 W
WOn March 27, 1980, a series of volcanic explosions and pyroclastic flows began at Mount St. Helens in Skamania County, Washington, United States. It initiated as a series of phreatic blasts from the summit then escalated on May 18, 1980, as a major explosive eruption. The eruption, which had a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 5, was the most significant to occur in the contiguous 48 U.S. states since the much smaller 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California. It has often been declared the most disastrous volcanic eruption in U.S. history.
 W
WMount Agung is an active volcano in Bali, Indonesia, southeast of Mount Batur volcano, also in Bali. It is the highest point on Bali, and dominates the surrounding area, influencing the climate, especially rainfall patterns. From a distance, the mountain appears to be perfectly conical. From the peak of the mountain, it is possible to see the peak of Mount Rinjani on the nearby island of Lombok, to the east, although both mountains are frequently covered in clouds. Agung is a stratovolcano, with a large and deep crater. Its most recent eruptions occurred from 2017–2019.
 W
WThe Armero tragedy occurred following the eruption of the Nevado del Ruiz stratovolcano in Tolima, Colombia, on November 13, 1985. After 69 years of dormancy, the volcano's eruption caught nearby towns unaware, even though the government had received warnings from volcanological organizations to evacuate the area after the detection of volcanic activity two months earlier.
 W
WAugustine Volcano is a stratovolcano consisting of a central complex of summit lava domes and flows surrounded by an apron of pyroclastic, lahar, avalanche, and ash deposits. The volcano is frequently active, with major eruptions recorded in 1883, 1935, 1963–64, 1976, 1986, and 2006. Minor eruptive events were reported in 1812, 1885, 1908, 1944, and 1971. The large eruptions are characterized by an explosive onset followed by the quieter effusion of lava. It forms Augustine Island in southwestern Cook Inlet in the Kenai Peninsula Borough of southcentral coastal Alaska, 174 miles (280 km) southwest of Anchorage. Augustine Island has a land area of 32.4 square miles (83.9 km2), while West Island, just off Augustine's western shores, has 2 sq mi (5.2 km2). The irregular coastline of Augustine Island is due to the repeated catastrophic collapse of the summit dome, forming debris avalanches down the flanks and into Cook Inlet.
 W
WMount Awu is the largest volcano in the Sangihe chain, located in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Powerful eruptions occurred in 1711, 1812, 1856, 1892 and 1966 with devastating pyroclastic flows and lahars that have resulted in more than 8,000 fatalities altogether. A 4.5 km wide crater is found at the summit and a deep valley forms a passageways for lahars, splitting the flanks from the crater. This is a volcano in the Ring of Fire.
 W
WCerro Azul, sometimes referred to as Quizapu, is an active stratovolcano in the Maule Region of central Chile, immediately south of Descabezado Grande. Part of the South Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit is 3,788 meters (12,428 ft) above sea level, and is capped by a summit crater that is 500 meters (1,600 ft) wide and opens to the north. Beneath the summit, the volcano features numerous scoria cones and flank vents.
 W
WBezymianny is an active stratovolcano in Kamchatka, Russia. Bezymianny volcano had been considered extinct until 1955. Activity started in 1955, culminating in a dramatic eruption on 30 March 1956. This eruption, similar to that of Mount St. Helens in 1980, produced a large horseshoe-shaped crater that was formed by collapse of the summit and an associated lateral blast. Subsequent episodic but ongoing lava dome growth, accompanied by intermittent explosive activity and pyroclastic flows, has largely filled the 1956 crater. The most recent eruption of lava flows occurred in February 2013. An explosive eruption on 20 December 2017 released an ash plume rising to a height of 15 kilometres (49,000 ft) above sea level, which drifted for 320 kilometres (200 mi) NE.
 W
WChiles is a volcano on the border of Colombia and Ecuador. It lies 3 kilometres (2 mi) south-east of the volcano Cerro Negro de Mayasquer, and the two peaks are considered part of the same Chiles-Cerro Negro volcanic complex. The volcanoes, together with the Cumbal are andesitic in rock type. A 1936 eruption reported by the Colombian government agency Ingeominas may have been from the Ecuadorean volcano Reventador, otherwise the volcano has not erupted for around 160,000 years.
 W
WCotopaxi is an active stratovolcano in the Andes Mountains, located in the Latacunga canton of Cotopaxi Province, about 50 km (31 mi) south of Quito, and 33 km (21 mi) northeast of the city of Latacunga, Ecuador, in South America. It is the second highest summit in Ecuador, reaching a height of 5,897 m (19,347 ft). It is one of the world's highest volcanoes.
