 W
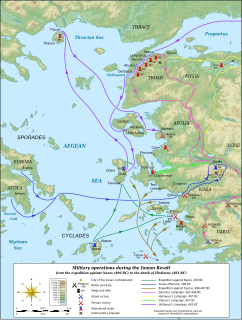
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
 W
WAristagoras, d. 497/496 BC, was the leader of the Ionian city of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC and a key player during the early years of the Ionian Revolt against the Persian Achaemenid Empire. He was the son-in-law of Histiaeus, and inherited the tyranny of Miletus from him.
 W
WArtaphernes, flourished circa 513–492 BC, was a brother of the Achaemenid king of Persia, Darius I, satrap of Lydia from the capital of Sardis, and a Persian general. In his position he had numerous contacts with the Greeks, and played an important role in suppressing the Ionian Revolt.
 W
WThe Battle of Lade was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisive victory for the Persians which all but ended the revolt.
 W
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
 W
WHistiaeus, the son of Lysagoras, was a Greek ruler of Miletus in the late 6th century BC. Histiaeus was a Tyrant under Darius I, king of Persia, who had subjugated Miletus and the other Ionian states in Asia Minor, and was in the habit of appointing Greek tyrants to rule the Greek cities of Ionia in his territory.
 W
WMegabates was a Persian military leader in the late 6th and early 5th centuries BC. According to Herodotus he was a cousin of Darius the Great and his brother Artaphernes, satrap of Lydia.
 W
WMiltiades, also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman.
 W
WThe siege of Naxos was a failed attempt by the Milesian tyrant Aristagoras, operating with support from, and in the name of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, to conquer the island of Naxos. It was the opening act of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would ultimately last for 50 years.
 W
WOtanes, son of Sisamnes, was an Achaemenid judge and later Satrap of Ionia during the reign of Darius the Great, circa 500 BC.
 W
WPixodarus (Πιξώδαρος) was a dignitary of Caria circa 500 BCE, son of a man named Mausolus, who was from the city of Cindye. Pixodarus led the Carians fighting on the Ionian side during the Ionian revolt in 490 BCE, but was defeated twice by the Achaemenids.
 W
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.