 W
WThe history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution.
 W
WAcademician Ridge is an underwater, structural high separating two of Lake Baikal's three basins, the Central and North basins. Situated in the central part of the Baikal Rift, it serves as an "accommodation zone", transferring "motion between faults of similar displacement but different orientation". The ridge is bounded by two large normal faults, the Primorsky Fault on the northwest and the Olkhon Fault on the southeast, and an oblique-slip fault, the Academician Fault, that runs along the crest of the ridge. The margins of the ridge, Olkhon Island to the southwest and the Ushkanie Islands to the northeast, are above lake level while the center of the ridge is submerged to depths of 350–400 m.
 W
WAmmachi Plavu literally translated from Malayalam, it means grandmother Jack-fruit tree or an old Jackfruit tree, Located in inside of Neyyattinkara Sree Krishna Swami Temple in Thiruvananthapuram Kerala.
 W
WAn aragonite sea contains aragonite and high-magnesium calcite as the primary inorganic calcium carbonate precipitates. The chemical conditions of the seawater must be notably high in magnesium content relative to calcium for an aragonite sea to form. This is in contrast to a calcite sea in which seawater low in magnesium content relative to calcium favors the formation of low-magnesium calcite as the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate.
 W
WThe Australian Shield, also called the Western Australian Shield or Western Plateau, occupies more than half of the continent of Australia. The word shield is used because it refers to ancient, molten rock which has cooled and solidified. The Australian Shield has a characteristic depth of 4.5 km and an estimated age of 2.8 to 3.5 billion years. In places younger sedimentary rock covers the shield's Precambrian surface.
 W
WThe Belt Supergroup is an assemblage of primarily fine-grained sedimentary rocks and mafic intrusive rocks of late Precambrian (Mesoproterozoic) age. It is more than 15 kilometres (10 mi) thick, covers an area of some 200,000 km2, and is considered to be one of the world's best-exposed and most accessible sequences of Mesoproterozoic rocks. It was named after the Big Belt Mountains in west-central Montana. It is present in western Montana and northern Idaho, with minor occurrences in northeastern Washington and western Wyoming. It extends into Canada where the equivalent rocks, which are called the Purcell Supergroup, are exposed in southeastern British Columbia and southwestern Alberta. The rocks of the Belt Supergroup contain economically significant deposits of lead, zinc, silver, copper, gold, and other metals in a number of areas, and some of the Belt rocks contain fossil stromatolites.
 W
WBeringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States.
 W
WA calcite sea is one in which low-magnesium calcite is the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate. An aragonite sea is the alternate seawater chemistry in which aragonite and high-magnesium calcite are the primary inorganic carbonate precipitates. The Early Paleozoic and the Middle to Late Mesozoic oceans were predominantly calcite seas, whereas the Middle Paleozoic through the Early Mesozoic and the Cenozoic are characterized by aragonite seas ).
 W
WCarbonate hardgrounds are surfaces of synsedimentarily cemented carbonate layers that have been exposed on the seafloor. A hardground is essentially, then, a lithified seafloor. Ancient hardgrounds are found in limestone sequences and distinguished from later-lithified sediments by evidence of exposure to normal marine waters. This evidence can consist of encrusting marine organisms, borings of organisms produced through bioerosion, early marine calcite cements, or extensive surfaces mineralized by iron oxides or calcium phosphates. Modern hardgrounds are usually detected by sounding in shallow water or through remote sensing techniques like side-scan radar.
 W
WThe Chatham Rise is an area of ocean floor to the east of New Zealand, forming part of the Zealandia continent. It stretches for some 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from near the South Island in the west, to the Chatham Islands in the east. It is New Zealand's most productive and important fishing ground, as well as important habitat for whales.
