 W
WSherman's March to the Sea was a military campaign of the American Civil War conducted through Georgia from November 15 until December 21, 1864, by William Tecumseh Sherman, major general of the Union Army. The campaign began with Sherman's troops leaving the captured city of Atlanta on November 15 and ended with the capture of the port of Savannah on December 21. His forces followed a "scorched earth" policy, destroying military targets as well as industry, infrastructure, and civilian property, disrupting the Confederacy's economy and transportation networks. The operation broke the back of the Confederacy and helped lead to its eventual surrender. Sherman's decision to operate deep within enemy territory and without supply lines is considered to be one of the major campaigns of the war, and is taught by some historians as an early example of modern warfare or total war.
 W
WThe Battle of Altamaha Bridge, also known as the Battle for the Doctortown Railroad Trestle, was an American Civil War engagement fought December 19, 1864, in Wayne County, Georgia, during Sherman's March to the Sea. The Confederate victory prevented Federal forces from destroying a vital railroad bridge during Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman's siege of Savannah, keeping open Confederate supply lines to the city.
 W
WThe Battle of Buck Head Creek was the second battle of Sherman's March to the Sea, fought November 28, 1864, during the American Civil War. Union Army cavalry under Brig. Gen. Hugh Judson Kilpatrick repulsed an attack by the small Confederate cavalry corps under Maj. Gen. Joseph Wheeler, but abandoned its attempt to destroy railroads and rescue Union prisoners of war.
 W
WThe Chatham Artillery has played a leading role in the history of the state of Georgia since the American Revolution. in 1776 Thomas Lee was authorized to enlist a provincial company of artillery for the defense of Savannah, the first such unit in Georgia's history. Commanded by Joseph Woodruff, they defended the right flank of American forces when the British attacked Savannah. They saw service in the Oconnee wars, The Embargo Wars, and The War of 1812. They were part of the force that occupied Fort Pulaski that opened the American Civil War, and served in and around Savannah and Charleston South Carolina before joining General Johnston's forces in Columbia, South Carolina. After the reorganization in 1872, they mustered out to the border with Mexico, to stop Pancho Villa's raids in the United States. They served with the "Dixie Division" in France during World War I, and landed on Normandy Beach on D-day plus 4 in World War II. They breached the Siegfried Line, and were at the Elbe River when the war ended. In 2005 they were mobilized again into federal service, as an element of the 48th Brigade Combat team serving in Iraq, part of Operation Iraqi Freedom. The Chatham Artillery was re-mobilized in 2009 to support Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan, personally training Afghan Troops and Police Forces. They were demobilized in 2010 at Fort Stewart, Georgia. Today they remain in service, as a modular artillery brigade of the Georgia Army National Guard, the 118th Field Artillery.
 W
W"Marching Through Georgia" is a marching song written by Henry Clay Work at the end of the American Civil War in 1865. The title and lyrics of the song refer to U.S. Army major general William T. Sherman's "March to the Sea" to capture the Confederate city of Savannah, Georgia in late 1864.
 W
WMarching Through Peachtree is the second novel in The War Between the Provinces series, a fantasy version of the American Civil War by Harry Turtledove.
 W
WSherman's neckties were a railway-destruction tactic used in the American Civil War. Named after Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman of the Union Army, Sherman's neckties were railway rails destroyed by heating them until they were malleable and twisting them into loops resembling neckties, often around trees. Since the Confederacy had limited supplies of iron, and few foundries to roll the rails, this destruction was very difficult to repair. They were also called Sherman's Bowties, Jeff Davis's Neckties, and Sherman's hairpins.
 W
WThe Terrell-Sadler House near Eatonton, Georgia was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000. It is located at 122 Harmony Road.
 W
WThe Battle of Tulifinny was an American Civil War engagement fought December 6–9, 1864 in South Carolina during General Sherman's March to the Sea, also known as the Savannah Campaign. Outnumbered 5-1 a Confederate force successfully defended a critical section of the Charleston-Savannah railroad.
 W
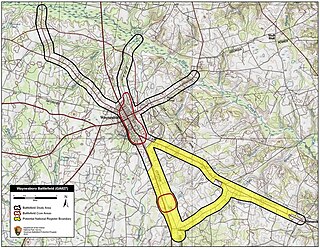
WThe Battle of Waynesboro was an American Civil War battle fought on December 4, 1864 in eastern Georgia, towards the end of Sherman's March to the Sea. Union cavalry forces under Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick defeated Confederate cavalry led by Maj. Gen. Joseph Wheeler, opening the way for William T. Sherman's armies to approach their objective, Savannah.