 W
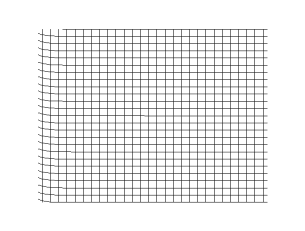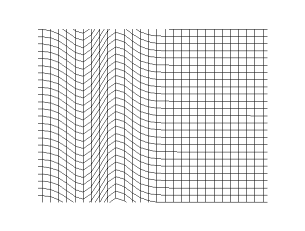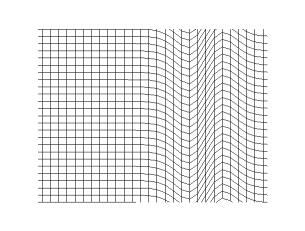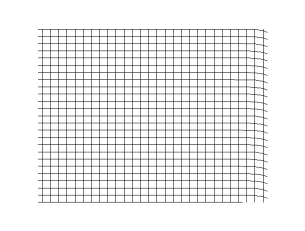
WPolarization is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string (see image); for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves in solids.
 W
WThe Babinet–Soleil compensator is a continuously variable, zero-order retarder. It consists of two birefringent wedges, one of which is movable, and another is fixed to a compensator plate. The orientation of the long axis of the wedges is perpendicular to the long axis of the compensator plate.
 W
WBirefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.
 W
WA Brewster angle microscope (BAM) is a microscope for studying thin films on liquid surfaces, most typically Langmuir films. In a Brewster angle microscope, both the microscope and a polarized light source are aimed towards a liquid surface at that liquid's Brewster angle, in such a way for the microscope to catch an image of any light reflected from the light source via the liquid surface. Because there is no p-polarized reflection from the pure liquid when both are angled towards it at the Brewster angle, light is only reflected when some other phenomenon such as a surface film affects the liquid surface. The technique was first introduced in 1991.
 W
WBrewster's angle is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781–1868).
 W
WIn chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir), meaning "hand"; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.
 W
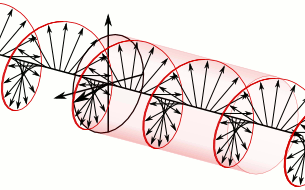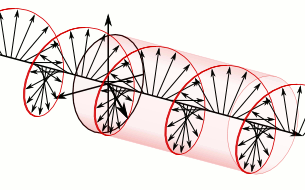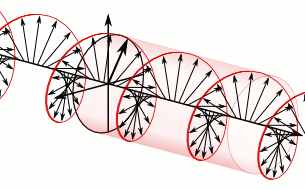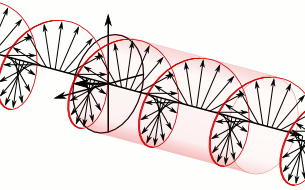
WIn electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
 W
WIn optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours), or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts.
 W
WThe extinction cross is an optical phenomenon that is seen when trying to extinguish a laser beam or non-planar white light using crossed polarizers. Ideally, crossed polarizers block all light, since light which is polarized along the polarization axis of the first polarizer is perpendicular to the polarization axis of the second. When the beam is not perfectly collimated, however, a characteristic fringing pattern is produced.
 W
WThe Fresnel equations describe the reflection and transmission of light when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, even though no one realized that the "vibrations" of the wave were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the s and p polarizations incident upon a material interface.
 W
WA Fresnel rhomb is an optical prism that introduces a 90° phase difference between two perpendicular components of polarization, by means of two total internal reflections. If the incident beam is linearly polarized at 45° to the plane of incidence and reflection, the emerging beam is circularly polarized, and vice versa. If the incident beam is linearly polarized at some other inclination, the emerging beam is elliptically polarized with one principal axis in the plane of reflection, and vice versa.
 W
WA Glan–Foucault prism is a type of prism which is used as a polarizer. It is similar in construction to a Glan–Thompson prism, except that two right-angled calcite prisms are spaced with an air gap instead of being cemented together. Total internal reflection of p-polarized light at the air gap means that only s-polarized light is transmitted straight through the prism.
 W
WA Glan–Taylor prism is a type of prism which is used as a polarizer or polarizing beam splitter. It is one of the most common types of modern polarizing prism. It was first described by Archard and Taylor in 1948.
 W
WA Glan–Thompson prism is a type of polarizing prism similar to the Nicol and Glan–Foucault prisms.
