 W
WWireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, a transmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thus increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.
 W
WAirPower is an unreleased wireless charging mat developed by Apple Inc. It was designed to charge up to three devices simultaneously, supporting two Qi devices, such as an iPhone and AirPods, and an Apple Watch. It was announced on September 12, 2017. Formerly scheduled to be released in early 2018, AirPower failed to materialize, leading to wide speculation over the product's future, until Apple announced on March 29, 2019 it had cancelled the release.
 W
WInductive charging is a type of wireless power transfer. It uses electromagnetic induction to provide electricity to portable devices. Inductive charging is also used in vehicles, power tools, electric toothbrushes and medical devices. The portable equipment can be placed near a charging station or inductive pad without needing to be precisely aligned or make electrical contact with a dock or plug.
 W
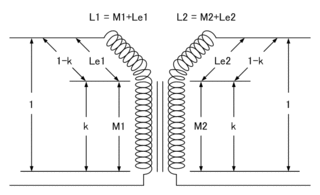
WIn electrical engineering, two conductors are said to be inductively coupled or magnetically coupled when they are configured in a way such that change in current through one wire induces a voltage across the ends of the other wire through electromagnetic induction. A changing current through the first wire creates a changing magnetic field around it by Ampere's circuital law. The changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force in the second wire by Faraday's law of induction. The amount of inductive coupling between two conductors is measured by their mutual inductance.
 W
WMagSafe is a proprietary magnetically-attached wireless power transfer and accessory-attachment standard developed by Apple Inc. for its iPhone and AirPods product lines. It was announced on 13 October 2020, in conjunction with the iPhone 12 and 12 Pro series. It provides up to 15 W of power and is backwards-compatible with the open Qi standard for up to 7.5 W of power. The connector also enables connecting non-charger accessories such as card holders and cases with communication through an integrated NFC loop.
 W
WMicrowave transmission is the transmission of information by electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the microwave range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Microwave signals are normally limited to the line-of-sight, so long-distance transmission using these signals requires a series of repeaters forming a microwave relay. It is possible to use microwave signals in over-the-horizon communications using tropospheric scatter, but such systems are expensive and generally used only in specialist roles.
 W
WPower Matters Alliance (PMA) was a global, not-for-profit, industry organization whose mission was to advance a suite of standards and protocols for wireless power transfer for mobile electronic devices. The organization was merged with Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) in 2015 to form AirFuel Allliance.
 W
WQi is an open interface standard that defines wireless power transfer using inductive charging over distances of up to 4 cm, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium. The system uses a charging pad and a compatible device, which is placed on top of the pad, charging via resonant inductive coupling.
 W
WResonant inductive coupling or magnetic phase synchronous coupling is a phenomenon with inductive coupling where the coupling becomes stronger when the "secondary" (load-bearing) side of the loosely coupled coil resonates. A resonant transformer of this type is often used in analog circuitry as a bandpass filter. Resonant inductive coupling is also used in wireless power systems for portable computers, phones, and vehicles.
 W
WRezence is an interface standard developed by the Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) for wireless electrical power transfer based on the principles of magnetic resonance. The Rezence system consists of a single power transmitter unit (PTU) and one or more power receiver units (PRUs). The interface standard supports power transfer up to 50 watts, at distances up to 5 centimeters. The power transmission frequency is 6.78 MHz, and up to eight devices can be powered from a single PTU depending on transmitter and receiver geometry and power levels. A Bluetooth Low Energy link is defined in the A4WP system intended for control of power levels, identification of valid loads and protection of non-compliant devices.
 W
WSonicEnergy is a U.S. company that claims to be developing a wireless charging system to work via ultrasound. Scientists have strongly criticised the plausibility under physics of this proposal.
 W
WNikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, mechanical engineer, and futurist best known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
 W
WWardenclyffe Tower (1901–1917), also known as the Tesla Tower, was an early experimental wireless transmission station designed and built by Nikola Tesla on Long Island in 1901–1902, located in the village of Shoreham, New York. Tesla intended to transmit messages, telephony and even facsimile images across the Atlantic to England and to ships at sea based on his theories of using the Earth to conduct the signals. His decision to scale up the facility and implement his ideas of wireless power transmission to better compete with Guglielmo Marconi's radio-based telegraph system was met with refusal to fund the changes by the project's primary backer, financier J. P. Morgan. Additional investment could not be found, and the project was abandoned in 1906, never to become operational.
 W
WThe Alliance For Wireless Power is an industry standard group that uses the principles of magnetic resonance to develop a wireless energy transfer system over distance. The WiPower system uses directed and controlled magnetic fields to replace traditional power cords. To do this, the transmitter utilizes one or more primary windings in order to induce an even magnetic field above its surface. A receiver in the magnetic field uses a secondary winding which captures the magnetic energy and converts it back to electrical energy.
 W
WThe World Wireless System was a turn of the 20th century proposed telecommunications and electrical power delivery system designed by inventor Nikola Tesla based on his theories of using Earth and its atmosphere as electrical conductors. He claimed this system would allow for "the transmission of electric energy without wires" on a global scale as well as point-to-point wireless telecommunications and broadcasting. He made public statements citing two related methods to accomplish this from the mid-1890s on. By the end of 1900 he had convinced banker J. P. Morgan to finance construction of a wireless station based on his ideas intended to transmit messages across the Atlantic to England and to ships at sea. His decision to change the design to include wireless power transmission to better compete with Guglielmo Marconi's new radio based telegraph system was met with Morgan's refusal to fund the changes. The project was abandoned in 1906, never to become operational.