 W
WIn chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid H3PO4.
 W
WAluminium dihydrogenphosphate describes inorganic compounds with the formula Al(H2PO4)3.xH2O where x = 0 or 3. They are white solids. Upon heating these materials convert sequentially to a family of related polyphosphate salts including aluminum triphosphate (AlH2P3O10.2H2O), aluminium hexametaphosphate (Al2P6O18), and aluminium tetrametaphosphate (Al4(P4O12)3). Some of these materials are used for fireproofing and as ingredients in specialized glasses.
 W
WWithin the field of biochemistry, 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine (HMP) also known as toxopyrimidine together with its mono phosphate (HMP-P) and pyrophosphate (HMP-PP) esters are biogenetic precursors to the important biochemical cofactor thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), a derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1).
 W
WAmmonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), also known as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)(H2PO4). ADP is a major ingredient of agricultural fertilizers and some fire extinguishers. It also has significant uses in optics and electronics.
 W
WAmmonium phosphate is an ammonium salt of orthophosphoric acid. It is a highly unstable compound with the formula (NH4)3PO4. Because of its instability, it is elusive and of no commercial value. A related "double salt", (NH4)3PO4.(NH4)2HPO4 is also recognized but is too unstable for practical use. Both triammonium salts evolve ammonia. In contrast to the unstable nature of the triammonium salts, the diammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 monoammonium salt (NH4)H2PO4, are stable materials that are commonly used as fertilizers to provide plants with fixed nitrogen and phosphorus.
 W
WBoranophosphates are salts with an anion consisting of borane (BH3) and phosphite groups. One of the simplest examples is [(CH3O)2OPBH3]−, prepared by base hydrolysis of the adduct of borane and trimethylphosphite.
 W
WCalcium pyrophosphate (Ca2P2O7) is a chemical compound, an insoluble calcium salt containing the pyrophosphate anion. There are a number of forms reported: an anhydrous form, a dihydrate, Ca2P2O7·2H2O and a tetrahydrate, Ca2P2O7·4H2O. Deposition of dihydrate crystals in cartilage are responsible for the severe joint pain in cases of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (pseudo gout) whose symptoms are similar to those of gout. Ca2P2O7 is commonly used as a mild abrasive agent in toothpastes, because of its insolubility and nonreactivity toward fluoride.
 W
WChromium(III) phosphate describes inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CrPO4.(H2O)n, where n = 0, 4, or 6. All are deeply colored solids. Anhydrous CrPO4 is green. The hexahydrate CrPO4•6H2O is violet.
 W
WCobalt phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula Co3(PO4)2. It is a commercial inorganic pigment known as cobalt violet. Thin films of this material are water oxidation catalysts.A swatch of cobalt violet, popular among the French impressionists.
 W
WCopper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2.n(H2O). They can be regarded as the cupric salt of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate is a blue solid. It is produced by a high-temperature reaction between diammonium phosphate and copper(II) oxide.2 (NH4)2HPO4 + 3 CuO → Cu3(PO4)2 + 3 H2O + 4 NH3
 W
WDiammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2HPO4) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid. Solid diammonium phosphate shows a dissociation pressure of ammonia as given by the following expression and equation:(NH4)2HPO4(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + (NH4)H2PO4(s)
 W
WDicalcium phosphate is the calcium phosphate with the formula CaHPO4 and its dihydrate. The "di" prefix in the common name arises because the formation of the HPO42– anion involves the removal of two protons from phosphoric acid, H3PO4. It is also known as dibasic calcium phosphate or calcium monohydrogen phosphate. Dicalcium phosphate is used as a food additive, it is found in some toothpastes as a polishing agent and is a biomaterial.
 W
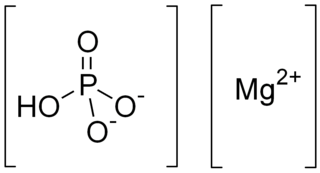
WDihydrogen phosphate or dihydrogenphosphate ion is an inorganic ion with the formula [H2PO4]−. Its formula can also be written as [PO2(OH)2]−, which shows the presence of two O-H bonds. Together with hydrogen phosphate, dihydrogen phosphate occurs widely in natural systems. Their salts are used in fertilizers and in cooking. Most dihydrogen phosphate salts are colorless, water soluble, and nontoxic.
 W
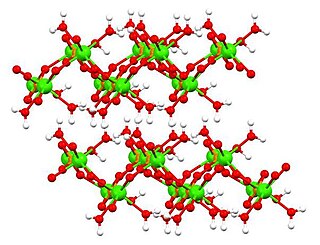
WDimagnesium phosphate is a compound with formula MgHPO4. It is a Mg2+ salt of monohydrogen phosphate. The trihydrate is well known, occurring as a mineral.
