 W
W100% renewable energy is where all energy use is sourced from renewable energy sources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating/cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues, as well as economic and energy security concerns. Shifting the total global primary energy supply to renewable sources requires a transition of the energy system, since most of today's energy is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels.
 W
WThe Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia. It escalated on 8 January 2007, when the Russian state-owned pipeline company Transneft stopped pumping oil into the Druzhba pipeline which runs through Belarus because Belarus was siphoning the oil off the pipe without mutual agreement. On 10 January, Transneft resumed oil exports through the pipeline after Belarus ended the tariff that sparked the shutdown, despite differing messages from the parties on the state of negotiations.
 W
WMorgan D. Bazilian is an American-Irish academic, who has spent the majority of his career as a diplomat and in public service. He is the Director of the Payne Institute for Public Policy, and a professor of public policy at the Colorado School of Mines. His research focuses on energy and climate change policy, national security, and international affairs. In 2019, he was asked to testify in front of the U.S. Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources as an expert witness.
 W
WThe Bolivian gas conflict was a social confrontation in Bolivia reaching its peak in 2003, centering on the exploitation of the country's vast natural gas reserves. The expression can be extended to refer to the general conflict in Bolivia over the exploitation of gas resources, thus including the 2005 protests and the election of Evo Morales as president. Before these protests, Bolivia had seen a series of similar earlier protests during the Cochabamba protests of 2000, which were against the privatization of the municipal water supply.
 W
WThe Doomsday Machine: The High Price of Nuclear Energy, the World's Most Dangerous Fuel is a 2012 book by Martin Cohen and Andrew McKillop which addresses a broad range of concerns regarding the nuclear industry, the economics and environmental aspects of nuclear energy, nuclear power plants, and nuclear accidents. The book has been described by The New York Times as "a polemic on the evils of splitting the atom".
 W
WEfficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses.
 W
WENBau is an initiative of Swiss universities for training in sustainable building with the goal of resource efficiency of buildings in the areas of energy, water, materials and processes.
 W
WEnergy Cities is the European Association of local authorities in energy transition. It represents 1000 towns and cities in 30 countries. From 2017 to 2020, Energy Cities is under the Presidency of the City of Heidelberg (DE). Energy Cities was established as an association of European local authorities in 1990 to put all this into practice. The association premises are located in Brussels (BE) and Besançon (FR). A part of the team works in Budapest (HU), Offenburg (DE), Freiburg im Breisgau (DE) and Zürich (CH).
 W
WAn energy certificate is a transferable certificate, record or guarantee, in any form in relation to the amount of a specific type of energy or material goods consumed by an energy conversion device in the production of a quantity of energy or material goods and/or the attributes of the method and quality of its production.
 W
WThe Energy Community, also referred to in the past as the Energy Community of South East Europe, is an international organisation established between the European Union (EU) and a number of third countries to extend the EU internal energy market to Southeast Europe and beyond. With their signatures, the Contracting Parties commit themselves to implement the relevant EU energy acquis communautaire, to develop an adequate regulatory framework and to liberalise their energy markets in line with the acquis under the Treaty.
 W
WEnergy conservation is the effort made to reduce the consumption of energy by using less of an energy service. This can be achieved either by using energy more efficiently or by reducing the amount of service used. Energy conservation is a part of the concept of Eco-sufficiency. Energy conservation measures (ECMs) in buildings reduce the need for energy services and can result in increased environmental quality, national security, personal financial security and higher savings. It is at the top of the sustainable energy hierarchy. It also lowers energy costs by preventing future resource depletion.
 W
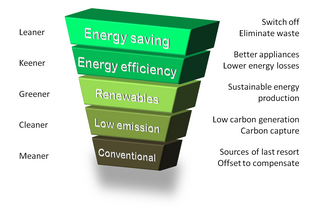
WThe Energy Hierarchy is a classification of energy options, prioritised to assist progress towards a more sustainable energy system. It is a similar approach to the waste hierarchy for minimising resource depletion, and adopts a parallel sequence.
