 W
WThe 1970 Colombia earthquake occurred in Colombia on July 31.
 W
WComet Bennett, formally known as C/1969 Y1, was one of two comets to pass earth in the 1970s, along with Comet West. The name is also borne by an altogether different comet, C/1974 V2. Discovered by John Caister Bennett on December 28, 1969 while still almost two AUs from the Sun, it reached perihelion on March 20, passing closest to Earth on March 26, 1970 as it receded, peaking at magnitude 0. It was last observed on February 27, 1971.
 W
WDNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.
 W
WFH Serpentis was a nova, which appeared in the constellation Serpens in 1970. It reached magnitude 4.4. It was discovered on February 13, 1970 by Minoru Honda located at Kurashiki, Japan. Other astronomers later studied this Nova, and calculated its distances based on the decay time of its light curves.
 W
WA partial lunar eclipse took place on February 21, 1970. A tiny bite out of the Moon may have been visible at maximum, though just 5% of the Moon was shadowed in a partial eclipse which lasted for 52 minutes and 42 seconds. A shading across the moon from the Earth's penumbral shadow should have been visible at maximum eclipse.
 W
WA partial lunar eclipse took place on August 17, 1970. The Earth's shadow on the Moon was clearly visible in this eclipse, with 41% of the Moon in shadow; the partial eclipse lasted for 2 hours and 11 minutes. It was the second of two lunar eclipses in 1970.
 W
WIn astronomical spectroscopy, the Lyman-alpha forest is a series of absorption lines in the spectra of distant galaxies and quasars arising from the Lyman-alpha electron transition of the neutral hydrogen atom. As the light travels through multiple gas clouds with different redshifts, multiple absorption lines are formed.
 W
WOn October 31 at 17:53 UTC the island of New Guinea was shaken by an earthquake of magnitude 6.9 Mw that particularly affected the city of Madang on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. Causing between five and eighteen fatalities, it triggered landslides that ran down steep hills into poorly reinforced wooden huts. The area that experienced the most powerful intensity extended 20 kilometers (12 mi) out from the epicenter. Underwater landslides caused minor tsunami over about 100 km of coast and severed underwater cables in several places.
 W
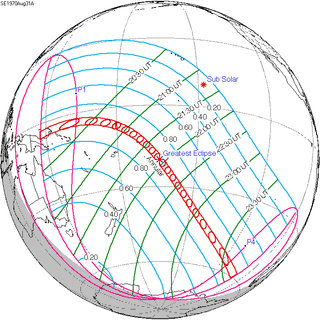
WAn annular solar eclipse occurred on Monday, August 31–Tuesday, September 1, 1970. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the Territory of Papua and New Guinea, Gilbert and Ellice Islands on September 1st (Tuesday), West Samoa and the whole American Samoa except Swains Island on August 31st (Monday).
 W
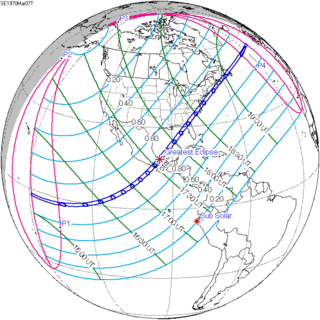
WA total solar eclipse occurred on March 7, 1970, visible across most of North America and Central America.