 W
WThe Churchill Craton is the northwest section of the Canadian Shield and stretches from southern Saskatchewan and Alberta to northern Nunavut. It has a very complex geological history punctuated by at least seven distinct regional tectonometamorphic intervals, including many discrete accretionary magmatic events. The Western Churchill province is the part of the Churchill Craton that is exposed north and west of the Hudson Bay. The Archean Western Churchill province contributes to the complicated and protracted tectonic history of the craton and marks a major change in the behaviour of the Churchill Craton with many remnants of Archean supracrustal and granitoid rocks.
 W
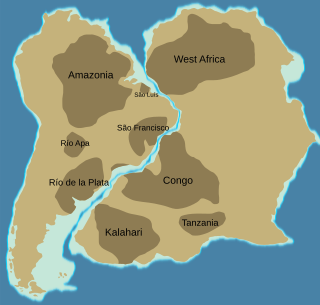
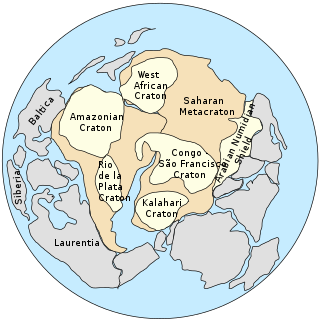
WThe Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.
 W
WThe Cornbrash Formation is a Middle Jurassic geological formation in England. It ranges in age from Bathonian to Callovian, the uppermost part of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus. The name Cornbrash is an old English agricultural name applied in Wiltshire to a variety of loose rubble or brash which, in that part of the country, forms a good soil for growing corn. The name was adopted by William Smith for a thin band of shelly limestone which, in the south of England, breaks up in the manner indicated. Although only a thin group of rocks, it is remarkably persistent; it may be traced from Weymouth to the Yorkshire coast, but in north Lincolnshire it is very thin, and probably dies out in the neighborhood of the Humber. It appears again, however, as a thin bed in Gristhorpe Bay, Cayton Bay, Wheatcroft, Newton Dale and Langdale. In the inland exposures in Yorkshire it is difficult to follow on account of its thinness, and the fact that it passes up into dark shales in many places the so-called clays of the Cornbrash, with Avicula echinata. The Cornbrash is of little value for building or road-making, although it is used locally; in the south of England it is not oolitic, but in Yorkshire it is a rubbly, marly, frequently ironshot oolitic limestone. In Bedfordshire it has been termed the Bedford limestone.
 W
WA craton is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. They are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots that extend as much as several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle.
 W
WThe Cretaceous Thermal Maximum (CTM), also known as Cretaceous Thermal Optimum, was a period of climatic warming that reached its peak approximately 90 million years ago during the Turonian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch. The CTM is notable for its dramatic increase in global temperatures characterized by high carbon dioxide levels.
 W
WCyclostratigraphy is the study of astronomically forced climate cycles within sedimentary successions. Astronomical cycles are variations of the Earth's orbit around the sun due to the gravitational interaction with other masses within the solar system. Due to this cyclicity, solar irradiation differs through time on different hemispheres and seasonality is affected. These insolation variations have influence on Earth's climate and so on the deposition of sedimentary rocks.
 W
WDoggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the southern North Sea, that connected Great Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BC. Geological surveys have suggested that it stretched from where Great Britain's east coast now is to the present-day Netherlands, western coast of Germany, and peninsula of Jutland. It was probably a rich habitat with human habitation in the Mesolithic period, although rising sea levels gradually reduced it to low-lying islands before its final submergence, possibly following a tsunami caused by the Storegga Slide.
 W
WDorkovo Museum in Dorkovo, Bulgaria, established in 2013 in a domed wooden structure, has a display of fossils collected from the Pliocene geological epoch of about five million years ago around the village of Dorkovo, a life-size model of a gomphothere, related to elephants, and a diorama.
 W
WAn erygmascope is the name given to a late 19th-century electric lighting apparatus designed for the examination of the strata of earth traversed by boring apparatus.
