 W
WNonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (values of atomic electric fields, typically 108 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds.
 W
W3D optical data storage is any form of optical data storage in which information can be recorded or read with three-dimensional resolution.
 W
WAcousto-optics is a branch of physics that studies the interactions between sound waves and light waves, especially the diffraction of laser light by ultrasound through an ultrasonic grating.
 W
WA bandwidth-limited pulse is a pulse of a wave that has the minimum possible duration for a given spectral bandwidth. Bandwidth-limited pulses have a constant phase across all frequencies making up the pulse. Optical pulses of this type can be generated by mode-locked lasers.
 W
WCLD-1 is a vibrant blue dye originally synthesized for application in nonlinear electro-optics.
 W
WCross polarized wave (XPW) generation is a nonlinear optical process that can be classified in the group of frequency degenerate [four wave mixing] processes. It can take place only in media with anisotropy of third order nonlinearity. As a result of such nonlinear optical interaction at the output of the nonlinear crystal it is generated a new linearly polarized wave at the same frequency, but with polarization oriented perpendicularly to the polarization of input wave
 W
WAn electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element exhibiting an electro-optic effect is used to modulate a beam of light. The modulation may be imposed on the phase, frequency, amplitude, or polarization of the beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser-controlled modulators.
 W
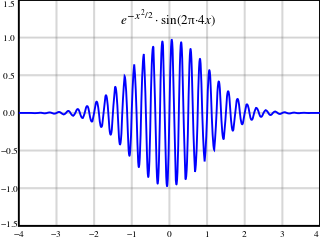
WIn optics, a frequency comb is a laser source whose spectrum consists of a series of discrete, equally spaced frequency lines. Frequency combs can be generated by a number of mechanisms, including periodic modulation of a continuous-wave laser, four-wave mixing in nonlinear media, or stabilization of the pulse train generated by a mode-locked laser. Much work has been devoted to this last mechanism, which was developed around the turn of the 21st century and ultimately led to one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics being shared by John L. Hall and Theodor W. Hänsch in 2005.
 W
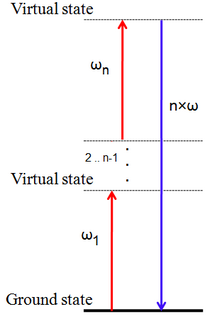
WHarmonic generation is a nonlinear optical process in which photons with the same frequency interact with a nonlinear material, are "combined", and generate a new photon with times the energy of the initial photons.
 W
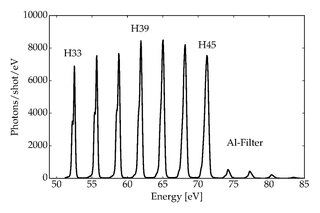
WHigh harmonic generation (HHG) is a non-linear process during which a target is illuminated by an intense laser pulse. Under such conditions, the sample will emit the high harmonics of the generation beam. Due to the coherent nature of the process, high harmonics generation is a prerequisite of attophysics.
 W
WIn electrical engineering, homodyne detection is a method of extracting information encoded as modulation of the phase and/or frequency of an oscillating signal, by comparing that signal with a standard oscillation that would be identical to the signal if it carried null information. "Homodyne" signifies a single frequency, in contrast to the dual frequencies employed in heterodyne detection.
 W
WHyper–Rayleigh scattering Optical Activity, is a nonlinear optical physical effect whereby chiral scatterers convert light to higher frequencies via harmonic generation processes, in a way that the intensity of generated light depends on the chirality of the scatterers. "Hyper–Rayleigh scattering" is a nonlinear optical counterpart to Rayleigh scattering. "Optical activity" refers to any changes in light properties that are due to chirality.
 W
WKerr-lens mode-locking (KLM) is a method of mode-locking lasers via the nonlinear optical Kerr effect. This method allows the generation of pulses of light with a duration as short as a few femtoseconds.
 W
WJohn Harmen "Jack" Marburger III was an American physicist who directed the Office of Science and Technology Policy in the administration of President George W. Bush, serving as the Science Advisor to the President. His tenure was marked by controversy regarding his defense of the administration against allegations from over two dozen Nobel Laureates, amongst others, that scientific evidence was being suppressed or ignored in policy decisions, including those relating to stem cell research and global warming. However, he has also been credited with keeping the political effects of the September 11 attacks from harming science research—by ensuring that tighter visa controls did not hinder the movement of those engaged in scientific research—and with increasing awareness of the relationship between science and government. He also served as the President of Stony Brook University from 1980 until 1994, and director of Brookhaven National Laboratory from 1998 until 2001.
