 W
WThe 2017–18 North American winter saw weather patterns across North America that were very active, erratic, and protracted, especially near the end of the season, resulting in widespread snow and cold across the continent during the winter. Significant events included rare snowfall in the South, an outbreak of frigid temperatures that affected the United States during the final week of 2017 and early weeks of January, and a series of strong nor'easters that affected the Northeastern U.S during the month of March. In addition, flooding also took place during the month of February in the Central United States. Finally the winter came to a conclusion with a powerful storm system that caused a tornado outbreak and blizzard in mid-April. The most intense event, however, was an extremely powerful cyclonic blizzard that impacted the northeastern United States in the first week of 2018. Similar to the previous winter, a La Niña was expected to influence the winter weather across North America.
 W
WIn April 2018, a series of thunderstorms produced record-breaking rainfall on the Hawaiian Islands of Kauaʻi and Oahu. An upper-level low moved across the area on April 13, generating a mesoscale convective system that moved over eastern Oahu, producing localized heavy rainfall that reached 5.55 in (141 mm). The heaviest rainfall occurred on northern Kauaʻi. There, a rain gauge owned by the Waipā Foundation, just west of Hanalei, recorded 49.69 in (1,262 mm) of rainfall in the 24 hours between 12:45 p.m. on April 14 and 15. This was the greatest 24-hour rainfall total on record in the United States, surpassing the previous record of 43 in (1,100 mm) in Alvin, Texas on July 25–26, 1979, set during Tropical Storm Claudette. Through the entire event, the same gauge recorded a total of 54.37 in (1,381 mm) of rain.
 W
WThe 2018–19 European winter occurred from late 2018 to early 2019. Notable events included the early snows in Spain and intense flooding in Italy, in cities such as Venice, the intense snow storms which affected central Europe in January, the snow storms in Greece over the New Year period, as well as the end of February. As well as severe winter weather, there was also exceptional warmth across western Europe in the last week of February. Parts of France had their warmest February day on record, with temperatures up to 28.1 °C (82.6 °F) at Eus on the 27th. Many places in the United Kingdom also broke temperature records, including the national record in Kew Gardens, at 21.2 °C (70.2 °F) on the 26th. Unlike previous winters, a developing El Niño was expected to influence weather patterns across Europe, although the affect is not fully known.
 W
WThe 2018–19 North American winter was unusually cold within the northern portions of the United States, with frigid temperatures being recorded within the middle of the season. Several notable events occurred, such as a rare snow in the Southeast in December, a strong cold wave and several major winter storms in the Midwest, and upper Northeast and much of Canada in late January and early February, record snowstorms in the Southwest in late February, deadly tornado outbreaks in the Southeast and a historic mid-April blizzard in the Midwest, but the most notable event of the winter was a record-breaking bomb cyclone that affected much of the central U.S. and Canada in mid March. Unlike previous winters, a developing weak El Niño was expected to influence weather patterns across North America. Overall, however, winter of 2018–19 was mild along the mid- and lower parts of the East Coast, West Coast, and most of the southern Plains.
 W
WStorm Adrian was an intense Mediterranean storm which brought severe conditions to Northern Italy and surrounding regions. it was one of the costliest of the 2018-19 named storms, causing £2.9 billion in damages. It formed over the western Mediterranean Sea on October 28, becoming the sixth named storm of the season and the first named storm of the season for Météo-France. The storm made landfall in Corsica on 29 October with powerful wind gusts in excess of 189 km/h (117 mph), winds the equivalent of a Category 3 hurricane. The storm made landfall along the French Riviera later that day, bringing high winds, heavy rain, thunderstorms and a severe storm surge along the south coast of France, causing coastal erosion in Nice. The storm's weather front brought similar problems to northern Italy and the Adriatic coast. Throughout Italy, 11 fatalities were reported. The storm damaged the Basilica of San Marco and left 75% of Venice underwater, but it also caused devastating damage to the Alpine forests south of the Dolomites. Additionally, as Storm Adrian pulled north, Central France experienced a winter storm with snowfall totals in excess of 50 cm (20 in) in higher elevations. The wintry weather cut power to 200,000+ and resulted in traffic chaos.
 W
WThe 2018 Britain and Ireland heat wave was a period of unusually hot weather that took place in June, July and August. It caused widespread drought, hosepipe bans, crop failures, and a number of wildfires. These wildfires worst affected northern moorland areas around the Greater Manchester region, the largest was at Saddleworth Moor and another was at Winter Hill, together these burned over 14 square miles (36 km2) of land over a period of nearly a month.
 W
WThe 2018 European drought and heat wave was a period of unusually hot weather that led to record-breaking temperatures and wildfires in many parts of Europe during the spring and summer of 2018. It is part of a larger heat wave affecting the northern hemisphere, caused in part by the jet stream being weaker than usual, allowing hot high-pressure air to linger in the same place. According to the European Drought Observatory, most of the areas affected by drought are across northern and central Europe. According to the World Meteorological Organization, the severe heat waves across the northern hemisphere in the summer of 2018, are linked to climate change in Europe, as well as events of extreme precipitation.
 W
WAnticyclone Hartmut was a storm that began on 22 February 2018, and brought a cold wave to Great Britain and Ireland. Anticyclone Hartmut also brought widespread unusually low temperatures and heavy snowfall to large areas. The cold wave combined with Storm Emma, part of the 2017–18 European windstorm season, which made landfall in southwest England and the south of Ireland on 2 March.
 W
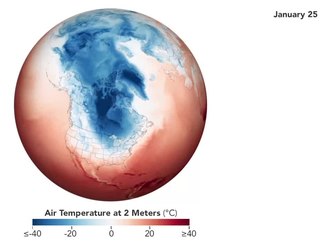
WThe December 2017–January 2018 North American cold wave was an extreme weather event in North America in which record low temperatures gripped much of the Central, Eastern United States, and parts of Central and Eastern Canada. Starting in late December as a result of the southward shift of the polar vortex, extremely cold conditions froze the eastern United States in the last few days of 2017 as well as into the new year. Following a brief respite in mid-January, cold temperatures swung back into the eastern U.S. shortly afterwards. The cold wave finally dissolved by around January 19, as near-average temperatures returned.
 W
WThis page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2018. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Brazil, Bangladesh and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina and Australia. Tornadic events are often accompanied with other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail.