 W
WThe Açu Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Albian) geologic formation of the Potiguar Basin in Ceará, northeastern Brazil. The formation comprises coarse-grained sandstones deposited in a fluvio-deltaic environment. The Açu Formation, belonging to the Apodi Group, has provided fossils of an indeterminate rebbachisaurid.
 W
WThe Agrio Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation that is up to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) thick and is located in the southern Mendoza Province and northern-central Neuquén Province, in the Neuquén Basin of northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. This formation is the youngest one of the Mendoza Group, overlying the Mulichinco and Bajada Colorada Formations and overlain by the Huitrín and La Amarga Formations. It is dated to the Late Valanginian to Early Hauterivian, Late Valanginian to Early Barremian, or Hauterivian to earliest Aptian.
 W
WThe La Amarga Formation is a geologic formation with outcrops in the Argentine provinces of Río Negro, Neuquén, and Mendoza. It is the oldest Cretaceous terrestrial formation in the Neuquén Basin.
 W
WThe Antenor Navarro Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Brazil. Fossil sauropod tracks have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Apón Formation is a geological formation in northwestern Venezuela and northern Colombia, whose thick-bedded limestone interbedded with subordinate amounts of dark gray calcareous shale and sandy shale strata date back to the Early Cretaceous. Pterosaur remains of Ornithocheiridae indet. are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Arcabuco Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consists of thick beds of light-coloured quartzitic sandstones and conglomerates with occasional shales and dates to the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods; Tithonian to Berriasian epochs. Dinosaur footprints have been found in the Arcabuco Formation near the Iguaque anticlinal outside Chíquiza, Boyacá.
 W
WThe Areado Group is a Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous geologic group in southeastern Brazil. The group was defined by Cardoso in 1968.
 W
WThe Bajada Colorada Formation is a geologic formation of the southern Neuquén Province in the Neuquén Basin of northern Patagonia, Argentina. The formation belongs to the Mendoza Group and is Late Berriasian to Early Valanginian in age. The formation is renowned for preserving fossil remains of Bajadasaurus pronuspinax, a genus of dicraeosaurid dinosaurs named after the formation.
 W
WThe Baños del Flaco Formation is a Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous (Tithonian to Berriasian geologic formation in central Chile. The formation comprises limestones and sandstones deposited in a shallow marine to fluvial environment. Fossil ornithopod tracks have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Caballos Formation is a geological formation of the Upper Magdalena Valley (VSM), Caguán-Putumayo Basin, Central and Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The sandstone and shale formation dates to the Middle Cretaceous period; Aptian to Albian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 411 metres (1,348 ft).
 W
WThe Caiuá Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Brazil and Paraguay. Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation. The formation, the lowermost unit of the Bauru Group, was deposited in the Barremian and Aptian epochs of the Early Cretaceous, around 130 to 120 Ma. The formation is unconformably overlain by the Santo Anastácio Formation and the unconformity probably represents the start of the opening of the South Atlantic and the formation of the Santos Basin.
 W
WThe La Cantera Formation is a Late Aptian, geologic formation in Argentina. Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation. The formation, deposited under lacustrine conditions, also has provided fossil plants, insects, fish and gastropods.
 W
WThe Capotes Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consists of calcareous black shales containing gypsum and ammonites and dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Early Albian epoch and has an approximate thickness at its type section of 550 metres (1,800 ft).
 W
WThe Casma Group is a stratigraphic group of Cretaceous sedimentary formations exposed along the coast and within the Cordillera Occidental near Casma, Peru.
 W
WThe Cazaderos Formation is an Albian geologic formation in southern Ecuador.
 W
WThe Chacarilla Formation is an Oxfordian to Early Cretaceous geologic formation of the Tarapacá Basin in northern Chile, close to the border with Bolivia. The marine and fluvial formation preserves several dinosaur trackways and has been declared a Natural Sanctuary in 2004.
 W
WThe Chachao Formation is a geological formation in the Mendoza Province in northern Patagonian Argentina. It is Valanginian in age and is predominantly marine, being deposited at a time of marine transgression in the Neuquén Basin, and predominantly consists of carbonate rocks.