 W
WThe first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959. The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory was introduced by Duarte and Piper in 1982.
 W
WIn optics, a nematicon is a spatial soliton in nematic liquid crystals (NLC). The name was invented in 2003 by G. Assanto. and used thereafter Nematicons are generated by a special type of optical nonlinearity present in NLC: the light induced reorientation of the molecular director. This nonlinearity arises from the fact that the molecular director tends to align along the electric field of light. Nematicons are easy to generate because the NLC dielectric medium exhibits the following properties:A very large nonlinear response : the effective nonlinearity is typically eight orders of magnitude larger than that of carbon disulfide. This means that much lower optical powers are necessary to obtain the same refractive index variation (increase) or self-focusing to balance out diffraction. A nonlocal response : the nonlinear response is not limited to the location of the optical field. Instead the response profile is wider than the light beam. A high nonlocality allows for stable soliton propagation even in the case of two transverse dimensions. Higher or lower powers than the exact value required for a soliton to exist lead to breathing solitons.
 W
WNon-degenerate two-photon absorption or two-color two-photon excitation is a type of two-photon absorption (TPA) where two photons with different energies are (almost) simultaneously absorbed by a molecule, promoting a molecular electronic transition from a lower energy state to a higher energy state. The sum of the energies of the two photons is equal to, or larger than, the total energy of the transition.
 W
WIn optics, various autocorrelation functions can be experimentally realized. The field autocorrelation may be used to calculate the spectrum of a source of light, while the intensity autocorrelation and the interferometric autocorrelation are commonly used to estimate the duration of ultrashort pulses produced by modelocked lasers. The laser pulse duration cannot be easily measured by optoelectronic methods, since the response time of photodiodes and oscilloscopes are at best of the order of 200 femtoseconds, yet laser pulses can be made as short as a few femtoseconds.
 W
WAn optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is a parametric oscillator that oscillates at optical frequencies. It converts an input laser wave with frequency into two output waves of lower frequency by means of second-order nonlinear optical interaction. The sum of the output waves' frequencies is equal to the input wave frequency: . For historical reasons, the two output waves are called "signal" and "idler", where the output wave with higher frequency is the "signal". A special case is the degenerate OPO, when the output frequency is one-half the pump frequency, , which can result in half-harmonic generation when signal and idler have the same polarization.
 W
WElectro-optic rectification (EOR), also referred to as optical rectification, is a non-linear optical process that consists of the generation of a quasi-DC polarization in a non-linear medium at the passage of an intense optical beam. For typical intensities, optical rectification is a second-order phenomenon which is based on the inverse process of the electro-optic effect. It was reported for the first time in 1962, when radiation from a ruby laser was transmitted through potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and potassium dideuterium phosphate (KDdP) crystals.
 W
WThe Peregrine soliton is an analytic solution of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation. This solution was proposed in 1983 by Howell Peregrine, researcher at the mathematics department of the University of Bristol.
 W
WThe Pockels effect, or Pockels electro-optic effect, changes or produces birefringence in an optical medium induced by an electric field. In the Pockels effect, also known as the linear electro-optic effect, the birefringence is proportional to the electric field. In the Kerr effect, the refractive index change (birefringence) is proportional to the square of the field. The Pockels effect occurs only in crystals that lack inversion symmetry, such as lithium niobate, and in other noncentrosymmetric media such as electric-field poled polymers or glasses.
 W
WA prism compressor is an optical device used to shorten the duration of a positively chirped ultrashort laser pulse by giving different wavelength components a different time delay. It typically consists of two prisms and a mirror. Figure 1 shows the construction of such a compressor. Although the dispersion of the prism material causes different wavelength components to travel along different paths, the compressor is built such that all wavelength components leave the compressor at different times, but in the same direction. If the different wavelength components of a laser pulse were already separated in time, the prism compressor can make them overlap with each other, thus causing a shorter pulse.
 W
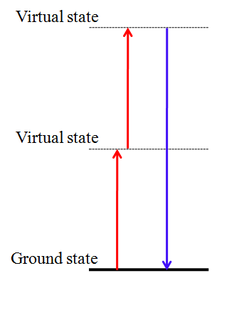
WSecond-harmonic generation is a nonlinear optical process in which two photons with the same frequency interact with a nonlinear material, are "combined", and generate a new photon with twice the energy of the initial photons, that conserves the coherence of the excitation. It is a special case of sum-frequency generation, and more generally of harmonic generation.
