 W
WAbd al Kuri is a rocky island in the Guardafui Channel. As a part of the Socotra Archipelago of the Socotra Governorate of Yemen, it lies about 65 miles (105 km) southwest of the island of Socotra. It is geographically closer to Somalia. It consists of granite and diorite covered by limestone. There is a dispute between Yemen and Somalia's government over the island's sovereignty.
 W
WAbu Musa is a 12.8-square-kilometre (4.9 sq mi) island in the eastern Persian Gulf near the entrance to the Strait of Hormuz. Due to the depth of sea, oil tankers and big ships have to pass between Abu Musa and Greater and Lesser Tunbs; this makes these islands some of the most strategic points in the Persian Gulf. The island is administered by Iran as part of its province of Hormozgan, but is also claimed by the United Arab Emirates as a territory of the emirate of Sharjah.
 W
WThe East China Sea Air Defense Identification Zone is an Air Defense Identification Zone covering most of the East China Sea where the People's Republic of China announced that it was introducing new air traffic restrictions in November 2013. The area consists of the airspace from about, and including, the Japanese controlled Senkaku Islands north to South Korean-claimed Socotra Rock. About half of the area overlaps with a Japanese ADIZ, while also overlapping to a small extent with the South Korean and Taiwanese ADIZ. When introduced the Chinese initiative drew criticism as the ADIZ overlapped with the ADIZ of other countries, imposed requirements on both civilian and military aircraft regardless of destination, and included contested maritime areas
 W
WIsla de Aves, or Aves Island, is a Federal Dependency of Venezuela. It has been the subject of numerous territorial disputes between the neighboring independent islands, such as Dominica, and European mother countries of surrounding dependent islands, such as the Netherlands. It is a part of the Aves Ridge and lies to the west of the Windward Islands chain at 15°40′18″N 63°36′59″W. It is 375 metres (1,230 ft) in length and never more than 50 metres (160 ft) in width, and rises 4 metres (13 ft) above the sea on a calm day. Under a particular interpretation of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea it could be classified as a rock, which would only give Venezuela a twelve nautical mile economic zone. However, Venezuela claims it is an island, which grants it a 200-mile (320 km) exclusive economic zone. Mostly sand, a small portion has some scrubby vegetation. It is sometimes completely submerged during hurricanes. It is 185 kilometres (115 mi) southwest of the closest land, Montserrat, 225 kilometres (140 mi) west of Dominica and 547 kilometres (340 mi) north of the Venezuelan mainland.
 W
WBajo Nuevo Bank, also known as the Petrel Islands, is a small, uninhabited reef with some small grass-covered islets, located in the western Caribbean Sea at 15°53′N 78°38′W, with a lighthouse on Low Cay at 15°51′N 78°38′W. The closest neighbouring land feature is Serranilla Bank, located 110 kilometres to the west.
 W
WBrazilian Island is a small uninhabited river island at the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Quaraí (Cuareim) River, between the borders of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, which is disputed by the two latter countries. The island is approximately 3.7 km (2.3 mi) long by 0.9 km (0.6 mi) wide, and it is located at 30°10′56″S 57°37′43″W.
 W
WThe British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is a British overseas territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islands – many very small – amounting to a total land area of 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi). The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, 27 km2 (10 sq mi), the site of a joint military facility of the United Kingdom and the United States.
 W
WThe Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands are a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 individual tropical islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean.
 W
WCorocoro Island is an island near the mouth of the Amacuro River and in the delta of the Barima River in South America. The northernmost part of the land border between Guyana and Venezuela runs through the island. It is one of the few islands that is divided between more than one sovereign state. The vast majority of the island is Venezuelan territory. The north side of the island is the Atlantic Ocean and the south side is the Barima River. Venezuela does not recognize the border that divides the island, since it considers its eastern part, as part of the claimed territory of Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela claims the island in its entirety.
 W
WDarsah is an uninhabited island in the Guardafui Channel. It is part of the Socotra Archipelago of Yemen. Darsah and neighboring Samhah are collectively known as "Al Akhawain" which means "The Brothers". There is a dispute between Yemen and Somalia's government over the island's sovereignty.