 W
WHaidinger's brush, more commonly known as Haidinger's brushes is an image produced by the eye, an entoptic phenomenon, first described by Austrian physicist Wilhelm Karl von Haidinger in 1844. Haidinger saw it when he looked through various minerals that polarized light.
 W
WIceland spar, formerly known as Iceland crystal, is a transparent variety of calcite, or crystallized calcium carbonate, originally brought from Iceland, and used in demonstrating the polarization of light. It occurs in large readily cleavable crystals, is easily divisible into rhombuses, and is remarkable for its birefringence. This means that the index of refraction of the crystal is different for light of different polarization. A ray of unpolarized light passing through the crystal divides into two rays of perpendicular polarization directed at different angles, called double refraction. So objects seen through the crystal appear doubled.
 W
WMagnetic circular dichroism (MCD) is the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light, induced in a sample by a strong magnetic field oriented parallel to the direction of light propagation. MCD measurements can detect transitions which are too weak to be seen in conventional optical absorption spectra, and it can be used to distinguish between overlapping transitions. Paramagnetic systems are common analytes, as their near-degenerate magnetic sublevels provide strong MCD intensity that varies with both field strength and sample temperature. The MCD signal also provides insight into the symmetry of the electronic levels of the studied systems, such as metal ion sites.
 W
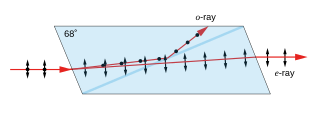
WA Nicol prism is a type of polarizer, an optical device made from calcite crystal used to produce and analyse plane polarized light. It is made in such a way that it eliminates one of the rays by total internal reflection, i.e. the ordinary ray is eliminated and only the extraordinary ray is transmitted through the prism. It was the first type of polarizing prism, invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770–1851) of Edinburgh. It consists of a rhombohedral crystal of Iceland spar that has been cut at an angle of 68° with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally, and then rejoined as shown, using a layer of transparent Canada balsam as a glue.
 W
WA Nomarski prism is a modification of the Wollaston prism that is used in differential interference contrast microscopy. It is named after its inventor, Polish and naturalized-French physicist Georges Nomarski. Like the Wollaston prism, the Nomarski prism consists of two birefringent crystal wedges cemented together at the hypotenuse. One of the wedges is identical to a conventional Wollaston wedge and has the optical axis oriented parallel to the surface of the prism. The second wedge of the prism is modified by cutting the crystal so that the optical axis is oriented obliquely with respect to the flat surface of the prism. The Nomarski modification causes the light rays to come to a focal point outside the body of the prism, and allows greater flexibility so that when setting up the microscope the prism can be actively focused.
 W
WOptical mineralogy is the study of minerals and rocks by measuring their optical properties. Most commonly, rock and mineral samples are prepared as thin sections or grain mounts for study in the laboratory with a petrographic microscope. Optical mineralogy is used to identify the mineralogical composition of geological materials in order to help reveal their origin and evolution.
 W
WOptical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror symmetry. Unlike other sources of birefringence which alter a beam's state of polarization, optical activity can be observed in fluids. This can include gases or solutions of chiral molecules such as sugars, molecules with helical secondary structure such as some proteins, and also chiral liquid crystals. It can also be observed in chiral solids such as certain crystals with a rotation between adjacent crystal planes or metamaterials.
 W
WThe term plane of polarization refers to the direction of polarization of linearly-polarized light or other electromagnetic radiation. Unfortunately the term is used with two contradictory meanings. As originally defined by Étienne-Louis Malus in 1811, the plane of polarization coincided with the plane containing the direction of propagation and the magnetic vector. In modern literature, the term plane of polarization, if it is used at all, is likely to mean the plane containing the direction of propagation and the electric vector, because the electric field has the greater propensity to interact with matter.
 W
WThe Pockels effect, or Pockels electro-optic effect, changes or produces birefringence in an optical medium induced by an electric field. In the Pockels effect, also known as the linear electro-optic effect, the birefringence is proportional to the electric field. In the Kerr effect, the refractive index change (birefringence) is proportional to the square of the field. The Pockels effect occurs only in crystals that lack inversion symmetry, such as lithium niobate, and in other noncentrosymmetric media such as electric-field poled polymers or glasses.
 W
WA polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance.
 W
WPolarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves. Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or diffracted by some material in order to characterize that object.
 W
WA polarization rotator is an optical device that rotates the polarization axis of a linearly polarized light beam by an angle of choice. Such devices can be based on the Faraday effect, on birefringence, or on total internal reflection. Rotators of linearly polarized light have found widespread applications in modern optics since laser beams tend to be linearly polarized and it is often necessary to rotate the original polarization to its orthogonal alternative.