 W
WSelf-focusing is a non-linear optical process induced by the change in refractive index of materials exposed to intense electromagnetic radiation. A medium whose refractive index increases with the electric field intensity acts as a focusing lens for an electromagnetic wave characterized by an initial transverse intensity gradient, as in a laser beam. The peak intensity of the self-focused region keeps increasing as the wave travels through the medium, until defocusing effects or medium damage interrupt this process. Self-focusing of light was discovered by Gurgen Askaryan.
 W
WSilicon photonics is the study and application of photonic systems which use silicon as an optical medium. The silicon is usually patterned with sub-micrometre precision, into microphotonic components. These operate in the infrared, most commonly at the 1.55 micrometre wavelength used by most fiber optic telecommunication systems. The silicon typically lies on top of a layer of silica in what is known as silicon on insulator (SOI).
 W
WIn ultrafast optics, spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction (SPIDER) is an ultrashort pulse measurement technique originally developed by Chris Iaconis and Ian Walmsley.
 W
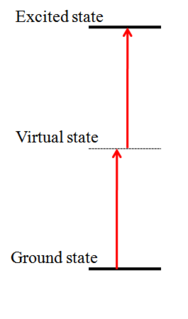
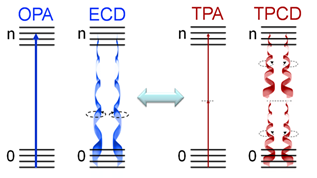
WTwo-photon absorption or two-photon excitation or non-linear absorption is the simultaneous absorption of two photons of identical or different frequencies in order to excite a molecule from one state to a higher energy, most commonly an excited electronic state. Absorption of two photons with different frequencies is called non-degenerate two-photon absorption. Since TPA depend on the simultaneous absorption of two photons, the probability of TPA is proportional to the square of the light intensity, thus it is a nonlinear optical process. The energy difference between the involved lower and upper states of the molecule is equal or smaller than the sum of the photon energies of the two photons absorbed. Two-photon absorption is a third-order process, with absorption cross section typically several orders of magnitude smaller than one-photon absorption cross section.
 W
WTwo-photon circular dichroism (TPCD), the nonlinear counterpart of electronic circular dichroism (ECD), is defined as the differences between the two-photon absorption (TPA) cross-sections obtained using left circular polarized light and right circular polarized light.
 W
WIn nonlinear optics z-scan technique is used to measure the non-linear index n2 and the non-linear absorption coefficient Δα via the "closed" and "open" methods, respectively. As nonlinear absorption can affect the measurement of the non-linear index, the open method is typically used in conjunction with the closed method to correct the calculated value. For measuring the real part of the nonlinear refractive index, the z-scan setup is used in its closed-aperture form. In this form, since the nonlinear material reacts like a weak z-dependent lens, the far-field aperture makes it possible to detect the small beam distortions in the original beam. Since the focusing power of this weak nonlinear lens depends on the nonlinear refractive index, it would be possible to extract its value by analyzing the z-dependent data acquired by the detector and by cautiously interpreting them using an appropriate theory. To measure the imaginary part of the nonlinear refractive index, or the nonlinear absorption coefficient, the z-scan setup is used in its open-aperture form. In open-aperture measurements, the far-field aperture is removed and the whole signal is measured by the detector. By measuring the whole signal, the beam small distortions become insignificant and the z-dependent signal variation is due to the nonlinear absorption entirely. Despite its simplicity, in many cases, the original z-scan theory is not completely accurate, i.e. when the nonlinear medium response to laser radiation is nonlocal in space. Whenever the laser induced nonlinear response at a certain point of the medium is not solely determined by the laser intensity at that point, but also depends on the laser intensity in the surrounding regions, it will be called a nonlocal nonlinear optical response. Generally, a variety of mechanisms may contribute to the nonlinearity, some of which may be nonlocal. For instance, when the nonlinear medium is dispersed inside a dielectric solution, reorientation of the dipoles as a result of the optical field action is nonlocal in space and changes the electric field experienced by the nonlinear medium. The nonlocal z-scan theory, can be used for systematically analyzing the role of various mechanisms in producing the nonlocal nonlinear response of different materials.