 W
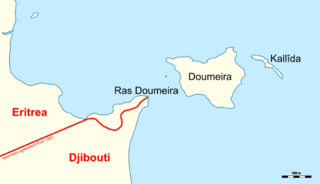
WThe Doumeira Islands are situated northeast of Djibouti and east of Eritrea near the Bab el-Mandeb in the Red Sea. They consist of Doumeira, located less than one kilometer off of the Eritrean and Djiboutian shore, and the much smaller island of Kallîda, which is 250 meters to the east.
 W
WEuropa Island is a 28-square-kilometre (11 sq mi) low-lying tropical atoll in the Mozambique Channel, about a third of the way from southern Madagascar to southern Mozambique. The island had never been inhabited until 1820, when the French family Rosier moved to it. The island officially became a possession of France in 1897.
 W
WThe Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 miles east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 miles from the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 square miles, comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, and the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The Falkland Islands' capital is Stanley on East Falkland.
 W
WThe Glorieuses or Glorioso Islands are a group of French islands and rocks totaling 5 square kilometres. They are part of the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean in the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, a French overseas territory. They are geographically part of the Comoro Islands between the French overseas region of Mayotte and the nation of Madagascar.
 W
WGraham Island was an island created by a now fully submerged volcano in the Mediterranean Sea. It was discovered when it last appeared on 1 August 1831 by Humphrey Fleming Senhouse, the captain of the first rate Royal Navy ship of the line St Vincent and named after Sir James Graham, the First Lord of the Admiralty. It was claimed by the United Kingdom. It forms part of the underwater volcano Empedocles, 30 km (19 mi) south of Sicily, and which is one of a number of submarine volcanoes known as the Campi Flegrei del Mar di Sicilia. Seamount eruptions have raised it above sea level several times before erosion submerged it again.
 W
WThe Glorieuses or Glorioso Islands are a group of French islands and rocks totaling 5 square kilometres. They are part of the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean in the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, a French overseas territory. They are geographically part of the Comoro Islands between the French overseas region of Mayotte and the nation of Madagascar.
 W
WGreater Tunb and Lesser Tunb are two small islands in the eastern Persian Gulf, close to the Strait of Hormuz. They lie at 26°15′N 55°16′E and 26°14′N 55°08′E respectively, some 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from each other and 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of the Iranian island of Qeshm. The islands are administered by Iran as part of its Hormozgan Province, but are also claimed by the United Arab Emirates as a territory of the Emirate of Ras al-Khaimah.
 W
WThe Isla Suárez (Bolivia) or Ilha de Guajará-Mirim (Brazil) is one of the world's many disputed territories. The island lies in the Rio Mamoré, which defines part of the boundary between the Bolivian department of Beni and the Brazilian state of Rondônia.
 W
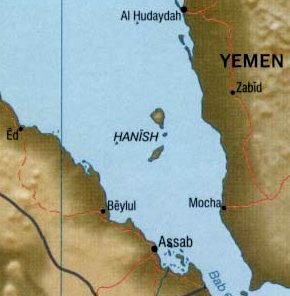
WThe Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that most of the archipelago belonged to Yemen.
 W
WHans Island is a barren uninhabited island measuring 1.3 km2 (0.5 sq mi), 1,290 m (4,230 ft) long and 1,199 m (3,934 ft) wide, in the centre of the Kennedy Channel of Nares Strait—the strait that separates Ellesmere Island from northern Greenland and connects Baffin Bay with the Lincoln Sea. Hans Island is the smallest of three islands in Kennedy Channel off the Washington Land coast; the others are Franklin Island and Crozier Island. The strait at this point is 35 km (22 mi) wide, placing the island within the territorial waters of both Canada and Greenland (Denmark). A theoretical line in the middle of the strait goes through the island.
 W
WThe Hawar Islands are an archipelago of desert islands owned by Bahrain, situated off the west coast of Qatar in the Gulf of Bahrain of the Persian Gulf.
 W
WÎle du Lys, also known as Le Lys or Ile du Lise, is one of the Glorioso Islands, north-west of Madagascar. It is administered by France.
 W
WIsla Calero is the largest island in Costa Rica, as well as along the San Juan River, which marks the border between Nicaragua and Costa Rica. The island lies between the San Juan, the Río Colorado of Costa Rica, and the Caribbean Sea. The entire island has an area of 151.6 km2 (58.5 sq mi).
 W
WThe Island of Vukovar is a disputed island on the river Danube. It is situated close to the city of Vukovar, Croatia.