 W
WThe Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, originally named the Clean Energy Act of 2007, is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States. As part of the Democratic Party's 100-Hour Plan during the 110th Congress, it was introduced in the United States House of Representatives by Representative Nick Rahall of West Virginia, along with 198 cosponsors. Even though Rahall was 1 of only 4 Democrats to oppose the final bill, it passed in the House without amendment in January 2007. When the Act was introduced in the Senate in June 2007, it was combined with Senate Bill S. 1419: Renewable Fuels, Consumer Protection, and Energy Efficiency Act of 2007. This amended version passed the Senate on June 21, 2007. After further amendments and negotiation between the House and Senate, a revised bill passed both houses on December 18, 2007 and President Bush, a Republican, signed it into law on December 19, 2007, in response to his "Twenty in Ten" challenge to reduce gasoline consumption by 20% in 10 years.
 W
WEnergy liberalisation refers to the liberalisation of energy markets, with specific reference to electricity generation markets, by bringing greater competition into electricity and gas markets in the interest of creating more competitive markets and reductions in price by privatisation. As the supply of electricity is a natural monopoly, this entails complex and costly systems of regulation to enforce a system of competition.
 W
WThe Energy Policy Act of 2005 is a federal law signed by President George W. Bush on August 8, 2005, at Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The act, described by proponents as an attempt to combat growing energy problems, changed US energy policy by providing tax incentives and loan guarantees for energy production of various types. The law also exempted hydraulic fracturing fluids from regulation under several environmental laws, and it repealed the Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935, effective February 2006.
 W
WEnergy recovery includes any technique or method of minimizing the input of energy to an overall system by the exchange of energy from one sub-system of the overall system with another. The energy can be in any form in either subsystem, but most energy recovery systems exchange thermal energy in either sensible or latent form.
 W
WEnergy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system. Historically, these changes have been driven by the demand for and availability of different fuels. Energy transitions can also result from depletion of energy sources, for example whale oil for illumination and wood for iron smelting in Europe. The current transition to renewable energy, and perhaps other types of sustainable energy, differs as it is largely driven by a recognition that global carbon emissions must be brought to zero, and since fossil fuels are the largest single source of carbon emissions, the quantity of fossil fuels that can be produced is limited by the COP21 Paris Agreement of 2015 to keep global warming below 1.5 °C. In recent years, the term energy transition has been coined in the framework of a move towards sustainability through increased integration of renewable energy in the realm of daily life.
 W
WEnergy Victory: Winning the War on Terror by Breaking Free of Oil is a 2007 book by Robert Zubrin. Zubrin's central argument is that the decisive front in the War on Terror is America's struggle for energy independence. He outlines the manner in which radical Islam has been financed by oil revenues, the technological feasibility of ethanol-fueled vehicles as well as the economic and agricultural imperatives for ethanol production, and the environmental implications of his plan.
 W
WThe EPS Service Parts Act of 2014 is a bill that would exempt certain external power supplies from complying with standards set forth in a final rule published by the United States Department of Energy in February 2014. The United States House Committee on Energy and Commerce describes the bill as a bill that "provides regulatory relief by making a simple technical correction to the 2007 Energy Independence and Security Act to exempt certain power supply (EPS) service and spare parts from federal efficiency standards."
 W
WCoal phase-out means stopping burning coal, and is part of fossil fuel phase-out. It is critical to limiting climate change, and several countries have taken initiatives to phase out coal. The health and environmental benefits of coal phase-out are greater than the cost. It has been suggested that developed countries could finance the process for developing countries provided they do not build any more coal plants and do a just transition.
 W
WFossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use of fossil fuels to zero. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition. Current efforts in fossil fuel phase-out involve replacing fossil fuels with sustainable energy sources in sectors such as transport, and heating. Alternatives to fossil fuels include electrification, hydrogen and aviation biofuel.