 W
WCumbal is a stratovolcano of the Caribe Terrane, located at the Nudo de los Pastos in Nariño, Colombia. It is the southernmost historically active volcano of Colombia and is together with Chiles and Azufral one of the few volcanoes of the Western Ranges. The volcano is dominated by andesites.
 W
WDoña Juana is a stratovolcano, located within the Doña Juana-Cascabel Volcanic Complex National Natural Park in Nariño, Colombia.
 W
WEl Chichón, also known as Chichonal, is an active volcano in Francisco León, north-western Chiapas, Mexico. El Chichón is part of a geologic zone known as the Chiapanecan Volcanic Arc. El Chichón is a complex of domes with a tuff ring, made of ejected volcanic material, located between the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt and the Central America Volcanic Arc. El Chichón erupted in 1982; prior to this, activity had not occurred since c.1360, although debates in literature occur around an eruption occurring in c.1850.
 W
WEldfell is a volcanic cone just over 200 metres (660 ft) high on the Icelandic island of Heimaey. It formed in a volcanic eruption, which began without warning on the eastern side of Heimaey, in the Westman Islands, on 23 January 1973. The name means Hill of Fire in Icelandic.
 W
WGaleras is an Andean stratovolcano in the Colombian department of Nariño, near the departmental capital Pasto. Its summit rises 4,276 metres (14,029 ft) above sea level. It has erupted frequently since the Spanish conquest, with its first historical eruption being recorded on December 7, 1580. A 1993 eruption killed nine people, including six scientists who had descended into the volcano's crater to sample gases and take gravity measurements in an attempt to be able to predict future eruptions. It is currently the most active volcano in Colombia.
 W
WThe Galeras tragedy occurred when six scientists and three tourists were killed as a result of the January 1993 eruption of the Galeras stratovolcano in Colombia. Geologist Stanley Williams and six others on the volcano survived.
 W
WMount Galunggung is an active stratovolcano in West Java, Indonesia, around 80 km (50 mi) southeast of the West Java provincial capital, Bandung. Mount Galunggung is part of the Sunda Arc extending through Sumatra, Java and Bali, which has resulted from the subduction of the Australian plate beneath the Eurasian plate. Galunggung had its first historical eruption in 1500 that produced pyroclastic flows and lahars that killed 4,011 people.
 W
WHekla, or Hecla, is a stratovolcano in the south of Iceland with a height of 1,491 m (4,892 ft). Hekla is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes; over 20 eruptions have occurred in and around the volcano since 874. During the Middle Ages, Europeans called the volcano the "Gateway to Hell".
 W
WMount Hudson is a stratovolcano in southern Chile, and the site of one of the largest eruptions in the twentieth century. The mountain itself is covered by a glacier. There is a caldera at the summit from an ancient eruption; modern volcanic activity comes from inside the caldera. Mount Hudson is named after Francisco Hudson, a 19th-century Chilean Navy hydrographer.
 W
WKatla is a large volcano in southern Iceland. It is very active; twenty eruptions have been documented between 930 and 1918, at intervals of 20–90 years. It has not erupted violently for 102 years, although there may have been small eruptions that did not break the ice cover, including ones in 1955, 1999, and 2011.
 W
WKelud is an active stratovolcano located in East Java, Indonesia. Like many Indonesian volcanoes and others on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Kelud is known for large explosive eruptions throughout its history. More than 30 eruptions have occurred since 1000 AD. In 2007, an effusive explosion filled the crater with a lava dome. It last erupted on February 13, 2014, destroying the lava dome and ejecting boulders, stones and ashes up to West Java about 500 kilometers from Mount Kelud. The crater filled with water during the rainy season.
 W
WKharimkotan ; Japanese 春牟古丹島; Harimukotan-tō, alternatively Harumukotan-tō or 加林古丹島; Karinkotan-tō) is an uninhabited volcanic island located 13 km (8 mi) from Onekotan near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language, from “village of many Cardiocrinum”.
 W
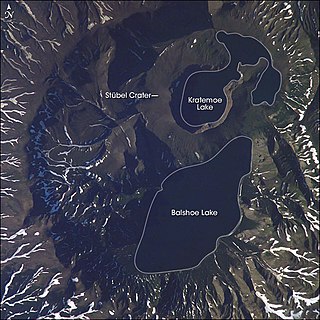
WKsudach is a stratovolcano in southern Kamchatka, Russia. The last eruption of Ksudach was in March 1907, on or around 28 March, which was one of the largest ever recorded in Kamchatka, with a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 5 and a volume of ejected ash at 2.4 km3 (0.58 cu mi). The 1907 eruption sent ash high into the atmosphere which was transported by the jet stream, leaving North America east of the Rocky Mountains unseasonably cold. The summit area comprises overlapping calderas. Two lakes, Bolshoe and Kraternoe, are located within calderas at the summit of Ksudach. These lakes, along with hot springs and the surrounding wilderness, make the Ksudach Volcano region a popular trekking destination. In the event of renewed volcanic activity, its remote location minimizes its potential hazard to humans.