 W
WIturup is one of the Kuril Islands. It was formerly known as Staten Island. It is the largest and northernmost island in the southern Kurils, ownership of which is disputed by Japan and Russia.
 W
WJabal al-Tair Island is a roughly oval volcanic island in Yemen, northwest of the constricted Bab al-Mandab passage at the mouth of the Red Sea, about halfway between mainland Yemen and Eritrea. From 1996 until it erupted in 2007, Yemen maintained two watchtowers and a small military base on the island.
 W
WThe Khuriya Muriya Islands are a group of five islands in the Arabian Sea, 40 km (25 mi) off the southeastern coast of Oman. The islands form part of the province of Shalim and the Hallaniyat Islands in the governorate of Dhofar.
 W
WKunashir Island, possibly meaning Black Island or Grass Island in Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands archipelago. The island is currently under Russian control, though Japan also claims the island.
 W
WThe Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands is a volcanic archipelago in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast that stretches approximately 1,300 km (810 mi) northeast from Hokkaido, Japan to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. It consists of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. The total land area is 10,503.2 square kilometres (4,055.3 sq mi), and the total population is 19,434.
 W
WThe Liancourt Rocks are a group of small islets in the Sea of Japan. While South Korea controls the islets, its sovereignty over them is contested by Japan.
 W
WThe Liancourt Rocks dispute is a territorial dispute between South Korea and Japan. Both countries claim sovereignty over the Liancourt Rocks, a group of small islets in the Sea of Japan which are referred to as "Dokdo" in Korean and "Takeshima" (竹島) in Japanese. North Korea also claims sovereignty of the islands.
 W
WThe Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands are a chain of atolls and coral islands. Kingman Reef is largely submerged and Filippo Reef is shown on some maps, although its existence is doubted. The islands were formed by volcanic activity and are located in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. The 11 islands stretch for 2,350 kilometres in a northwest–southeast direction, making it one of the longest island chains of the world. Eight of the islands form part of Kiribati, while the remaining three are United States territories grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands. Only Kiritimati and Tabuaeran atolls and Teraina Island have a permanent population.
 W
WThe Los Monjes islands is a federal dependency of Venezuela are located to the northwest 80 kilometres of the Gulf of Venezuela, 34.8 kilometres off the coast of Guajira Peninsula at the border between Colombia and the Venezuelan state of Zulia. The archipelago is contested by Colombia since over 200 years.
 W
WMachias Seal Island is an island in disputed water between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy, about 16 km (10 mi) southeast from Cutler, Maine, United States and 19 km (12 mi) southwest of Southwest Head, New Brunswick, Canada on Grand Manan Island. It is a neighbour to North Rock. Sovereignty of the island is disputed. The Canadian Coast Guard continues to staff a lighthouse on the island; the first lighthouse was constructed there in 1832.
 W
WMatthew Island and Hunter Island are two small and uninhabited high islands in the South Pacific, located 300 kilometres (190 mi) east of New Caledonia and south-east of Vanuatu archipelago. Hunter Island and Matthew Island, 70 km (43 mi) apart, are claimed by Vanuatu as part of Tafea Province, and considered by the people of Aneityum part of their custom ownership, and as of 2007 were claimed by France as part of New Caledonia.
 W
WMayotte is an overseas department and region of France officially named the Department of Mayotte. It consists of a main island, Grande-Terre, a smaller island, Petite-Terre, and several islets around these two. Mayotte is part of the Comoros archipelago, located in the northern Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Southeast Africa, between northwestern Madagascar and northeastern Mozambique. The department status of Mayotte is recent and the region remains, by a significant margin, the poorest in France. Mayotte is nevertheless much more prosperous than the other countries of the Mozambique Channel, making it a major destination for illegal immigration.
 W
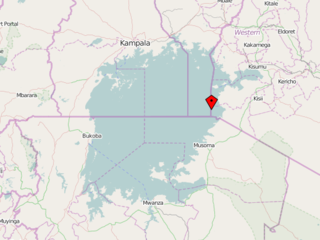
WMigingo is a 2,000-square-metre island in Lake Victoria. The island was the center of a low-level territorial dispute between Kenya and Uganda and is extremely densely populated.
 W
WFrance v United Kingdom [1953] ICJ 3 was an International Court of Justice case concerning sovereignty over seas.
