 W
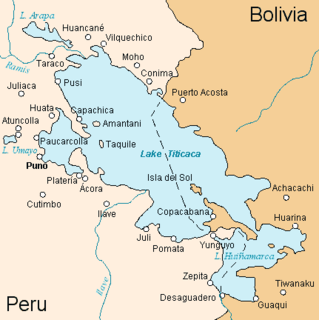
WLake Titicaca is a large, deep, freshwater lake in the Andes on the border of Bolivia and Peru, often called the "highest navigable lake" in the world. By volume of water and by surface area, it is the largest lake in South America.
 W
WThe Chiripa culture existed between the Initial Period/Early Horizon, from 1400 to 850 BCE along the southern shore of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia.
 W
WExercise Paddington Diamond was a joint Bolivian-British-Swiss scuba diving expedition to Lake Titicaca in 1987.
 W
WThe Strait of Tiquina is the passage that connects the larger and smaller parts of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia. This is a land isthmus.
 W
WTaraco is a peninsula jutting into Lake Wiñaymarka, the southern branch of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia. It is located in the La Paz Department, Ingavi Province, Tiwanaku Municipality, Taraco Canton. There is also a town of the same name on the peninsula.
 W
WThe Titicaca National Reservation is located in the Puno Region, Peru, in the Puno and Huancané provinces. Its main purpose is to preserve the ecosystems and landscapes of the Titicaca lake and surrounding Central Andean wet puna ecoregion.
 W
WTotora is a subspecies of the giant bulrush sedge. It is found in South America, notably on Lake Titicaca, the middle coast of Peru and on Easter Island in the Pacific Ocean. The genus Schoenoplectus is closely related to Scirpus and sometimes included therein. This plant can reach a height of 6 m (20 ft) and commonly reaches 4 m (13 ft). The word totora comes from the Quechua language.
 W
WWiñaymarka Lake is the southern branch of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia and Peru.
 W
WYampupata is a Bolivian peninsula of Lake Titicaca situated in the north-western part of the Copacabana Peninsula in the La Paz Department, Manco Kapac Province, Copacabana Municipality, Zampaya Canton. It is located near the islands Isla de la Luna and Isla del Sol forming the Strait of Yampupata together with the latter one.