 W
WDipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (also dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate; potassium phosphate dibasic) is the inorganic compound with the formula K2HPO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 6). Together with monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4.(H2O)x), it is often used as a fertilizer, food additive, and buffering agent. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water.
 W
WDisodium phosphate (DSP), or sodium hydrogen phosphate, or sodium phosphate dibasic, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2HPO4. It is one of several sodium phosphates. The salt is known in anhydrous form as well as forms with 2, 7, 8, and 12 hydrates. All are water-soluble white powders; the anhydrous salt being hygroscopic.
 W
WFluoride glass is a class of non-oxide optical glasses composed of fluorides of various metals. Due to their low viscosity, it is very difficult to completely avoid the occurrence of any crystallization while processing it through the glass transition.
 W
WIron(II) phosphate, also ferrous phosphate, Fe3(PO4)2, is an iron salt of phosphoric acid.
 W
WIron(III) phosphate, also ferric phosphate, is the inorganic compound with the formula FePO4. Several related materials are known, including four polymorphs of FePO4 and two polymorphs of the dihydrate FePO4·(H2O)2. These materials find few technical applications as well as occurring in the mineral kingdom.
 W
WLithium iron phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula LiFePO4. It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosphate batteries, a type of Li-ion battery. This battery chemistry is targeted for use in power tools, electric vehicles, and solar energy installations. It is also used in OLPC XO education laptops.
 W
WMagnesium phosphate is a general term for salts of magnesium and phosphate appearing in several forms and several hydrates:Monomagnesium phosphate (Mg(H2PO4)2).xH2O Dimagnesium phosphate (MgHPO4).xH2O Trimagnesium phosphate (Mg3(PO4)2).xH2O
 W
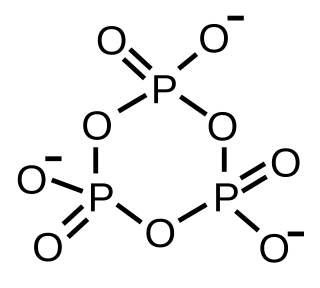
WA metaphosphate ion is an oxyanion that has the empirical formula PO−3. The structure of a metaphosphate ion can be described as being made up of PO4 structural units in which each unit shares two corners with another unit. This can come about in two ways.Formation of a ring, as in trimetaphosphate, illustrated. Formation of an infinite chain, with the same structure as in ammonium metavanadate
 W
WMonocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents..
 W
WMonohydrogen phosphate is the inorganic ion with the formula [HPO4]2-. Its formula can also be written as [PO3(OH)]2-, which shows the presence of a O-H bond. Together with dihydrogen phosphate, monohydrogen phosphate occurs widely in natural systems. Their salts are used in fertilizers and in cooking. Most monohydrogenphosphate salts are colorless, water soluble, and nontoxic.
 W
WMonomagnesium phosphate is one of the forms of magnesium phosphate. It is a magnesium acid salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Mg(H2PO4)2. Di- and tetrahydrates are known also. It dissolves in water, forming phosphoric acid and depositing a solid precipitate of Mg(HPO4).3H2O, dimagnesium phosphate.
 W
WMonopotassium phosphate (MKP) (also, potassium dihydrogenphosphate, KDP, or monobasic potassium phosphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2PO4. Together with dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4.(H2O)x) it is often used as a fertilizer, food additive, and buffering agent. The salt often cocrystallizes with the dipotassium salt as well as with phosphoric acid.
 W
WMonosodium phosphate (MSP), also known as monobasic sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, is an inorganic compound of sodium with a dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4−) anion. One of many sodium phosphates, it is a common industrial chemical. The salt exists in an anhydrous form, as well as mono- and dihydrates.
 W
WNickel(II) phosphate is an inorganic compound with the formula Ni3(PO4)2. It is a mint green paramagnetic solid thaht is insoluble in water.
 W
WPhosphate soda is a type of beverage that has a tangy or sour taste. These beverages became popular among children in the 1870s in the United States. Phosphate beverages were made with fruit flavorings, egg, malt, or wine. In the 1900s, the beverages became popular, and fruit-flavoured phosphate sodas were served at soda fountains, before losing popularity to ice cream based treats in the 1930s.
 W
WPhosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid, is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is normally encountered as a colorless syrup of 85% concentration in water. The pure compound is a colorless solid.
 W
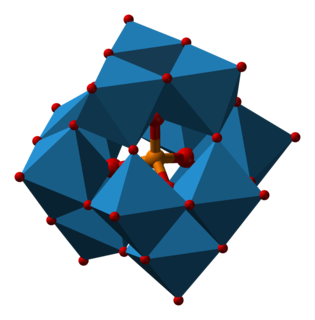
WA phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is Hn+2−2xPnO3n+1−x, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and (n+2)/2.
