 W
WAn afterburner is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and combat. Afterburning injects additional fuel into a combustor in the jet pipe behind the turbine, "reheating" the exhaust gas. Afterburning significantly increases thrust as an alternative to using a bigger engine with its attendant weight penalty, but at the cost of very high fuel consumption which limits its use to short periods. This aircraft application of reheat contrasts with the meaning and implementation of reheat applicable to gas turbines driving electrical generators and which reduces fuel consumption.
 W
WThe Modesto Manifesto or Billy Graham rule is an extra-biblical Christian practice among select evangelical Protestant men, in which they avoid spending time alone with women to whom they are not married. It is adopted as a display of integrity, a means of avoiding sexual temptation, to avoid any appearance of doing something considered morally objectionable, as well as for avoiding being accused of sexual harassment or assault.
 W
WIn theoretical physics, a Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior and interaction of subatomic particles. The scheme is named after American physicist Richard Feynman, who introduced the diagrams in 1948. The interaction of subatomic particles can be complex and difficult to understand; Feynman diagrams give a simple visualization of what would otherwise be an arcane and abstract formula. According to David Kaiser, "Since the middle of the 20th century, theoretical physicists have increasingly turned to this tool to help them undertake critical calculations. Feynman diagrams have revolutionized nearly every aspect of theoretical physics." While the diagrams are applied primarily to quantum field theory, they can also be used in other fields, such as solid-state theory. Frank Wilczek wrote that the calculations which won him the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics "would have been literally unthinkable without Feynman diagrams, as would [Wilczek's] calculations that established a route to production and observation of the Higgs particle."
 W
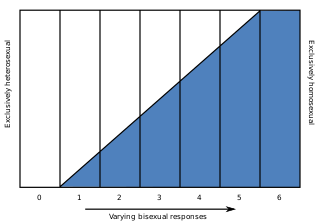
WThe Kinsey scale, also called the Heterosexual–Homosexual Rating Scale, is used in research to describe a person's sexual orientation based on one’s experience or response at a given time. The scale typically ranges from 0, meaning exclusively heterosexual, to a 6, meaning exclusively homosexual. In both the male and female volumes of the Kinsey Reports, an additional grade, listed as "X", indicated "no socio-sexual contacts or reactions". The reports were first published in Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) by Alfred Kinsey, Wardell Pomeroy, and others, and were also prominent in the complementary work Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953).
 W
WThe Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is a standardized test administered by the Law School Admission Council (LSAC) for prospective law school candidates. It is designed to assess reading comprehension as well as logical and verbal reasoning proficiency. The test is an integral part of the law school admission process in the United States, Canada, the University of Melbourne, Australia, and a growing number of other countries.
 W
WRosa 'Alain' is a red Floribunda rose variety, bred by Francis Meilland before 1946. Meilland International introduced the rose in France in 1948. It was named for Meilland's son, Alain, who was born in 1940. It won the Geneva Gold Medal in 1948.
 W
WRosa 'Michele Meilland' is a light pink Floribunda rose cultivar, bred by Francis Meilland in 1945. Meilland International introduced the rose in France in 1948. It was named for Meilland's daughter, Michele, who was born in 1943. It was named the most beautiful rose in France in 1945.
 W
WTetracycline, sold under the brand name Sumycin among others, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
 W
WUnited Nations Day is an annual commemorative day, reflecting the official creation of the United Nations on 24 October 1945. In 1947, the United Nations General Assembly declared 24 October, the anniversary of the Charter of the United Nations, to "be devoted to making known to the people of the world the aims and achievements of the United Nations and to gaining their support for" its work.