 W
WThe formation of Europe as a coherent landmass dates to after the breakup of Pangaea, taking place during the Oligocene and completed by the early Neogene period, some 20 million years ago.
 W
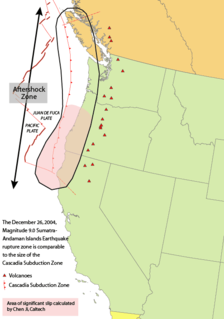
WThe Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate that began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate—then located in modern Utah—as Pangaea broke apart during the Jurassic period. It is named for the Farallon Islands, which are located just west of San Francisco, California.
 W
WThe geologic record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata. That is, deposits laid down by volcanism or by deposition of sediment derived from weathering detritus. This includes all its fossil content and the information it yields about the history of the Earth: its past climate, geography, geology and the evolution of life on its surface. According to the law of superposition, sedimentary and volcanic rock layers are deposited on top of each other. They harden over time to become a solidified (competent) rock column, that may be intruded by igneous rocks and disrupted by tectonic events.
 W
WThe geology of Ontario consists of the study of the rock formations in the most populated province of Canada. Ontario has some of the oldest rocks on Earth. It is made up of ancient Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rock and overlain by younger sedimentary rocks and soils.
 W
WThe Giebichenstein in Stöckse, Germany, is one of the largest erratic boulders of northern Germany. A picture of the Giebichenstein is part of the emblem of the Stöckse municipality.
 W
WA Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, abbreviated GSSP, is an internationally agreed upon reference point on a stratigraphic section which defines the lower boundary of a stage on the geologic time scale. The effort to define GSSPs is conducted by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, a part of the International Union of Geological Sciences. Most, but not all, GSSPs are based on paleontological changes. Hence GSSPs are usually described in terms of transitions between different faunal stages, though far more faunal stages have been described than GSSPs. The GSSP definition effort commenced in 1977. As of 2012, 64 of the 101 stages that need a GSSP have been formally defined.
 W
WThe Hearne Craton is a craton in northern Canada which, together with the Rae Craton, forms the Western Churchill Province. Hearne is one of the six Archaean cratons of the Canadian Shield that are bound together by Palaeoproterozoic orogenic belts. Before being merged these six cratons formed independent microcontinents.
 W
WA Heinrich event is a natural phenomenon in which large groups of icebergs break off from glaciers and traverse the North Atlantic. First described by marine geologist Hartmut Heinrich, they occurred during five of the last seven glacial periods over the past 640,000 years. Heinrich events are particularly well documented for the last glacial period but notably absent from the penultimate glaciation. The icebergs contained rock mass, eroded by the glaciers, and as they melted, this material was dropped to the sea floor as ice rafted debris.
 W
WThe Ice Age Floods National Geologic Trail or Ice Age Floods Trail is designated as the first National Geologic Trail in the United States. It will consist of a network of routes connecting facilities that will provide interpretation of the geological consequences of the Glacial Lake Missoula floods of the last glacial period that began about 110,000 years ago.
 W
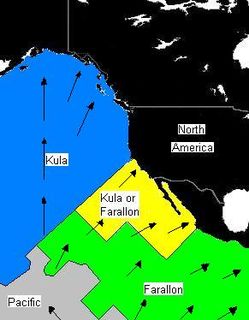
WThe Kula Plate was an oceanic tectonic plate under the northern Pacific Ocean south of the Near Islands segment of the Aleutian Islands. It has been subducted under the North American Plate at the Aleutian Trench, being replaced by the Pacific Plate.
 W
WA land bridge, in biogeography, is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonise new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea levels fall, exposing shallow, previously submerged sections of continental shelf; or when new land is created by plate tectonics; or occasionally when the sea floor rises due to post-glacial rebound after an ice age.
 W
WLost lands are islands or continents believed by some to have existed during pre-history, but to have since disappeared as a result of catastrophic geological phenomena. Such continents are generally thought to have subsided into the sea, leaving behind only a few traces or legends by which they may be known.