 W
WKuchinoerabu-jima (口永良部島), is one of the Satsunan Islands, usually classed with the Ōsumi Islands belonging to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. The island, 38.04 km² in area, has a population of 147. The island can only be reached by boat as it has no airport. There is regular ferry service with Yakushima, which is about 15 km to the east. Travel time is approximately 1 hour. The islanders are dependent mainly on fishing, agriculture and seasonal tourism. The entire island is within the borders of the Kirishima-Yaku National Park.
 W
WOn 21 August 1986, a limnic eruption at Lake Nyos in northwestern Cameroon killed 1,746 people and 3,500 livestock.
 W
WMount Lamington is an andesitic stratovolcano in the Oro Province of Papua New Guinea. The forested peak of the volcano had not been recognised as such until its devastating eruption in 1951 that caused about 3,000 deaths.
 W
WLassen Peak, commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range of the Western United States. Located in the Shasta Cascade region of Northern California, it is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which stretches from southwestern British Columbia to northern California. Lassen Peak reaches an elevation of 10,457 feet (3,187 m), standing above the northern Sacramento Valley. It supports many flora and fauna among its diverse habitats, which are subject to frequent snowfall and reach high elevations.
 W
WManam, known locally as Manam Motu, is an island located in the Bismarck Sea across the Stephan Strait from Yawar on the northeast coast of mainland Papua New Guinea's Bogia District. The island is 10 kilometers wide, and was created by the activity of the Manam Volcano, one of the country’s most active. It was evacuated in 2004 and its residents resettled elsewhere in Papua New Guinea, but many have begun to return despite concerns of future volcanic activity.
 W
WThe 1975 eruption of Mauna Loa was a short-lived Hawaiian eruption that followed 25 years of quiescence at the Hawaiian volcano Mauna Loa. The eruption began just before midnight on July 5 and involved fissures extending across the length of Moku‘āweoweo, Mauna Loa's summit caldera, and into the upper ends of the volcano's northeast and southwest rift zones. After only 6 hours, activity in Moku‘āweoweo and on the southwest rift zone ended, but lava fountaining continued along the northeast rift zone until 7:30 p.m. on July 6, when all activity ceased.
 W
WThe 1984 eruption of Mauna Loa was a Hawaiian eruption in the U.S. state of Hawaii that lasted from March 25 to April 15, 1984. It ended a 9-year period of quiescence at the volcano and continued for 22 days, during which time lava flows and lava fountains issued from the summit caldera and fissures along the northeast and southwest rift zones. Although the lava threatened Hilo, the flow stopped before reaching the outskirts of town.
 W
WMayon Volcano, also known as Mount Mayon, is a sacred and active stratovolcano in the province of Albay in Bicol Region, on the large island of Luzon in the Philippines. A popular tourist spot, it is renowned for its "perfect cone" because of its symmetric conical shape.
 W
WLake Monoun is a lake in West Province, Cameroon, that lies in the Oku Volcanic Field 5.58°N 10.59°E. On August 15, 1984, the lake exploded in a limnic eruption, which resulted in the release of a large amount of carbon dioxide that killed 37 people. At first, the cause of the deaths was a mystery, and causes such as terrorism were suspected. Further investigation and a similar event two years later at Lake Nyos led to the currently accepted explanation.
 W
WMount Agrihan is a stratovolcano on the uninhabited island of Agrihan in the Pacific Ocean, located in the Northern Mariana Islands, an insular area and commonwealth of the United States. The volcano has an elevation of 3,166 feet (965 m), making its summit the highest point in the Northern Mariana Islands, as well as all of Micronesia.
 W
WColo is a stratovolcano in Indonesia. It forms the small island of Una-Una at the middle of the Gulf of Tomini, the northern part of Sulawesi. The volcano is broad and has a low profile with only 507 metres (1,663 ft) above the sea level. It contains a 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) wide caldera with a small volcanic cone inside. Only three eruptions have been recorded in the history with two of them causing damage.
