 W
WThe Siege of Avignon, in which Frankish forces led by Charles Martel beat the Umayyad garrison of Avignon and destroyed the stronghold, was contested in 737.
 W
WThe first Arab siege of Constantinople in 674–678 was a major conflict of the Arab–Byzantine wars, and the first culmination of the Umayyad Caliphate's expansionist strategy towards the Byzantine Empire, led by Caliph Mu'awiya I. Mu'awiya, who had emerged in 661 as the ruler of the Muslim Arab empire following a civil war, renewed aggressive warfare against Byzantium after a lapse of some years and hoped to deliver a lethal blow by capturing the Byzantine capital, Constantinople.
 W
WThe second Arab siege of Constantinople in 717–718 was a combined land and sea offensive by the Muslim Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate against the capital city of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople. The campaign marked the culmination of twenty years of attacks and progressive Arab occupation of the Byzantine borderlands, while Byzantine strength was sapped by prolonged internal turmoil. In 716, after years of preparations, the Arabs, led by Maslama ibn Abd al-Malik, invaded Byzantine Asia Minor. The Arabs initially hoped to exploit Byzantine civil strife and made common cause with the general Leo III the Isaurian, who had risen up against Emperor Theodosius III. Leo, however, tricked them and secured the Byzantine throne for himself.
 W
WThe siege of Kamarja was fought in 729 between the Arab Muslims of the Umayyad Caliphate and the Türgesh Khaganate, along with its Soghdian allies. The Umayyad conquest of Transoxiana had been undone in the 720s by the uprisings of the local Soghdian princes and the Türgesh invasions. By 729, the small fortress of Kamarja near Samarkand was one of the last remaining Arab strongholds in Transoxiana, when it was attacked by the Türgesh under the personal direction of their ruler, Suluk. The subsequent siege, for which a detailed account survives in the history of al-Tabari, lasted for 58 days and ended with the negotiated withdrawal of its garrison to Samarkand. The stubborn defence of Kamarja was celebrated in Arabic literature, but the Arab hold over the region was broken after the Battle of the Defile two years later. It was only following the collapse of the Türgesh Khaganate after 738 that the Arabs re-established their rule over Transoxiana.
 W
WThe siege of Mecca in September–November 683 was one of the early battles of the Second Fitna. The city of Mecca was a sanctuary for Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr, who was among the most prominent challengers to the dynastic succession to the Caliphate by the Umayyad Yazid I. After nearby Medina, the other holy city of Islam, also rebelled against Yazid, the Umayyad ruler sent an army to subdue Arabia. The Umayyad army defeated the Medinans and took the city, but Mecca held out in a month-long siege, during which the Kaaba was damaged by fire. The siege ended when news came of Yazid's sudden death. The Umayyad commander, Husayn ibn Numayr al-Sakuni, after vainly trying to induce Ibn al-Zubayr to return with him to Syria and be recognized as Caliph, departed with his forces. Ibn al-Zubayr remained in Mecca throughout the civil war, but he was nevertheless soon acknowledged as Caliph across most of the Muslim world. It was not until 692, that the Umayyads were able to send another army which again besieged and captured Mecca, ending the civil war.
 W
WThe siege of Mecca occurred at the end of the Second Fitna in 692 when the forces of the Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan besieged and defeated his rival, the caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr in his center of power, the Islamic holy city of Mecca.
 W
WThe Siege of Narbonne was fought in 737 between the forces of Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri, Umayyad governor of Narbonne, and a Frankish army led by Charles Martel.
 W
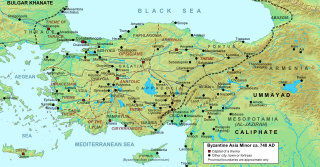
WThe siege of Nicaea of 727 was an unsuccessful attempt by the Umayyad Caliphate to capture the Byzantine city of Nicaea, the capital of the Opsician Theme. Ever since its failure to capture the Byzantine Empire's capital, Constantinople, in 717–718, the Caliphate had launched a series of raids into Byzantine Asia Minor. In 727, the Arab army, led by one of the Caliph's sons, penetrated deep into Asia Minor, sacked two Byzantine fortresses and in late July arrived before Nicaea. Despite constant attacks for 40 days, the city held firm and the Arabs withdrew and returned to the Caliphate. The successful repulsion of the attack was a major boost for Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian's recently initiated campaign to abolish the veneration of icons in the Empire; Leo claimed it as evidence of divine favour for his policy. The siege of Nicaea marks also the high point of the Umayyad raids, as new threats and defeats on their far-flung frontiers decreased Umayyad strength elsewhere, while Byzantine power strengthened afterwards.
 W
WThe Relief of Qasr al-Bahili was the successful relief of the Arab garrison of the small fortress of Qasr al-Bahili from the siege by the Turkic Türgesh Khaganate. Sent by the Umayyad governor of Khurasan, an Arab relief force under al-Musayyab ibn Bishr al-Riyahi managed to break the siege and escort the garrison to safety in Samarkand.
 W
WThe siege of Tyana was carried out by the Umayyad Caliphate in 707–708 or 708–709 in retaliation for a heavy defeat of an Umayyad army under Maimun the Mardaite by the Byzantine Empire in c. 706. The Arab army invaded Byzantine territory and laid siege to the city in summer 707 or 708. The date is uncertain, as virtually each of the extant Greek, Arabic, and Syriac parallel sources has in this respect a different date. Tyana initially withstood the siege with success, and the Arab army faced great hardship during the ensuing winter and was on the point of abandoning the siege in spring, when a relief army sent by Emperor Justinian II arrived. Quarrels among the Byzantine generals, as well as the inexperience of a large part of their army, contributed to a crushing Umayyad victory. Thereupon the inhabitants of the city were forced to surrender. Despite the agreement of terms, the city was plundered and largely destroyed, and according to Byzantine sources its people were made captive and deported, leaving the city deserted.