 W
WAfter the Deluge, also known as The Forty-First Day, is a Symbolist oil painting by English artist George Frederic Watts, first exhibited as The Sun in an incomplete form in 1886 and completed in 1891. It shows a scene from the story of Noah's Flood, in which after 40 days of rain Noah opens the window of his Ark to see that the rain has stopped. Watts felt that modern society was in decline owing to a lack of moral values, and he often painted works on the topic of the Flood and its cleansing of the unworthy from the world. The painting takes the form of a stylised seascape, dominated by a bright sunburst breaking through clouds. Although this was a theme Watts had depicted previously in The Genius of Greek Poetry in 1878, After the Deluge took a radically different approach. With this painting he intended to evoke a monotheistic God in the act of creation, but avoid depicting the Creator directly.
 W
WA break away! is an 1891 painting by Australian artist Tom Roberts.
 W
WThe Canal du Loing in Winter is a painting of the Canal du Loing, produced by Alfred Sisley in winter 1891. It is now in the National Museum of Fine Arts of Algiers.
 W
WCirce Offering the Cup to Ulysses is an oil painting in the Pre-Raphaelite style by John William Waterhouse that was created in 1891.
 W
WThe Circus is an oil on canvas painting by Georges Seurat. It was his last painting, made in a Neo-Impressionist style in 1890-91, and remained unfinished at his death in March 1891. The painting is located at the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.
 W
WThe Constitution of 3 May 1791 is an 1891 Romantic oil painting on canvas by the Polish artist Jan Matejko. It is a large piece, and one of Matejko's best known. It memorializes the Polish Constitution of 3 May 1791, a milestone in the history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and a high point of the Polish Enlightenment.
 W
WThe Doctor is an 1891 painting by Luke Fildes that depicts a Victorian doctor observing the critical stage in a child's illness while the parents gaze on helplessly from the periphery. It has been used to portray the values of the ideal physician and the inadequacies of the medical profession. Different theories exist as to the painting's origin but it is most likely based upon Fildes' own experience of the death of his son. Critics have noted that Fildes omitted common medical equipment of his era in order to focus on the relationship between physician and patient.
 W
WEgyptian Woman with Earrings is a late 19th-century painting by American artist John Singer Sargent. Done in oil on canvas, the work portrays an Egyptian woman. The painting is in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York.
 W
WEgyptians Raising Water from the Nile is an 1890–1891 painting by John Singer Sargent. It is part of the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
 W
WFire's on is an 1891 oil on canvas landscape painting by Australian artist Arthur Streeton. The painting depicts the construction of the Glenbrook Tunnel through the Blue Mountains. Unusually for a landscape, the painting is upright with a high horizon line. The painting's title refers to the warning call before the blast of the explosive.
 W
WThe Gauja Valley is a painting by Latvian painter Jūlijs Feders from 1891.
 W
WThe Goose Girl is an 1891 painting by William-Adolphe Bouguereau, a French academic painter. The Goose Girl is one of many examples that Bouguereau specialized in paintings of beautiful women and innocent, barefoot, young peasant girls.
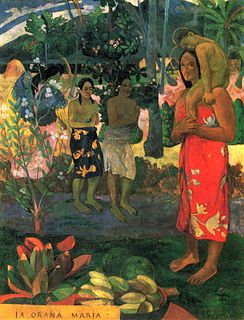 W
WIa Orana Maria is an 1891 oil on canvas painting by Paul Gauguin, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. It is one of the first works in his Tahitian period and shows two Polynesians (centre) greeting the Madonna and Child.
 W
WThe Man of Sorrows is an 1891 oil painting by the Flemish expressionist painter James Ensor. This painting is enlisted on the official inventories of Flemish masterpieces and is a part of the great masters collection of the Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp.
 W
WA Man with an Axe is an 1891 oil on canvas painting by Paul Gauguin, now in a Swiss private collection. A study for it is now in the Art Institute of Chicago.
 W
WMaria Sèthe at the Harmonium is an oil on canvas painting by the Belgian neo-impressionist painter Théo van Rysselberghe. The painting depicts a woman with blonde, worn-up hair and a purple dress staring dreamily into space, while smiling. The sitter was Maria Sèthe, who belonged to an affluent musical family with an interest in the arts. In the painting, she is depicted sitting at a harmonium, but she's not playing it.
 W
WMelancholy is a painting by the Norwegian artist Edvard Munch. Munch painted multiple variant versions of the expressionist work in oil on canvas during the period 1891–1893. The painting depicts a man with his head resting in his hand in a pensive mood at the edge of a shoreline.
 W
WMiss Amelia Van Buren or Portrait of Amelia C. Van Buren is a ca. 1891 painting by the American artist Thomas Eakins (1844–1916), now in The Phillips Collection. It depicts Amelia Van Buren, an artist who studied with Eakins, and was called "one of his most gifted pupils." The painting is considered one of Eakins's finest works.