 W
WThe Chon Aike Formation is an extensive geological formation, present in the Deseado Massif in north-central Santa Cruz Province, Patagonia, Argentina. It covers an area of approximately 100,000 square kilometres (39,000 sq mi) and consists of rhyolitic volcanic rocks, particularly ignimbrites and lavas, with smaller amounts of agglomerates and tuffs. Within dacitic rocks, plant fossils have been found.
 W
WThe Chulec Formation (Ki-chu) is a geological formation in Peru whose strata date back to the Albian. The formation has a thickness of about 100 to 200 metres and comprises limestones, marls and calcareous sandstones that were deposited during a marine transgression from the west. Pterosaur remains and ammonites are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Coihaique Group is a group of geological formations in northwestern Patagonia. From top to bottom the formations that make the group are Apeleg, Katterfeld and Toqui. The contact between the formations of the group are diachronous with Katterfeld Formation interfingering with the formations on top and below it. The lower and upper boundaries of the group are unconformities formed by erosion. The older parts of Coihaique Group represent a marine transgression while the younger parts evidences a return to non-marine conditions.
 W
WThe Corda Formation is a red sandstone geologic formation in the Parnaíba Basin in Tocantins, Brazil. It was formed during the Neoaptian to Eoalbian series of the Early Cretaceous.
 W
WThe Crato Formation is a geologic formation of Early Cretaceous (Aptian) age in northeastern Brazil's Araripe Basin. It is an important Lagerstätte for palaeontologists. The strata were laid down mostly during the early Aptian age, about 113 million years ago, in a shallow inland sea. At that time, the South Atlantic was opening up in a long narrow shallow sea.
 W
WThe Divisadero Group is a group of geological formations in the Magallanes Basin (Chile) or Austral Basin (Argentina) of northwestern Patagonia. It overlies the Coihaique Group. The group is chiefly made up of pyroclastic rocks and lavas of the calc-alkaline magma series. Rocks are of andesite and rhyolite composition.
 W
WThe El Jume Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Argentina. Indeterminate fossil dinosaur tracks have been reported from the formation. The formation, belonging to the El Gigante Group, overlies the Los Riscos Formation and is overlain by the El Toscal Formation. The sandstones and claystones of the formation were deposited in a fluvial environment. Part of the formation was assigned to a new formation, Balde de Leyes Formation in 2015.
 W
WThe El Peñón Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consists of calcareous shales and siltstones and dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Late Aptian epoch and has a measured thickness at its type section of 381 metres (1,250 ft). Ammonite fossils have been found in the formation, deposited in a shallow marine platform environment.
 W
WThe Exu Formation is an Albian geologic formation in Brazil. Pterosaur fossils of Lophocratia indet. have been recovered from the formation.
 W
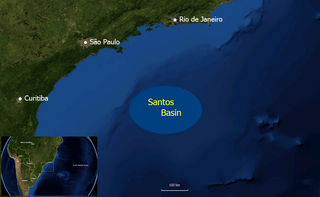
WThe Florianópolis Formation is a geological formation of the Santos Basin offshore of the Brazilian states of Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná and Santa Catarina. The predominantly sandstone formation with interbedded shales and siltstones dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Albian epoch and has a thickness in the type oil well of 343 metres (1,125 ft).
 W
WThe Fómeque Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly organic shale formation dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Barremian to Late Aptian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 1,200 metres (3,900 ft).
 W
WThe Guaratiba Group is a geological group of the Santos Basin offshore of the Brazilian states of Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná and Santa Catarina. The group forms the pre-salt layer in the petroleum-rich basin and hosts the biggest oil fields of Brazil, as Tupi, Júpiter and many more. The group contains, depending on the definition, three to four formations and dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Hauterivian to Early Aptian epochs. The total thickness of the group, representing the first phase of sedimentation after the break-up of Gondwana in the Santos Basin, is estimated at 4,200 metres (13,800 ft).
