 W
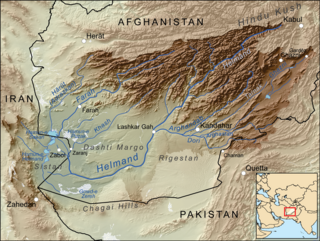
WThe Helmand River (also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin.
 W
WArghandab is a river in Afghanistan, about 400 km (250 mi) in length. It rises in the Hazarajat country north-west of Ghazni, flows south-west passing near the city of Kandahar, and then falls into the Helmand 30 km (19 mi) below Girishk. In its lower course it is much used for irrigation, under the control of the Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority, and the valley is cultivated and populous; yet the water is said to be somewhat brackish. It is doubtful whether the ancient Arachotus is to be identified with the Arghandab or with its chief confluent the Tarnak, which joins it on the left 50 km (31 mi) southwest of Kandahar. The Tarnak, which flows south of Kandahar, is much shorter and less copious.
 W
WThe Grishk Dam is a dam and power plant on the Helmand River, located near Grishk in Helmand Province, Afghanistan.
 W
WLake Hāmūn or "Hamoun Oasis" is a term applied to wetlands in endorheic Sīstān Basin on the Irano-Afghan border in the Sistan region. In Iran, it is also known as Hāmūn-e Helmand, Hāmūn-e Hīrmand, or Daryācheh-ye Sīstān.
 W
WThe Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority (HAVA) based in Lashkar Gah, Afghanistan, originally named the Helmand Valley Authority (HVA) until its expansion in 1965, was established on December 4, 1952 as an agency of the Afghan Government. The agency was modelled on the Tennessee Valley Authority in the United States, with a remit covering lands in Farah Province, Ghazni Province, Helmand Province, Herat Province, and Kandahar Province.
 W
WThe Kajaki Dam is one of the two major hydroelectric power dams of Helmand province in southern Afghanistan. The dam is located on the Helmand River 100 miles (161 km) north-west of Kandahar and is operated by the Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority. It has a dual function, to provide electricity and to irrigate some 650,000 acres (1800 km2) of an otherwise arid land. Water discharging from the dam traverses some 300 miles (500 km) of downstream irrigation canals feeding farmland. As of October 2016 it produces 52.5 megawatts of electricity.
 W
WThe Sistan Basin is an inland endorheic basin encompassing large parts of southwestern Afghanistan and minor parts of southeastern Iran, one of the driest regions in the world and an area subjected to prolonged droughts. Its watershed is a system of rivers flowing from the highlands of Afghanistan into freshwater lakes and marshes and then to its ultimate destination: Afghanistan's saline Godzareh depression, part of the extensive Sistan terminal basin. The Helmand River drains the basin's largest watershed, fed mainly by snowmelt from the mountains of Hindu Kush, but other rivers contribute also.