 W
WThe Gas Exporting Countries Forum (GECF) is an intergovernmental organization of 11 of the world's leading natural gas producers made up of Algeria, Bolivia, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Iran, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Russia, Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela. GECF members together control over 70% of the world's natural gas reserves, 38% of the pipeline trade and 85% of the liquefied natural gas (LNG) production. The three largest reserve-holders in the GECF – Russia, Iran and Qatar – together hold about 57% of global gas reserves.
 W
WThe Hype About Hydrogen: Fact and Fiction in the Race to Save the Climate is a book by Joseph J. Romm, published in 2004 by Island Press and updated in 2005. The book has been translated into German as Der Wasserstoff-Boom. Romm is an expert on clean energy, advanced vehicles, energy security, and greenhouse gas mitigation.
 W
WThe indirect land use change impacts of biofuels, also known as ILUC or iLUC, relates to the unintended consequence of releasing more carbon emissions due to land-use changes around the world induced by the expansion of croplands for ethanol or biodiesel production in response to the increased global demand for biofuels.
 W
WThe International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis. The IEA was initially dedicated to responding to physical disruptions in the supply of oil, as well as serving as an information source on statistics about the international oil market and other energy sectors.
 W
WThe International Energy Agency Energy in Buildings and Communities Programme, formerly known as the Energy in Buildings and Community Systems Programme (ECBCS), is one of the International Energy Agency’s Technology Collaboration Programmes (TCPs). The Programme "carries out research and development activities toward near-zero energy and carbon emissions in the built environment".
 W
WIn economics, the Jevons paradox occurs when technological progress or government policy increases the efficiency with which a resource is used, but the rate of consumption of that resource rises due to increasing demand. The Jevons paradox is perhaps the most widely known paradox in environmental economics. However, governments and environmentalists generally assume that efficiency gains will lower resource consumption, ignoring the possibility of the paradox arising.
 W
WMicrogeneration is the small-scale generation of heat and electric power by individuals, small businesses and communities to meet their own needs, as alternatives or supplements to traditional centralized grid-connected power. Although this may be motivated by practical considerations, such as unreliable grid power or long distance from the electrical grid, the term is mainly used currently for environmentally-conscious approaches that aspire to zero or low-carbon footprints or cost reduction. It differs from micropower in that it is principally concerned with fixed power plants rather than for use with mobile devices.
 W
WThe New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (新エネルギー・産業技術総合開発機構), or NEDO, is Japan's largest public management organization promoting research and development as well as deployment of industrial, energy and environmental technologies. In 2003, NEDO was reorganized as an Independent Administrative Institution. NEDO has approximately 1,000 personnel and domestic offices in Hokkaido, Kansai, and Kyushu and international offices in Washington D.C., Silicon Valley (California), Paris, Beijing, Bangkok, Jakarta and New Delhi. Its budget for fiscal year 2009 was 234,700,000,000 yen, the vast majority of which was provided by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). Its head office is located just outside Tokyo in Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture.
 W
WNon-Nuclear Futures: The Case for an Ethical Energy Strategy is a 1975 book by Amory B. Lovins and John H. Price. The main theme of the book is that the most important parts of the nuclear power debate are not technical disputes but relate to personal values, and are the legitimate province of every citizen, whether technically trained or not. Lovins and Price suggest that the personal values that make a high-energy society work are all too apparent, and that the values associated with an alternate view relate to thrift, simplicity, diversity, neighbourliness, craftsmanship, and humility. They also argue that large nuclear generators could not be mass-produced. Their centralization requires costly transmission and distribution systems. They are inefficient, not recycling excess thermal energy. The authors believed that nuclear reactors were less reliable and take longer to build, exposing them to escalated interest costs, mistimed demand forecasts, and wage pressure by unions.