 W
WThe Guarujá Formation is a geological formation of the Santos Basin offshore of the Brazilian states of Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná and Santa Catarina. The predominantly calcarenite formation with marls dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Early Albian epoch and has a maximum thickness of 2,500 metres (8,200 ft). The formation is the second-most important post-salt reservoir rock of the Santos Basin.
 W
WThe Guavio Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consists of conglomerates, shales and limestones, dates to the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods; Tithonian to Berriasian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft).
 W
WLa Herradura Formation is a sedimentary formation of Lower Cretaceous age exposed near Lima in Peru. The sediments of the formation reflect a marine near-shore depositional environment.
 W
WThe Hiló Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly shale formation dates to the Middle Cretaceous period; Late Albian to Early Cenomanian epochs and has a measured thickness at its type section of 470 metres (1,540 ft). The fossiliferous formation has provided a great abundance of ammonites and other marine species.
 W
WThe Ipubi Formation is the middle geological formation of the Santana Group, the middle part of the Araripe Group, in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil. The formation is dated to the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous, unconformably overlying the Crato Formation and unconformably overlain by the Romualdo Formation, formerly known as the Romualdo Member of the Santana Formation. The averaging 15 metres (49 ft) thick Ipubi Formation comprises shales and sandstones in the lower section and evaporites in the upper part of the formation, deposited in a transgressive to highstand lacustrine environment in the Araripe rift basin.
 W
WThe Itanhaém Formation is a geological formation of the Santos Basin offshore of the Brazilian states of Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná and Santa Catarina. The predominantly shale formation with marls, siltstones and sandstones dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Early Albian epoch and has a maximum thickness of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft). The formation is the reservoir rock of the Tambaú Field in the Santos Basin.
 W
WThe Itapecuru Formation is a geological formation in Itapecuru Mirim, Maranhão, Brazil.
 W
WThe La Cruz Formation is an Aptian geologic formation in Argentina. Pterosaur fossils of Pterodaustro guinazui have been recovered from the formation. The formation, the uppermost unit of the El Gigante Group, overlies the El Toscal Formation, and is overlain by the Lagarcito Formation. The unit comprises sandstones and conglomerates, deposited in an alluvial plain to fluvial environment.
 W
WThe La Puerta Formation is a Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous geologic formation of southern Bolivia. The fluvial and eolian sandstones preserve ichnofossils of Theropoda indet., Thyreophora indet., Ankylosauria indet. and Stegosauria indet. at the Tunasniyoj tracksite. The formation is possibly a distal extension of the Botucatu Formation. The Tunasniyoj assemblage is the oldest dinosaur tracksite for Bolivia, and includes the oldest known evidence assigned to ankylosaurs and stegosaurs for South America.
 W
WThe Lohan Cura Formation is a geologic formation with outcrops in the Argentine provinces of Río Negro, Neuquén, and Mendoza. It is the second oldest Cretaceous terrestrial formation in the Neuquén Basin.
 W
WLos Adobes Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Aptian) geologic formation in Chubut Province, in the Cañadón Asfalto Basin of central Patagonia, Argentina. The formation belongs to the Chubut Group and represents the Early Cretaceous K1 megasequence in the basin, unconformably overlying the Late Jurassic Cañadón Calcáreo Formation and is overlain by the Albian Cerro Barcino Formation.
 W
WThe Macanal Formation or Macanal Shale is a fossiliferous geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and Tenza Valley in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly organic shale formation dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Berriasian to Valanginian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 2,935 metres (9,629 ft). The Macanal Formation contains numerous levels of fossiliferous abundances. Bivalves, ammonites and fossil flora have been found in the formation.
 W
WThe Malhada Vermelha Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Ceará, northeastern Brazil. The formation preserves reptile, fish and ichnofossils.
 W
WThe Missão Velha Formation is an early Aptian geologic formation in northeastern Brazil's Araripe Basin where the states of Pernambuco, Piauí and Ceará come together. The formation is the middle stratigraphic unit of the Vale do Carirí Group, overlying the Brejo Santo Formation and overlain by the Abaiara Formation.
