 W
WDer Alte Schwede or Alter Schwede is a glacial erratic, found during dredging of the river Elbe near Hamburg in 1999, at a depth of 15 m. The rock has a circumference of 19.7 m, a height of 4.5 m and weighs 217 tons. During the Elster maximum glaciation of the ice age 400 000 years ago, it was carried from Småland to the site where it was found. In June 2000, it was given its current name. It is Germany's oldest glacial erratic.
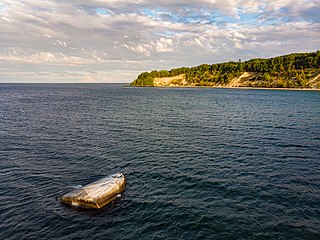 W
WThe Buskam, also Buhskam or Buskamen is a large glacial erratic boulder, 325 metres off the coast of Göhren, Rügen, northern Germany. Erratics have been scattered all over northern Germany by the glaciers of the Ice Age, but are usually much smaller. The Buskam has a volume of about 600 m3, a circumference of about 40 metres, and weights about 1,600 tons. A third of it (206 m3) lies above the water surface.
 W
WThe Dreifrankenstein is a boundary stone that marks the tripoint where the three Franconian provinces of Upper, Middle and Lower Franconia meet in southern Germany. As part of the regional reforms in 1972 the boundary marker was moved around 7 kilometres as the crow flies to the southeast. Today both points are marked by stones that are referred to as the Old and New Dreifrankenstein.
 W
WThe Giebichenstein in Stöckse, Germany, is one of the largest erratic boulders of northern Germany. A picture of the Giebichenstein is part of the emblem of the Stöckse municipality.
 W
WThis is a list of erratics on and around Rügen – the largest island off the Baltic coast of Germany. An erratic is usually defined as an individual block of rock lying on the surface of the land which has a volume of at least one cubic metre and which was transported by a glacier to its present site during the ice age.
 W
WThe Möwenstein is a glacial erratic that was transported south from the area of the present-day island of Bornholm by the ice sheet during the last glaciation. It is located on the island of Ummanz in the west of Rügen within the Western Pomerania Lagoon Area National Park. Erratics are relatively uncommon here, most of them lie east of the island of Rügen.
 W
WThe Nardevitz Erratic, also called the Great Rock of Nardewitz, is one of the largest glacial erratics in North Germany. It lies about 400 metres north of Nardevitz, a village in the parish of Lohme on the island of Rügen. Surrounded by trees and bushes as well as other drift material that was in the way of farming, it lies in the middle of a field. Its volume is estimated at 104 m³, which gives it a mass of 281 tonnes. The above-ground portion has a volume of 71 m³. It is therefore, apart from Buskam which lies in the Baltic Sea off Göhren, the largest erratic on Rügen and an important geological sight.
 W
WThe Schwanenstein is a glacial erratic on the island of Rügen in Germany. It lies about 100 metres east of the harbour at Lohme on the northern shore of the Jasmund peninsula about 20 metres off the beach in the Baltic Sea. It weighs 162 tonnes and has a volume of 60 m³. It is thus the fifth largest erratic of about 20 other large glacial boulders that are part of Rügen's legally protected geotopes. It is stylistically portrayed in Lohme's coat of arms.
 W
WThe Siebenschneiderstein (Söbenschniedersteen) is a glacial erratic on the island of Rügen. It lies about 22 metres away from the cliffs of Gellort on the Baltic Sea beach, one kilometre northwest of Cape Arkona. It has a mass of 165 tonnes and a volume of 61 m³. It belongs, like about 20 other erratics, to the legally protected geotopes on the Island of Rügen.