 W
WNuclear energy policy is a national and international policy concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy and the nuclear fuel cycle, such as uranium mining, ore concentration, conversion, enrichment for nuclear fuel, generating electricity by nuclear power, storing and reprocessing spent nuclear fuel, and disposal of radioactive waste.
 W
WThe Öko-Institut is a non-profit, private-sector environmental research institute with its head office in Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany.
 W
WThe Partnership for a New Generation of Vehicles was a cooperative research program between the U.S. government and the three major domestic auto corporations, aimed at bringing extremely fuel-efficient (up to 80 mpg‑US vehicles to market by 2003.
 W
WPetrocaribe is an oil alliance involving 18 Caribbean member states. The alliance was founded on 29 June 2005 in Puerto La Cruz, Venezuela, Venezuela offering the other member states oil supplies based on a concessionary financial agreement. Petrocaribe has been part of the "pink tide" in Latin America seeking to achieve post-neoliberal development in the region. In 2013 Petrocaribe established links with the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA) aiming to go beyond oil trade and promoting economic cooperation.
 W
WThe United States is divided into five Petroleum Administration for Defense Districts, or PADDs. These were created during World War II under the Petroleum Administration for War to help organize the allocation of fuels derived from petroleum products, including gasoline and diesel fuel. Today, these regions are still used for data collection purposes.
 W
WThe Pickens Plan is an energy policy proposal announced July 8, 2008, by American businessman T. Boone Pickens. Pickens wanted to reduce American dependence on imported oil by investing approximately $US1 trillion in new wind turbine farms for power generation, which he believed would allow the natural gas used for power generation to be shifted to fuel trucks and other heavy vehicles with Compressed natural gas. Pickens stated that his plan could reduce by $300 billion (43%) the amount the country spends annually on foreign oil.
 W
WPower Shift is an annual youth summit which has been held in New Zealand, Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States. Other Power Shift Conferences are also being organised by members of the International Youth Climate Movement including Africa, Japan and India. The focus of the events is on climate change policy.
 W
WThe Powering Past Coal Alliance (PPCA) is a group of 104 countries, cities, regions and organisations aiming to accelerate the fossil-fuel phase out of coal-fired power stations, except the very few which have carbon capture and storage. It has been described as a "non-proliferation treaty" for fossil fuels. The project was undertaken with financial support from the Government of Canada, through their environmental department known as Environment and Climate Change Canada.
 W
WThe Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935 (PUHCA), also known as the Wheeler-Rayburn Act, was a US federal law giving the Securities and Exchange Commission authority to regulate, license, and break up electric utility holding companies. It limited holding company operations to a single state, thus subjecting them to effective state regulation. It also broke up any holding companies with more than two tiers, forcing divestitures so that each became a single integrated system serving a limited geographic area. Another purpose of the PUHCA was to keep utility holding companies engaged in regulated businesses from also engaging in unregulated businesses. The act was based on the conclusions and recommendations of the 1928-35 Federal Trade Commission investigation of the electric industry. On March 12, 1935, President Franklin D. Roosevelt released a report he commissioned by the National Power Policy Committee. This report became the template for the PUHCA. The political battle over its passage was one of the bitterest of the New Deal, and was followed by eleven years of legal appeals by holding companies led by the Electric Bond and Share Company, which finally completed its breakup in 1961.
 W
WReaction Time: Climate Change and the Nuclear Option is a book by Professor Ian Lowe which was officially launched by science broadcaster Robyn Williams at the Writers' Festival in Brisbane in September 2007. The book is about energy policy, and Lowe argues that nuclear power does not make sense on any level: economically, environmentally, politically or socially.
 W
WRenewable Electricity and the Grid: The Challenge of Variability is a 2007 book edited by Godfrey Boyle which examines the significance of the issue of variability of renewable energy supplies in the electricity grid.
 W
WRenewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. As of 2012, renewable energy accounts for about half of new nameplate electrical capacity installed and costs are continuing to fall.
