though the reservoir is in the county, the City of Baltimore owns the reservoir and the surrounding land of forested watershed. The reservoir is one of three reservoirs created to supply the Metropolitan Baltimore municipal water system for Baltimore City, Baltimore County and northern Anne Arundel County constructed by the Baltimore City Department of Public Works. Prettyboy Reservoir, along with Loch Raven Reservoir that is downstream of the Gunpowder Falls, provide about 61% of the drinking water for the Baltimore Metropolitan system. For this reason, the Prettyboy is considered a "source water" or drinking water watershed. The reservoir on average contains about 19 billion US gallons (72,000,000 m3) of water.
 W
WRocky Gorge Reservoir is located on the Patuxent River in Howard County, Montgomery County and Prince George's County, Maryland between Laurel and Burtonsville, Maryland. The reservoir was created in 1952 by the construction of the T. Howard Duckett Dam on the Patuxent. The dam is visible from Interstate 95 near mile marker 34. Because of its close association with a dam by the name, the reservoir is sometimes called the T. Howard Duckett Reservoir. It has a surface area of 773 acres (3.13 km2). The reservoir is maintained as a drinking water source by the Washington Suburban Sanitary Commission (WSSC).
 W
WSpruce Knob, at 4,863 feet (1,482 m), is the highest point in the state of West Virginia and the summit of Spruce Mountain, the highest peak in the Allegheny Mountains.
 W
WThe St. Marys River is a 22.3-mile-long (35.9 km) river in southern Maryland in the United States. It rises in southern St. Mary's County, and flows to the southeast through Great Mills, widening into a tidal estuary near St. Mary's City, approximately 2 miles (3 km) wide at its mouth on the north bank of the Potomac River, near the Chesapeake Bay to the east.
 W
WStony River Reservoir was constructed on the Stony River in 1888 by Westvaco to supply the source of water for the company's main pulp mill. William Luke's summer residence was located on the lake. The dam suffered from structural weakness and was periodically drained for repairs. The center portion of the dam has since been demolished and the reservoir drained. The majority of the dam still stands on either side of the, now, free flowing river.
 W
WThe Tidal Basin is a partially man-made reservoir between the Potomac River and the Washington Channel in Washington, D.C. It is part of West Potomac Park and is a focal point of the National Cherry Blossom Festival held each spring. The Jefferson Memorial, the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial, the Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial, and the George Mason Memorial are situated adjacent to the Tidal Basin. The basin covers an area of about 107 acres (43 ha) and is 10 feet (3.0 m) deep.
 W
WTriadelphia Reservoir is located on the Patuxent River, in Howard County and Montgomery County, Maryland near the town of Brookeville.
 W
WTrout Pond — formerly called Old Pond — located near Wardensville in Hardy County, West Virginia, USA, is the state's only natural lake. The small "lake" is situated in the Trout Pond Recreation Area (TPRA) of the George Washington National Forest. Formerly, the pond had fluctuated in surface area between 2 and 3 acres, but recently it has appeared to be disappearing due to underground structural changes.
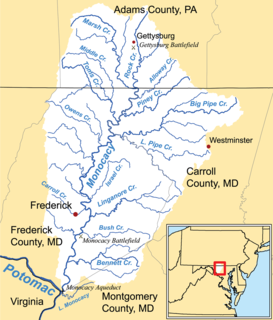 W
WA proposed Union Mills Reservoir represents a half century of efforts by the Commissioners of the Carroll County, Maryland, to build variations on a "dam" or "reservoir" near Union Mills, Maryland, on the Big Pipe Creek, defeated by a petition led by the Carroll County Taxpayers' Committee in the 1970s. The plan may be alive among some county officials but may also be postponed "indefinitely." Land threatened by the reservoir includes the Whittaker Chambers Farm, also known as the Pipe Creek Farm, a National Historic Landmark as well as protected under the Maryland Agricultural Land Preservation Foundation (MALPF).
 W
WWarden Lake is a reservoir on Moores Run near Wardensville in northern Hardy County, West Virginia, United States. Warden Lake is located within the Warden Lake Wildlife Management Area nestled between Baker Mountain and Big Ridge.
 W
WThe Washington Aqueduct is an aqueduct that provides the public water supply system serving Washington, D.C., and parts of its suburbs. One of the first major aqueduct projects in the United States, the Aqueduct was commissioned by Congress in 1852, and construction began in 1853 under the supervision of Montgomery C. Meigs and the US Army Corps of Engineers. Portions of the Aqueduct went online on January 3, 1859, and the full pipeline began operating in 1864. The system has been in continuous use ever since. It is listed as a National Historic Landmark, and the Union Arch Bridge within the system is listed as a Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.
 W
WThe Washington Channel is a channel that parallels the Potomac River in Washington, D.C. It is located between the Southwest Waterfront on the east side and East Potomac Park on the west side. The channel is two miles (3.2 km) long, receives outflow from the Tidal Basin at its north end, and empties into the Anacostia River at Hains Point at its south end. The channel's depth ranges from 8.8 feet (2.7 m) to 23 feet (7.0 m).
 W
WThe Washington City Canal operated from 1815 until the mid-1850s in Washington, D.C. The canal connected the Anacostia River, termed the "Eastern Branch" at that time, to Tiber Creek, the Potomac River, and later the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O). The canal became disused during the late 19th century and the city government covered over or filled in various sections in 1871.