 W
WThe Barkhausen–Kurz tube, also called the retarding-field tube, reflex triode, B–K oscillator, and Barkhausen oscillator was a high frequency vacuum tube electronic oscillator invented in 1920 by German physicists Heinrich Georg Barkhausen and Karl Kurz. It was the first oscillator that could produce radio power in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) portion of the radio spectrum, above 300 MHz. It was also the first oscillator to exploit electron transit time effects. It was used as a source of high frequency radio waves in research laboratories, and in a few UHF radio transmitters through World War 2. Its output power was low which limited its applications. However it inspired research that led to other more successful transit time tubes such as the klystron, which made the low power Barkhausen-Kurz tube obsolete.
 W
WThe Great Debate, also called the Shapley–Curtis Debate, was held on 26 April 1920 at the Smithsonian Museum of Natural History, between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis. It concerned the nature of so-called spiral nebulae and the size of the universe. Shapley believed that distant nebulae were relatively small and lay within the outskirts of the Milky Way galaxy, while Curtis held that they were in fact independent galaxies, implying that they were exceedingly large and distant.
 W
WThe Little Albert experiment was a controlled experiment showing empirical evidence of classical conditioning in humans. The study also provides an example of stimulus generalization. It was carried out by John B. Watson and his graduate student, Rosalie Rayner, at Johns Hopkins University. The results were first published in the February 1920 issue of the Journal of Experimental Psychology.
 W
WA total lunar eclipse took place on May 3, 1920. It was visible from North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Middle east and Antarctica.
 W
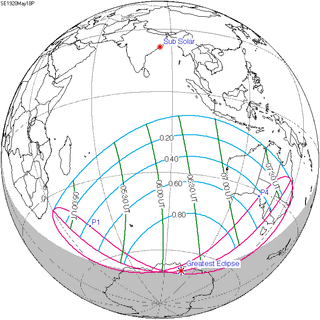
WA partial solar eclipse occurred on May 18, 1920. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
 W
WA partial solar eclipse occurred on November 10, 1920. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
 W
WV476 Cygni or Nova Cygni 1920 was a nova which occurred in the constellation Cygnus in 1920. It was discovered by William Frederick Denning, an English amateur astronomer, at 09:30 GMT on 20 August 1920, at which time it had a magnitude of 3.7. It reached a peak brightness of magnitude 1.7 on 23 August 1920. Its quiescent brightness is magnitude 17.09.