 W
WNavassa Island is a small uninhabited island in the Caribbean Sea. Located northeast of Jamaica, south of Cuba, 40 nautical miles west of Jérémie on the south west peninsula of Haiti, it is subject to an ongoing territorial dispute between Haiti and the United States, which administers the island through the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. The U.S. has claimed the island since 1857, based on the Guano Islands Act of 1856. Haiti's claim over Navassa goes back to the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 that established French possessions in mainland Hispaniola, that were transferred from Spain by the treaty as well as other specifically named nearby islands. Its 1801 constitution also claimed unnamed "other adjacent islands", with Navassa not specifically named. Since its 1874 Constitution, and after the establishment of the 1857 U.S. claim, Haiti has explicitly named "la Navase" as one of the territories it claims. Médéric Louis Élie Moreau de Saint-Méry, who was a member of the French Parliament best known for his publications on Saint-Domingue, referred to la Navasse as the "small French island of Saint-Domingue" in 1798.
 W
WNorth Rock is an offshore rock near the boundary between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy east of the North American continent. Its ownership is disputed between the Canadian province of New Brunswick and the U.S. state of Maine as part of the territorial and maritime boundary dispute surrounding Machias Seal Island nearby to the south. The disputed area is referred to colloquially as the "Grey Zone".
 W
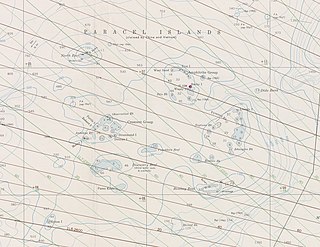
WThe Paracel Islands, also known as Xisha Islands and Hoang Sa Archipelago, are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea.
 W
WPerejil Island, also known as Parsley Island, is a small, uninhabited rocky islet located off the coast of Morocco, just 200 metres (660 ft) from the mainland coast. Its sovereignty is disputed between Spain and Morocco. It was the subject of an armed incident between the two countries in 2002.
 W
WPratas Island is an island in the northern part of the South China Sea administered as part of Cijin District, Kaohsiung, Republic of China (Taiwan). It is located about 170 nautical miles southeast of Hong Kong. It has an area of about 240 hectares, including 64 hectares of lagoon, and is the largest of the South China Sea Islands. It is the location of the Dongsha Airport.
 W
WSabrina Island was an islet formed during the months of June and July 1811 by a submarine volcanic eruption off the coast of Ponta da Ferraria, São Miguel Island, Azores. The first person to land on the island was Commander James Tillard, captain of the British warship HMS Sabrina, who hoisted the Union Jack on the island and claimed sovereignty for Great Britain. A diplomatic row with Portugal over the issue ensued, which the island's sinking back into the sea rendered moot.
 W
WSamhah or Samha is an inhabited island in the Guardafui Channel. A part of the Socotra archipelago, it is located between the island of Socotra and Somalia. Like the whole group, it belongs to Yemen, and is part of Socotra Governorate. There is a dispute between Yemen and Somalia's government over the island's sovereignty.
 W
WThe Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean consist of four small coral islands, an atoll, and a reef in the Indian Ocean, and have constituted the 5th district of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF), though sovereignty over some or all of the Islands is contested by Madagascar, Mauritius, and the Comoros. None of the islands has ever had a permanent population.
 W
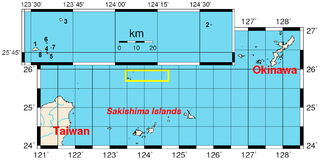
WThe Senkaku Islands are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea. They are located east of mainland China, northeast of Taiwan, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known in mainland China as the Diaoyu Islands or Diaoyu Dao and its affiliated islands, in Taiwan as the Tiaoyutai Islands / Diaoyutai Islands, and in the Western World are sometimes impartially referred to by the historical name Pinnacle Islands. In Okinawan they are called yukunkubajima. In Yaeyama dialect, they are called iigunkubajima.
 W
WThe Senkaku Islands dispute, or Diaoyu Islands dispute, concerns a territorial dispute over a group of uninhabited islands known as the Senkaku Islands in Japan, the Diaoyu Islands in the People's Republic of China (PRC), and Tiaoyutai Islands in the Republic of China. Aside from a 1945 to 1972 period of administration by the United States as part of the Ryukyu Islands, the archipelago has been controlled by Japan since 1895. According to Lee Seokwoo, the People's Republic of China (PRC) started taking up the question of sovereignty over the islands in the latter half of 1970 when evidence relating to the existence of oil reserves surfaced. Taiwan also claims the islands. The territory is close to key shipping lanes and rich fishing grounds, and there may be oil reserves in the area.