 W
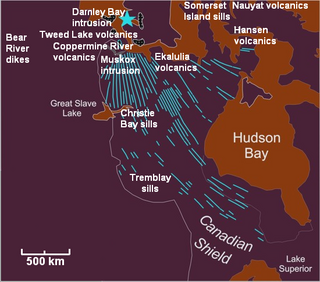
WThe Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.
 W
WBenoît de Maillet was a well-travelled French diplomat and natural historian. He was French consul general at Cairo, and overseer in the Levant. He formulated an evolutionary hypothesis to explain the origin of the earth and its contents.
 W
WThe Palaeobotanical Garden is a natural reserve in the town of Mata, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
 W
WPaleomagnetism is the study of the record of the Earth's magnetic field in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Magnetic minerals in rocks can lock-in a record of the direction and intensity of the magnetic field when they form. This record provides information on the past behavior of Earth's magnetic field and the past location of tectonic plates. The record of geomagnetic reversals preserved in volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences (magnetostratigraphy) provides a time-scale that is used as a geochronologic tool. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called paleomagnetists.
 W
WThe Paleontological Site Arroio Cancela is located within the city of Santa Maria, a municipality of Rio Grande do Sul, the southernmost state of Brazil. The site is situated in the neighbourhood Nossa Senhora de Lourdes at an altitude of 107 metres above sea level. The fossils have been discovered within the sediments of the Santa Maria Formation, they are vertebrates from the Triassic period and are about 225 million years old.
 W
WThe Palaeontological Site Chiniquá is located in the Brazilian municipality of São Pedro do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, along highway BR-287, about 70 kilometers west of the city of Santa Maria. The site occupies an area of about 250 hectares and is part of the geopark of paleorrota. It yielded fossils of Middle Triassic (Ladinian) age.
 W
WThe Paleontological Sites of Santa Maria are located in the city of Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil and dating from the Triassic. Are in the Santa Maria Formation and Caturrita Formation.
 W
WPaleontology, also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch. It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study interactions with each other and their environments. Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BCE. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, "old, ancient", ὄν, on, "being, creature", and λόγος, logos, "speech, thought, study".
 W
WPaleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines.
 W
WIn the geosciences, paleosol can have two meanings. The first meaning, common in geology and paleontology, refers to a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments or volcanic deposits, which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock. In Quaternary geology, sedimentology, paleoclimatology, and geology in general, it is the typical and accepted practice to use the term "paleosol" to designate such "fossil soils" found buried within sedimentary and volcanic deposits exposed in all continents as illustrated by Retallack (2001), Kraus (1999), and other published papers and books.
 W
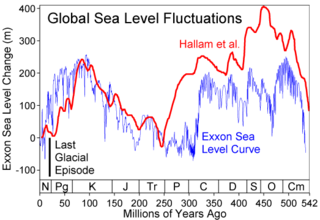
WGlobal or eustatic sea level has fluctuated significantly over Earth's history. The main factors affecting sea level are the amount and volume of available water and the shape and volume of the ocean basins. The primary influences on water volume are the temperature of the seawater, which affects density, and the amounts of water retained in other reservoirs like rivers, aquifers, lakes, glaciers, polar ice caps and sea ice. Over geological timescales, changes in the shape of the oceanic basins and in land/sea distribution affect sea level. In addition to eustatic changes, local changes in sea level are caused by tectonic uplift and subsidence.
 W
WThe Pilbara Craton is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere located in Pilbara, Western Australia.
 W
WThe Rae Craton is an Archean craton located in northern Canada north of the Superior Craton.
 W
WRed Rock Pass is a low mountain pass in southern Bannock County Idaho, United States, south of Downey. It is geologically significant as the spillway of ancient Lake Bonneville. It is located along highway U.S. Route 91 at an elevation of 4,785 feet above sea level, bounded by two mountain ranges; the Portneuf to the east and the Bannock to the west.