 W
WThe Morro Solar Group is a stratigraphic group of Mesozoic-aged sedimentary formations exposed near Lima, Peru. The groups formations more specifically of Berriasian and Valanginian age and overlies the Jurassic Puente Piedra Group and underlies the Cretaceous Pamplona Formation. The Morro Solar Group is intruded by sills of andesitic composition. Together with the Casma and Imperial Groups, the Morro Solar Group contains clastic volcanosedimentary material derivative of the Mesozoic Casma Volcanic Arc. The formations of the group hosts mostly local fossils which do not have counterparts for biochronological correlation in other regions.
 W
WThe Mulichinco Formation is a geological formation in Argentina. It is Valanginian in age and is predominantly terrestrial, being deposited at a time of marine regression in the Neuquén Basin, and predominantly consists of siliciclastic rocks.
 W
WThe Pacho Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consisting of alternating siltstones and shales with siderite concretions dates to the Middle Cretaceous period; Late Albian to Cenomanian epochs and has an approximate thickness of 1,050 metres (3,440 ft).
 W
WThe Quiricó Formation is a geological formation of the Areado Group in Minas Gerais, Brazil whose strata date back to the Lower Cretaceous. Many occurrences of fossils are reported in the lacustrine deposits of the Quiricó Formation.
 W
WThe Rayoso Formation is a geological formation in the Neuquén Province of Argentina whose strata date back to the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Santana Group is a geologic group, formerly included as the middle part of the Araripe Group, in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil. The group comprises the Crato, Ipubi and Romualdo Formations and is dated to the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. The formations of the group were deposited in a lacustrine to subtidal shallow marine environment in the Araripe rift basin.
 W
WThe Socotá Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consisting of a lower unit of calcareous sandstones and an upper sequence of shales dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Late Aptian epoch and in Quipile has a measured thickness of 255 metres (837 ft) with large regional variations. The formation hosts ammonite fossils.
 W
WThe Trincheras Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consisting of a lower unit of calcareous shales and an upper sequence of shales dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Early Aptian epoch and has a maximum thickness of 1,260 metres (4,130 ft). The formation, deposited in a marine platform environment, part of a transgressive cycle, hosts ammonite, bryozoan, mollusc and echinoid fossils.
 W
WThe Une Formation is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly sandstone formation dates to the Middle Cretaceous period; Albian to Cenomanian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 1,100 metres (3,600 ft).
 W
WThe Vaca Muerta Formation, commonly known as Vaca Muerta is a geologic formation of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous age, located in the Neuquén Basin in northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is well known as the host rock for major deposits of shale oil and shale gas.
 W
WThe Villeta Group is a geological group of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, to the west of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense. The group, a sequence of shales, limestones and sandstones, is subdivided into various formations; Conejo, La Frontera, Simijaca, Hiló, Pacho, Chiquinquirá, Capotes, Socotá, El Peñón, and Trincheras, and dates to the Cretaceous period; Aptian-Coniacian epochs. The group stretches out across four departments, from Huila in the south, through Cundinamarca and Boyacá to southern Santander in the north. The upper part of the Villeta Group is time-equivalent with the La Luna Formation of the Middle Magdalena Valley (VMM) and Sierra Nevada del Cocuy, the Oliní and Güagüaquí Groups of the Guaduas-Vélez synclinal and the Chipaque Formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense. The lower part has been correlated with the Simití, Tablazo and Paja Formations of the VMM, the upper Tibasosa, Une and Fómeque Formations of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and the Capacho, Aguardiente, Tibú-Mercedes and upper Río Negro Formations of the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy.
 W
WZapata Formation is a sedimentary formation of Lower Cretaceous age in the Magallanes or Austral Basin of Argentina and Chile. Much of the formation is folded and faulted as consequence of the Andean orogeny. In outcrops of the Zapata Formation near Torres del Paine, the southernmost fossil of the ichthyosaur genus Platypterygius has been found.