 W
W1566 Icarus is a large near-Earth object of the Apollo group and the lowest numbered potentially hazardous asteroid. It has is an extremely eccentric orbit (0.83) and measures approximately 1.4 km (0.87 mi) in diameter. In 1968, it became the first asteroid ever observed by radar. Its orbit brings it closer to the Sun than Mercury and further out than the orbit of Mars, which also makes it a Mercury-, Venus-, and Mars-crossing asteroid. This stony asteroid and relatively fast rotator with a period of 2.27 hours was discovered on 27 June 1949, by German astronomer Walter Baade at the Palomar Observatory in California. It was named after the mythological Icarus.
 W
WA breaker is a powerful percussion hammer fitted to an excavator for demolishing hard structures. It is powered by an auxiliary hydraulic system from the excavator, which is fitted with a foot-operated valve for this purpose. Additionally, demolition crews employ the hoe ram for jobs too large for jackhammering or areas where blasting is not possible due to safety or environmental issues.
 W
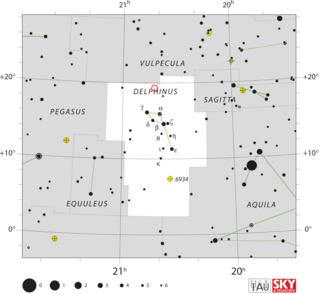
WHR Delphini, also known as Nova Delphini 1967, was a nova which appeared in the constellation Delphinus in 1967. It was discovered by George Alcock at 22:35 UT on 8 July 1967, after searching the sky for over 800 hours with binoculars. At the time of discovery it had an apparent magnitude of 5.0. It reached a peak brightness of magnitude 3.5 on 13 December 1967, making it easily visible to the naked eye around that time. Pre-outburst photographs taken with the Samuel Oschin telescope showed it as a ~12th magnitude star which might have been variable.
 W
WA total lunar eclipse took place on April 24, 1967, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the second being on October 18, 1967.
 W
WA total lunar eclipse took place on October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.
 W
WIn particle physics, proton decay is a hypothetical form of particle decay in which the proton decays into lighter subatomic particles, such as a neutral pion and a positron. The proton decay hypothesis was first formulated by Andrei Sakharov in 1967. Despite significant experimental effort, proton decay has never been observed. If it does decay via a positron, the proton's half-life is constrained to be at least 1.67×1034 years.
 W
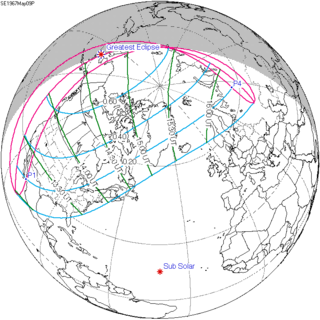
WA partial solar eclipse occurred on May 9, 1967. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
 W
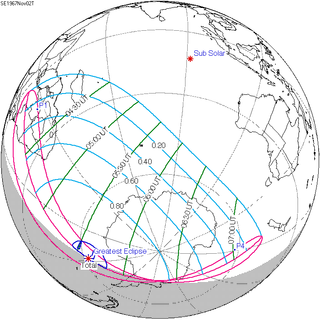
WA total solar eclipse occurred on November 2, 1967. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.