 W
WPhosphotungstic acid (PTA), tungstophosphoric acid (TPA), is a heteropoly acid with the chemical formula H3PW12O40. It is normally present as a hydrate. EPTA is the name of ethanolic phosphotungstic acid, its alcohol solution used in biology. It has the appearance of small, colorless-grayish or slightly yellow-green crystals, with melting point 89 °C (24 H2O hydrate). It is odorless and soluble in water (200 g/100 ml). It is not especially toxic, but is a mild acidic irritant. The compound is known by a variety of different names and acronyms (see 'other names' section of infobox).
 W
WDeuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KD2PO4) or DKDP single crystals are widely used in non-linear optics as the second, third and fourth harmonic generators for Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF lasers. They are also found in electro-optical applications as Q-switches for Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Alexandrite and Ti-sapphire lasers, as well as for Pockels cells.
 W
WPotassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) is an inorganic compound with the formula KTiOPO4. It is a white solid. KTP is an important nonlinear optical material that is commonly used for frequency-doubling diode-pumped solid-state lasers such as Nd:YAG and other neodymium-doped lasers.
 W
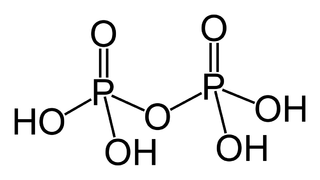
WPyrophosphoric acid, also known as diphosphoric acid, is the inorganic compound with the formula H4P2O7 or, more descriptively, [(HO)2P(O)]2O. Colorless and odorless, it is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. The anhydrous acid crystallizes in two polymorphs, which melt at 54.3 °C and 71.5 °C. The compound is not particularly useful, except that it is a component of polyphosphoric acid and the conjugate acid of the pyrophosphate anion. Anions, salts, and esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates.
 W
WSilver phosphate or silver orthophosphate is a light sensitive, yellow, water-insoluble chemical compound composed of silver and phosphate ions of formula Ag3PO4.
 W
WSodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) is a salt of composition Na6[(PO3)6]. Sodium hexametaphosphate of commerce is typically a mixture of metaphosphates (empirical formula: NaPO3), of which the hexamer is one, and is usually the compound referred to by this name. Such a mixture is more correctly termed sodium polymetaphosphate. They are white solids that dissolve in water.
 W
WSodium monofluorophosphate, commonly abbreviated MFP, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2PO3F. Typical for a salt, MFP is odourless, colourless, and water-soluble. This salt is an ingredient in some toothpastes.
 W
WSodium trimetaphosphate (also STMP), with formula Na3P3O9, is a metaphosphate of sodium. It has the empirical formula NaPO3. It is the sodium salt of trimetaphosphoric acid. It is a colourless solid that finds specialised applications in food and construction industries. STMP is prepared by heating samples sodium polyphosphate.
 W
WSodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP),) is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10. It is the sodium salt of the polyphosphate penta-anion, which is the conjugate base of triphosphoric acid. It is produced on a large scale as a component of many domestic and industrial products, especially detergents. Environmental problems associated with eutrophication are attributed to its widespread use.
 W
WSugar phosphates are often used in biological systems to store or transfer energy. They also form the backbone for DNA and RNA. Sugar phosphate backbone geometry is altered in the vicinity of the modified nucleotides.
 W
WTricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Most commercial samples of "tricalcium phosphate" are in fact hydroxyapatite.
 W
WTrimagnesium phosphate describes inorganic compounds with formula Mg3(PO4)2.xH2O. They are magnesium acid salts of phosphoric acid, with varying amounts of water of crystallization: x = 0, 5, 8, 22.
 W
WTriphosphono phosphate is the simplest branched polypohsphoric acid. It is a hexaprotic acid. It is used to prepare phosphoric monoesters.
 W
WTripotassium phosphate, also called tribasic potassium phosphate is a water-soluble salt with the chemical formula K3PO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 7, 9). Tripotassium phosphate is a strong base.
 W
WTrisodium phosphate (TSP) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na3PO4. It is a white, granular or crystalline solid, highly soluble in water, producing an alkaline solution. TSP is used as a cleaning agent, builder, lubricant, food additive, stain remover, and degreaser.
 W
WTributylammonium TRISPHAT is an organic salt with the formula [(C4H9)3NH+][P(O2C6Cl4)−3]. The anion features phosphorus(V) bonded to three tetrachlorocatecholate ligands. This anion can be resolved into the enantiomers, which are optically stable.
 W
WYttrium phosphate, YPO4, is a phosphate of yttrium. It occurs in nature as mineral xenotime.