 W
WMiss Nightingale at Scutari, 1854, also known as The Lady with the Lamp, is an 1891 painting by Henrietta Rae. It depicts Florence Nightingale at Scutari Hospital during the Crimean War.
 W
WMy Wife's Lovers is a canvas painting by Austrian artist Carl Kahler (1855–1906) depicting forty-two of American millionaire Kate Birdsall Johnson's Turkish Angora cats. The title of the painting was potentially conceived by her husband, who may have referred to the cats with the phrase. Measuring 6 by 8.5 feet, the canvas weighs 227 pounds (103 kg).
 W
WPerseus and Andromeda is an oil painting by Lord Frederic Leighton. Completed in 1891, the year it was displayed at the Royal Academy of Arts, it depicts the Greek mythological story of Andromeda. In contrast to the basis of a classical tale, Leighton used a Gothic style for the artwork. The painting is in the collection of National Museums Liverpool at the Walker Art Gallery.
 W
WThe Poplars series paintings were made by Claude Monet in the summer and fall of 1891. The trees were in a marsh along the banks of the Epte River a few kilometers upstream from Monet's home and studio. To reach his floating painting studio that was moored in a place he went by small boat up the nearby waterway to where it joined the mainstream. The trees were along the riverside in single file, following along an S-curve. There were three groups of paintings — in one group the paintings have towering Poplars that go off the top edge of the canvas, in another group, there are seven trees and in another group three or four Poplars on the banks of the Epte River near Giverny. The trees, which actually belonged to the commune of Limetz, were put up for auction before Monet had completed all of his paintings. At a certain point, Monet was forced into buying the trees because he still wasn't finished with his paintings. After he finished the series he sold the trees back to the lumber merchant who wanted them.
 W
WThe Punishment of Lust, also called The Punishment of Luxury, is an 1891 oil painting on canvas by the artist Giovanni Segantini.
 W
WReply of the Zaporozhian Cossacks to Sultan Mehmed IV of the Ottoman Empire, also known as Cossacks of Saporog Are Drafting a Manifesto, is a painting by Russian artist Ilya Repin. The 2.03 m (6 foot 7 inch) by 3.58 m (11 foot 9 inch) canvas was started in 1880 and finished in 1891. Repin recorded the years of work along the lower edge of the canvas. Alexander III bought the painting for 35,000 rubles, at the time the greatest sum ever paid for a Russian painting. Since then, the canvas has been exhibited in the State Russian Museum in Saint Petersburg.
 W
WSelf-Portrait with the Yellow Christ is an 1890 or 1891 painting by Paul Gauguin, produced in Pont-Aven in Brittany and now in the musée d'Orsay in Paris, to which it was assigned after its purchase by the French state in 1994 with financial assistance from Philippe Meyer and a Japanese patron.
 W
WSkeletons Fighting over a Hanged Man is an 1891 oil painting by the Belgian Expresssionist painter James Ensor which is in the collection of the Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp.
 W
WSponsa de Libano is a painting by the Pre-Raphaelite artist Edward Burne-Jones dated 1891.
 W
WSpring Blossoms, Montclair, New Jersey is a late 19th-century painting by Scottish-American artist George Inness. The work is currently in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
 W
WSunlight in the Blue Room is an 1891 painting by Anna Ancher, an innovative Danish painter who was a central figure with the Skagen Painters. With its many shades of blue and the sunlight pouring through the window, the painting is one of her most prominent works.
 W
WTahitian Woman with a Flower is an 1891 painting by Paul Gauguin, now in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek in Copenhagen.
 W
WTahitian Women on the Beach is an 1891 painting by Paul Gauguin. The painting depicts two women on the Pacific island of Tahiti on the beach.
 W
WThe Shepherd's Song is a late 19th-century painting by French artist Pierre Puvis de Chavannes. Done in oil on canvas, the painting depicts shepherds lounging and foraging in an arid landscape. The painting - which was inspired by one of de Chavannes' earlier works - is now in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
 W
WTiger in a Tropical Storm or Surprised! is an 1891 oil-on-canvas painting by Henri Rousseau. It was the first of the jungle paintings for which the artist is chiefly known. It shows a tiger, illuminated by a flash of lightning, preparing to pounce on its prey in the midst of a raging gale.
 W
WLe Travail interrompu is a painting by nineteenth-century French painter William-Adolphe Bouguereau in 1891. The painting is currently held in the Mead Art Museum in Amherst, Massachusetts.
 W
WUlysses and the Sirens is an 1891 painting by Pre-Raphaelite artist John William Waterhouse. It is currently held in the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Australia.