 W
WThe Boulder Batholith is a relatively small batholith in southwestern Montana, United States, exposed at the surface as granite and serving as the host rock for rich mineralized deposits at Butte and other locations. The batholith lies roughly between Butte and Helena, and between the Deer Lodge Valley and the Broadwater Valley. The volcanic Elkhorn Mountains are a large mass of forested lava associated with the batholith.
 W
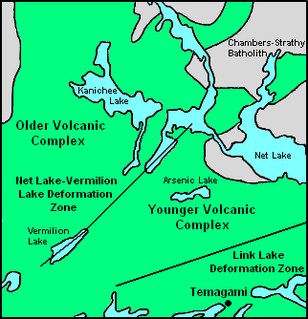
WThe Chambers-Strathy Batholith, also called the Strathy-Chambers Batholith, is a large granitoid batholith complex in the Temagami region of Northeastern Ontario, Canada. Named for the Chambers and Strathy townships, its compositions range from pink to grey quartz monzonite to granodiorite and intrudes through rocks of the Temagami Greenstone Belt.
 W
WThe Chilliwack Batholith is a large batholith that forms much of the North Cascades in southwestern British Columbia, Canada and the U.S. state of Washington.
 W
WEnchanted Rock is a pink granite mountain located in the Llano Uplift approximately 17 miles (27 km) north of Fredericksburg, Texas and 24 miles (39 km) south of Llano, Texas, United States. Enchanted Rock State Natural Area, which includes Enchanted Rock and surrounding land, spans the border between Gillespie County and Llano County, south of the Llano River. Enchanted Rock covers approximately 640 acres (260 ha) and rises approximately 425 feet (130 m) above the surrounding terrain to elevation of 1,825 feet (556 m) above sea level. It is the largest pink granite monadnock in the United States. Enchanted Rock State Natural Area, a part of the Texas state park system, includes 1,644 acres (665 ha). In 1936, the area was designated a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark. In 1971, Enchanted Rock was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.
 W
WThe Idaho Batholith is a granitic and granodioritic batholith of Cretaceous-Paleogene age that covers approximately 25,000 square kilometres (9,700 sq mi) of central Idaho and adjacent Montana. The batholith has two lobes that are separated from each other geographically and geologically. The smaller Bitterroot lobe in the north is separated from the larger Atlanta lobe in the south by the Belt Supergroup metamorphic rocks that compose the Salmon River Arch. The Bitterroot lobe is 75 to 53 million years old, and the Atlanta lobe is 98 to 68 million years old. A separate and unrelated igneous center, the Kaniksu batholith, is present in the Idaho Panhandle but is generally older. Much of the Atlanta and Bitterroot lobes are in the Idaho Batholith ecoregion while the Kaniksu batholith is in the Northern Rockies ecoregion.
 W
WThe Idaho Batholith ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Idaho and Montana. It is contained within the following biomes designated by the World Wild Fund for Nature (WWF): temperate coniferous forests; temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands; and deserts and xeric shrublands.
 W
WThe Sierra Nevada Batholith is a large batholith which forms the core of the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California, exposed at the surface as granite.