 W
WPolarization is a property of light waves that describes the orientation of their oscillations. Polarized light pollution is a subset of the various forms of light pollution referring specifically to polarized light.
 W
WA polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam of well-defined polarization, that is polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and LCD technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides visible light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.
 W
WA polarizing filter or polarising filter is often placed in front of the camera lens in photography in order to darken skies, manage reflections, or suppress glare from the surface of lakes or the sea. Since reflections tend to be at least partially linearly-polarized, a linear polarizer can be used to change the balance of the light in the photograph. The rotational orientation of the filter is adjusted for the preferred artistic effect. For modern cameras, a circular polarizer (CPL) is typically used; this comprises firstly a linear polarizer which performs the artistic function just described, followed by a quarter-wave plate which further transforms the now-linearly polarized light into circularly-polarized light before entering the camera. This additional step avoids problems with autofocus and light-metering sensors within some cameras, which otherwise may not function reliably with a simple linear polarizer.
 W
WA beam of light has radial polarization if at every position in the beam the polarization vector points towards the centre of the beam. In practice, an array of waveplates may be used to provide an approximation to a radially polarized beam. In this case the beam is divided into segments, and the average polarization vector of each segment is directed towards the beam centre.
 W
WThe Rayleigh sky model describes the observed polarization pattern of the daytime sky. Within the atmosphere, Rayleigh scattering of light by air molecules, water, dust, and aerosols causes the sky's light to have a defined polarization pattern. The same elastic scattering processes cause the sky to be blue. The polarization is characterized at each wavelength by its degree of polarization, and orientation.
 W
WA Rochon prism is a type of polariser. It is made from two prisms of a birefringent material such as calcite, which are cemented together.
 W
WThe Sénarmont prism is a type of polariser. It is made from two prisms of a birefringent material such as calcite, usually cemented together. The Sénarmont prism is named after Henri Hureau de Sénarmont. It is similar to the Rochon and Wollaston prisms.
 W
WShear wave splitting, also called seismic birefringence, is the phenomenon that occurs when a polarized shear wave enters an anisotropic medium. The incident shear wave splits into two polarized shear waves. Shear wave splitting is typically used as a tool for testing the anisotropy of an area of interest. These measurements reflect the degree of anisotropy and lead to a better understanding of the area's crack density and orientation or crystal alignment. We can think of the anisotropy of a particular area as a black box and the shear wave splitting measurements as a way of looking at what is in the box.
 W
WThe sunstone is a type of mineral attested in several 13th–14th century written sources in Iceland, one of which describes its use to locate the sun in a completely overcast sky. Sunstones are also mentioned in the inventories of several churches and one monastery in 14th–15th century Iceland and Germany.
 W
WIn physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations.
 W
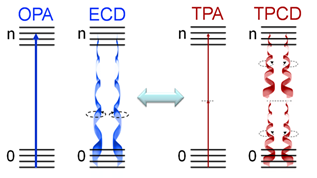
WTwo-photon circular dichroism (TPCD), the nonlinear counterpart of electronic circular dichroism (ECD), is defined as the differences between the two-photon absorption (TPA) cross-sections obtained using left circular polarized light and right circular polarized light.
 W
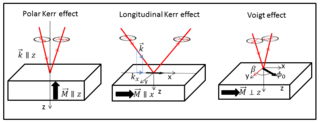
WThe Voigt effect is a magneto-optical phenomenon which rotates and elliptizes linearly polarised light sent into an optically active medium. Unlike many other magneto-optical effects such as the Kerr or Faraday effect which are linearly proportional to the magnetization, the Voigt effect is proportional to the square of the magnetization and can be seen experimentally at normal incidence. There are several denominations for this effect in the literature: the Cotton–Mouton effect, the Voigt effect, and magnetic-linear birefringence. This last denomination is closer in the physical sense, where the Voigt effect is a magnetic birefringence of the material with an index of refraction parallel and perpendicular ) to the magnetization vector or to the applied magnetic field.
 W
WA waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the half-wave plate, which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the quarter-wave plate, which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well.
 W
WA Wollaston prism is an optical device, invented by William Hyde Wollaston, that manipulates polarized light. It separates light into two separate linearly polarized outgoing beams with orthogonal polarization. The two beams will be polarized according to the optical axis of the two right angle prisms.