 W
WMount Merapi, Gunung Merapi, is an active stratovolcano located on the border between Central Java and Special Region of Yogyakarta provinces, Indonesia. It is the most active volcano in Indonesia and has erupted regularly since 1548. It is located approximately 28 kilometres (17 mi) north of Yogyakarta city which has a population of 2.4 million, and thousands of people live on the flanks of the volcano, with villages as high as 1,700 metres (5,600 ft) above sea level.
 W
WMount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is 50 miles (80 km) northeast of Portland, Oregon and 96 miles (154 km) south of Seattle, Washington. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a friend of explorer George Vancouver who made a survey of the area in the late 18th century. The volcano is located in the Cascade Range and is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, a segment of the Pacific Ring of Fire that includes over 160 active volcanoes. This volcano is well known for its ash explosions and pyroclastic flows.
 W
WCerro Negro de Mayasquer is a volcano on the border of Colombia and Ecuador. It lies 3 kilometres (2 mi) north-west of the volcano Chiles, and the two peaks are considered part of the same Chiles-Cerro Negro volcanic complex. These volcanoes, together with Cumbal are andesitic in rock type. A 1936 eruption reported by the Colombian government agency INGEOMINAS may have been from the Ecuadorean volcano Reventador, otherwise the volcano has not erupted for around 160,000 years.
 W
WThe Nevado del Ruiz, also known as La Mesa de Herveo is a volcano on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, about 129 kilometers (80 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Volcanic activity at Nevado del Ruiz began about two million years ago, since the Early Pleistocene or Late Pliocene, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150,000 years ago.
 W
WNishi-no-shima is a volcanic island located around 940 km (584 mi) south-southeast of Tokyo, that is part of the Volcano Islands arc.
 W
WNovarupta is a volcano that was formed in 1912, located on the Alaska Peninsula in Katmai National Park and Preserve, about 290 miles (470 km) southwest of Anchorage. Formed during the largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century, Novarupta released 30 times the volume of magma of the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens.
 W
WParícutin is a cinder cone volcano located in the Mexican state of Michoacán, near the city of Uruapan and about 322 kilometers (200 mi) west of Mexico City. The volcano surged suddenly from the cornfield of local farmer Dionisio Pulido in 1943, attracting both popular and scientific attention.
 W
WThe 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée was one the deadliest volcanic eruptions of all time that occurred on the island of Martinique in the Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc of the eastern Caribbean. Eruptive activity began on 23 April as a series of phreatic explosions from the summit of Mount Pelée. Within days, the vigor of the explosions exceeded anything witnessed since the island was settled by Europeans. The intensity then subsided for a few days until early May when the explosions had increased again. Lightning laced the eruption clouds and trade winds dumped ash on villages to the west. Heavy ash fall at times caused total darkness. Some of the afflicted residents panicked and headed for the perceived safety of larger settlements, especially Saint-Pierre, about 10 km (6.2 mi) south of Pelée's summit. Saint-Pierre received its first ash fall on 3 May.
 W
WThe 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines' Luzon Volcanic Arc was the second-largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century, behind only the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in Alaska. Eruptive activity began on April 2 as a series of phreatic explosions from a fissure that opened on the north side of Mount Pinatubo. Seismographs were set up and began monitoring the volcano for earthquakes. In late May, the number of seismic events under the volcano fluctuated from day-to-day. Beginning June 6, a swarm of progressively shallower earthquakes accompanied by inflationary tilt on the upper east flank of the mountain, culminated in the extrusion of a small lava dome.
 W
WPuracé is an andesitic stratovolcano located in the Puracé National Natural Park in the Cauca Department, Colombia. It is part of the North Volcanic Zone of the Andean Volcanic Belt. The volcano is located at the intersection of the Coconucos and Morras Faults.
 W
WThe Rabaul caldera, or Rabaul Volcano, is a large volcano on the tip of the Gazelle Peninsula in East New Britain, Papua New Guinea, and derives its name from the town of Rabaul inside the caldera. The caldera has many sub-vents, Tavurvur being the most well known for its devastating eruptions over Rabaul. The outer flanks of the highest peak, a 688-metre-high asymmetrical pyroclastic shield, are formed by thick pyroclastic flow deposits. There is no sign of a pyroclastic shield along the rim of the caldera, making the location likely underwater, on the caldera's floor.
 W
WRedoubt Volcano, or Mount Redoubt, is an active stratovolcano in the largely volcanic Aleutian Range of the U.S. state of Alaska. Located at the head of the Chigmit Mountains subrange in Lake Clark National Park and Preserve, the mountain is just west of Cook Inlet, in the Kenai Peninsula Borough about 110 miles (180 km) southwest of Anchorage. At 10,197 feet (3,108 m), in just over 5 miles (8 km) Mount Redoubt attains 9,150 feet (2,700 m) of prominence over its surrounding terrain. It is the highest summit in the Aleutian Range. In 1976, Redoubt Volcano was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.