 W
WThe renewable energy transition is the ongoing energy transition which is replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy. This transition can impact many aspects of life including the environment, society, the economy and governance.
 W
WThe RETScreen Clean Energy Management Software is a software package developed by the Government of Canada. RETScreen Expert was highlighted at the 2016 Clean Energy Ministerial held in San Francisco. The Government of Canada's Treasury Board Secretariat uses RETScreen Expert as its greenhouse gas reporting tool for all federal departments and agencies required to report emissions.
 W
WRocky Mountain Institute (RMI) is an organization in the United States dedicated to research, publication, consulting, and lecturing in the general field of sustainability, with a special focus on profitable innovations for energy and resource efficiency. RMI was established in 1982 and has grown into a broad-based institution with 220+ staff and an annual budget of some $52 million. RMI's work is independent and non-adversarial, with a strong emphasis on market-based solutions. The institute, which includes the Carbon War Room, operates in a number of initiative areas: Electricity Platform, Renewables Solutions, Buildings, Reinventing Fire: China, Smart Island Economies, Mobility Transformation, Shipping Efficiency, Sunshine for Mines, Sustainable Aviation, and Trucking Efficiency. The work of RMI has benefited more than 80 Fortune 500 companies in a diverse range of sectors. RMI is headquartered in Basalt, Colorado, and also maintains offices in Boulder, Colorado, New York City, Washington D.C. and Beijing, China.
 W
WThe Russia–Ukraine gas disputes refer to a number of disputes between Ukrainian oil and gas company Naftohaz Ukrayiny and Russian gas supplier Gazprom over natural gas supplies, prices, and debts. These disputes have grown beyond simple business disputes into transnational political issues—involving political leaders from several countries—that threaten natural gas supplies in numerous European countries dependent on natural gas imports from Russian suppliers, which are transported through Ukraine. Russia provides approximately a quarter of the natural gas consumed in the European Union; approximately 80% of those exports travel through pipelines across Ukrainian soil prior to arriving in the EU.
 W
WThe South American Energy Council is a body set up to co-ordinate the regional energy policy of the Union of South American Nations. Its establishment was agreed at the first South American Energy Summit, which took place on April 16–17 2007 on Isla Margarita in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta.
 W
WBenjamin K. Sovacool is an American academic who is director of the Danish Center for Energy Technology at the Department of Business Technology and Development and a professor of social sciences at Aarhus University. He is also professor of energy policy at the University of Sussex, where he directs the Center on Innovation and Energy Demand and the Sussex Energy Group. He has written on energy policy, environmental issues, and science and technology policy. Sovacool is editor-in-chief of Energy Research & Social Science.
 W
WSustainable Energy for All (SEforALL) is an international organization working in partnership with the United Nations, leaders in government, the private sector, financial institutions and civil society with as goal to drive further, faster action toward the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 7, which calls for universal access to sustainable energy by 2030, and the Paris Agreement, which calls for reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit climate warming to below 2° Celsius.
 W
WWinning the Oil Endgame: Innovation for Profits, Jobs and Security is a 2005 book by Amory B. Lovins, E. Kyle Datta, Odd-Even Bustnes, Jonathan G. Koomey, and Nathan J. Glasgow, published by the Rocky Mountain Institute. It presents an independent, transdisciplinary analysis of four ways to reduce petroleum dependence in the United States:Using oil more efficiently, through smarter technologies that wring more services from less oil (pp. 29–102). Substituting for petroleum fuels other liquids made from biomass or wastes (pp. 103–111). Substituting saved natural gas for oil in uses where they’re interchangeable, such as furnaces and boilers (pp. 111–122). Replacing oil with hydrogen made from non-oil resources (pp. 228–242).
 W
WWorld energy consumption is the total energy produced and used by humans. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards activity across all industrial and technological sectors, in every country. It does not include energy from food. World energy consumption has implications for the socio-economic-political sphere.