 W
WSerranilla Bank is a partially submerged reef, with small uninhabited islets, in the western Caribbean Sea. It is situated about 350 kilometres (220 mi) northeast of Punta Gorda, Nicaragua, and roughly 280 kilometres (170 mi) southwest of Jamaica. The closest neighbouring land feature is Bajo Nuevo Bank, located 110 kilometres (68 mi) to the east.
 W
WShikotan, also known as Shpanberg, is an island in the Kurils administered by the Russian Federation as part of Yuzhno-Kurilsky District of Sakhalin Oblast. It is claimed by Japan as the nominal Shikotan District , part of Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture.
 W
WSir Creek, originally Ban Ganga, is a 96-km (60-mi) tidal estuary in the uninhabited marshlands of the Indus River Delta on the border between India and Pakistan. The creek flows into the Arabian Sea and separates Gujarat state in India from Sindh province in Pakistan. The long-standing India-Pakistan Sir Creek border dispute stems from the demarcation "from the mouth of Sir Creek to the top of Sir Creek, and from the top of Sir Creek eastward to a point on the line designated on the Western Terminus". From this point onward, the boundary is unambiguously fixed as defined by the Tribunal Award of 1968.
 W
WSocotra or Soqotra, located between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea, is the largest of the four islands in Socotra Archipelago. The territory is located near major shipping routes and is officially part of Yemen, and had long been a subdivision of Aden Governorate. In 2004, it became attached to the Hadhramaut Governorate, which is much closer to the island than Aden. In 2013, the archipelago became its own governorate: Socotra Governorate.
 W
WThe South China Sea Islands consist of over 250 islands, atolls, cays, shoals, reefs and seamounts in the South China Sea. The islands are mostly low and small, and have few inhabitants. The islands and surrounding seas are subject to overlapping territorial claims by the countries bordering the South China Sea.
 W
WSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI) is a British Overseas Territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands known as the South Sandwich Islands. South Georgia is 165 kilometres (103 mi) long and 35 kilometres (22 mi) wide and is by far the largest island in the territory. The South Sandwich Islands lie about 700 kilometres (430 mi) southeast of South Georgia. The territory's total land area is 3,903 km2 (1,507 sq mi). The Falkland Islands are about 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) west from its nearest point.
 W
WThe South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about 604 kilometres (375 mi) north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and 844 kilometres (524 mi) south-west of South Georgia Island. They have a total area of about 620 square kilometres (240 sq mi). The islands are claimed both by Britain, and by Argentina as part of Argentine Antarctica. Under the 1959 Antarctic Treaty, sovereignty claims are held in abeyance.
 W
WThe Spratly Islands are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea. Composed of islands, islets and cays and more than 100 reefs, sometimes grouped in submerged old atolls, the archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam. Named after the 19th-century British whaling captain Richard Spratly who sighted Spratly Island in 1843, the islands contain less than 2 km2 of naturally occurring land area, which is spread over an area of more than 425,000 km2 (164,000 sq mi).
 W
WSwains Island is a remote coral atoll in the Tokelau Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The island is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute between Tokelau and the United States, which has administered it as part of American Samoa since 1925. Privately owned by the family of Eli Hutchinson Jennings since 1856, Swains Island was used as a copra plantation until 1967. It has not been permanently inhabited since 2008 but has often been visited by members of the Jennings family, scientific researchers, and amateur radio operators.
 W
WTaiping Island, also known as Itu Aba, and also known by various other names, is the largest of the naturally occurring Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. The island is elliptical in shape being 1.4 kilometres (0.87 mi) in length and 0.4 kilometres (0.25 mi) in width, with an area of 46 hectares. It is located on the northern edge of the Tizard Bank. The runway of the Taiping Island Airport is easily the most prominent feature on the island, running its entire length.
 W
WUkatnyy or Ukatny is an island in the northern Caspian Sea. It is located off the eastern end of the mouths of the Volga.
 W
WZuqar Island is an island in the Red Sea that belongs to Yemen. It lies between the coasts of mainland Yemen and Eritrea, near the Bab-el-Mandeb straits which connect the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden. Despite its proximity to the African continent, Zuqar Island is considered a part of Asia because it sits on the Asian continental shelf.