 W
WThe History of the Lombards or the History of the Langobards is the chief work by Paul the Deacon, written in the late 8th century. This incomplete history in six books was written after 787 and at any rate no later than 796, maybe at Montecassino.
 W
WLombardic or Langobardic is an extinct West Germanic language that was spoken by the Lombards (Langobardi), the Germanic people who settled in Italy in the sixth century. It was already declining by the seventh century because the invaders quickly adopted the Latin vernacular spoken by the local population. Lombardic may have been in use in scattered areas until as late as c. 1000 AD. A number of place names in the Lombardy Region in Northern Italy and items of Lombard vocabulary derive from Lombardic.
 W
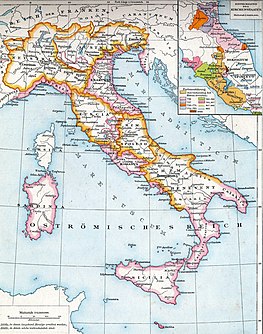
WThe Lombards or Langobards were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774, with origins near the Elbe in northern Germany and Scania in southern Sweden before the Migration Period.
 W
WThe Comacine masters were early medieval Lombard stonemasons working in a region of excellent building stone who gave to Lombardy its preeminence in the stone architecture that preceded Romanesque style.
 W
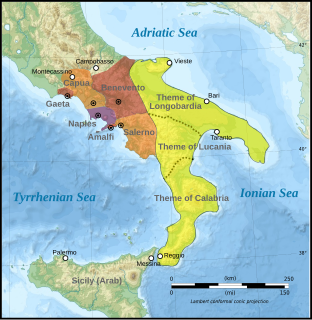
WThe Duchy of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conquered by the Normans for four years before it was given to the Pope. Being cut off from the rest of the Lombard possessions by the papal Duchy of Rome, Benevento was practically independent from the start. Only during the reigns of Grimoald, King of the Lombards and the kings from Liutprand on was the duchy closely tied to the kingdom. After the fall of the kingdom, however, it was the sole Lombard territory to continue to exist as a rump state, maintaining its de facto independence for nearly 300 years, although it was divided after 849.
 W
WThe Duchy of Friuli was a Lombard duchy in present-day Friuli, the first to be established after the conquest of the Italian peninsula in 568. It was one of the largest domains in Langobardia Major and an important buffer between the Lombard kingdom and the Slavs, Avars, and the Byzantine Empire. The original chief city in the province was Roman Aquileia, but the Lombard capital of Friuli was Forum Julii, modern Cividale.
 W
WIn 566, Lombard king Alboin concluded a treaty with the Pannonian Avars, to whom he promised the Gepids' land if they defeated them. The Gepids were destroyed by the Avars and Lombards in 567. Gepid King Cunimund was killed by Alboin himself. The Avars(leaded by their khagan Bayan I )subsequently occupied "Gepidia", forming the Avar Khaganate. The Byzantine Emperor intervened and took control of Sirmium, also giving refuge to Gepid leader Usdibad, although the rest of Gepidia was taken by the Avars. Gepid military strength was significantly reduced; according to H. Schutz (2001) many of them joined Lombard ranks, while the rest took to Constantinople. According to R. Collins (2010) the remnants were absorbed either by the Avars or Lombards. Although later Lombard sources claim they had a central role in this war, it is clear from contemporary Byzantine sources that the Avars had the principal role. The Gepids disappeared and the Avars took their place as a Byzantine threat. The Lombards disliked their new neighbours and decided to leave for Italy, forming the Kingdom of the Lombards.
 W
WLongobardia was a Byzantine term for the territories controlled by the Lombards in the Italian Peninsula. In the ninth and tenth centuries, it was also the name of a Byzantine military-civilian province known as the Theme of Longobardia located in southeastern Italy.
 W
WThe Origo Gentis Langobardorum is a short, 7th-century AD Latin account offering a founding myth of the Longobard people. The first part describes the origin and naming of the Lombards, the following text more resembles a king-list, up until the rule of Perctarit (672–688).
 W
WThe Lombard Principality of Salerno was a Southern Italian state, formed in 851 out of the Principality of Benevento after a decade-long civil war. It was centred on the port city of Salerno. Although it owed allegiance at its foundation to the Carolingian emperor, it was de facto independent throughout its history and alternated its allegiance between the Carolingians and their successors in the West and the Byzantine emperors in the east.
 W
WThe Duchy of Spoleto was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard dux Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.