 W
WMount Ruapehu is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupo Volcanic Zone in New Zealand. It is 23 kilometres (14 mi) northeast of Ohakune and 23 km (14 mi) southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupo, within Tongariro National Park. The North Island's major ski resorts and only glaciers are on its slopes.
 W
WSakurajima is an active stratovolcano, formerly an island and now a peninsula, in Kagoshima Prefecture in Kyushu, Japan. The lava flows of the 1914 eruption connected it with the Ōsumi Peninsula. It is the most active volcano in Japan.
 W
WSanta María Volcano is a large active volcano in the western highlands of Guatemala, in the Quetzaltenango Department near the city of Quetzaltenango.
 W
WShiveluch is the northernmost active volcano in Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It, and Karymsky are Kamchatka's largest, and most active and most continuous erupting volcanoes.
 W
WShōwa Iōjima (昭和硫黄島), also known as Shōwa Shintō (昭和新島), is one of the Satsunan Islands, usually classed with the Ōsumi Islands, belonging to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. A deserted volcanic island, it is located just off the northern shore of Iōjima, Kagoshima.
 W
WLa Soufrière or Soufrière Saint Vincent is an active volcano on the island of Saint Vincent in the Windward Islands of the Caribbean. Many volcanoes in the Caribbean are named Soufrière. These include Soufrière Hills on Montserrat and La Grande Soufrière on Guadeloupe, the subject of Werner Herzog's 1977 film La Soufrière.
 W
WThe Soufrière Hills are an active, complex stratovolcano with many lava domes forming its summit on the Caribbean island of Montserrat. Many volcanoes in the Caribbean are named Soufrière. These include La Soufrière or Soufrière Saint Vincent on the island of Saint Vincent, and La Grande Soufrière on Guadeloupe. After a long period of dormancy, the Soufrière Hills volcano became active in 1995 and has continued to erupt ever since. Its eruptions have rendered more than half of Montserrat uninhabitable, destroying the capital city, Plymouth, and causing widespread evacuations: about two thirds of the population have left the island.
 W
WMount Spurr is a stratovolcano in the Aleutian Arc of Alaska, named after United States Geological Survey geologist and explorer Josiah Edward Spurr, who led an expedition to the area in 1898. The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) currently rates Mount Spurr as Level of Concern Color Code Green. The mountain is known aboriginally by the Dena'ina Athabascan name K'idazq'eni, literally 'that which is burning inside'.
 W
WSurtsey is a volcanic island located in the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago off the southern coast of Iceland. At 63.303°N 20.605°W, Surtsey is the southernmost point of Iceland. It was formed in a volcanic eruption which began 130 metres below sea level, and reached the surface on 14 November 1963. The eruption lasted until 5 June 1967, when the island reached its maximum size of 2.7 km2 (1.0 sq mi). Since then, wave erosion has caused the island to steadily diminish in size: as of 2012, its surface area was 1.3 km2 (0.50 sq mi). The most recent survey (2007) shows the island's maximum elevation at 155 m (509 ft) above sea level.
 W
WTaal Volcano is a large caldera filled by Taal Lake in the Philippines. Located in the province of Batangas, the volcano is the second-most active volcano in the Philippines, with 34 recorded historical eruptions, all of which were concentrated on Volcano Island, near the middle of Taal Lake. The caldera was formed by prehistoric eruptions between 140,000 and 5,380 BP.
 W
WTori-shima 'Bird Island', is an uninhabited Japanese island in the Pacific Ocean. The volcanic island is part of the Izu Islands.
 W
WMount Unzen is an active volcanic group of several overlapping stratovolcanoes, near the city of Shimabara, Nagasaki on the island of Kyushu, Japan's southernmost main island.
 W
WMount Vesuvius is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about 9 km (5.6 mi) east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes which form the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera caused by the collapse of an earlier and originally much higher structure.
 W
WThe Volcán de Colima, 3,820 m (12,533 ft), also known as Volcán de Fuego, is part of the Colima Volcanic Complex (CVC) consisting of Volcán de Colima, Nevado de Colima and the eroded El Cántaro. It is the youngest of the three and as of 2015 is one of the most active volcanos in Mexico and in North America. It has erupted more than 40 times since 1576. One of the largest eruptions was on January 20–24, 1913. Nevado de Colima, also known as Tzapotépetl, lies 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of its more active neighbor and is the taller of the two at 4,271 meters (14,015 ft). It is the 26th-most prominent peak in North America.