 W
WThe River Warren Falls was a massive waterfall on the glacial River Warren initially located in present-day Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The waterfall was 2700 feet (823 m) across and 175 feet (53 m) high.
 W
WThe Sahara pump theory is a hypothesis that explains how flora and fauna migrated between Eurasia and Africa via a land bridge in the Levant region. It posits that extended periods of abundant rainfall lasting many thousands of years in Africa are associated with a "wet-Sahara" phase, during which larger lakes and more rivers existed. This caused changes in the flora and fauna found in the area. Migration along the river corridor was halted when, during a desert phase 1.8–0.8 million years ago (mya), the Nile ceased to flow completely and possibly flowed only temporarily in other periods due to the geologic uplift of the Nile River region.
 W
WThe Saharan Metacraton is a term used by some geologists to describe a large area of continental crust in the north-central part of Africa. Whereas a craton is an old and stable part of the lithosphere, the term "metacraton" is used to describe a craton that has been remobilized during an orogenic event, but where the characteristics of the original craton are still identifiable. The geology of the continent has only been partially explored, and other names have been used to describe the general area that reflect different views of its nature and extent. These include "Nile Craton", "Sahara Congo Craton", "Eastern Saharan Craton" and "Central Saharan Ghost Craton". This last term is because the older rocks are almost completely covered by recent sediments and desert sands, making geological analysis difficult.
 W
WSiccar Point is a rocky promontory in the county of Berwickshire on the east coast of Scotland. It is famous in the history of geology for Hutton's Unconformity found in 1788, which James Hutton regarded as conclusive proof of his uniformitarian theory of geological development.
 W
WThe Slave Craton is an Archaean craton in the north-western Canadian Shield, in Northwest Territories and Nunavut. The Slave Craton includes the 4.03 Ga-old Acasta Gneiss which is one of the oldest dated rocks on Earth. Covering about 300,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi), it is a relatively small but well-exposed craton dominated by ~2.73–2.63 Ga greenstones and turbidite sequences and ~2.72–2.58 Ga plutonic rocks, with large parts of the craton underlain by older gneiss and granitoid units. The Slave Craton is one of the blocks that compose the Precambrian core of North America, also known as the palaeocontinent Laurentia.
 W
WThe three Storegga Slides are considered to be amongst the largest known submarine landslides. They occurred under water, at the edge of Norway's continental shelf in the Norwegian Sea, approximately 6225–6170 BC. The collapse involved an estimated 290 km (180 mi) length of coastal shelf, with a total volume of 3,500 km3 (840 cu mi) of debris, which caused a megatsunami in the North Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WSundaland is a biogeographical region of Southeastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It includes the Malay Peninsula on the Asian mainland, as well as the large islands of Borneo, Java, and Sumatra and their surrounding small islands.
 W
WIn geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some earth scientists use a different definition: "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times, although a minimum of about 75% of the continental crust then in existence has been proposed as a limit to separate supercontinents from other groupings.
 W
WTouqan Palace is one of the most important historical buildings in the city of Nablus and its number is more than one hundred rooms located to the western side of the Al-Beik Mosque and was built by the head of Nablus scholars Ibrahim Bey bin Saleh Pasha Touqan with funding from his father and that was in the eighteenth century AD, associated with historical and literary figures that gave him fame Significant, in particular for his association with the poet and writer Ibrahim Toukan and his poet sister Fadwa Toukan and the legal personality Qadri Toukan.
 W
WThe Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield, the North American Craton, and the forging of the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0-1.8 billion years ago.
 W
WThe Tuareg Shield is a geological formation lying between the West African craton and the Saharan Metacraton in West Africa. Named after the Tuareg people, it has complex a geology, reflecting the collision between these cratons and later events. The landmass covers parts of Algeria, Niger and Mali.
 W
WAn unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788.