 W
WBattle of Al-Anbar was between the Muslim Arab army under the command of Khalid ibn al-Walid and the Sasanian Empire. The battle took place at Anbar which is located approximately 80 miles from the ancient city of Babylon. Khalid besieged the Sassanian Persians in the city fortress, which had strong walls. Scores of Muslim archers were used in the siege. The Persian governor, Shirzad, eventually surrendered and was allowed to retire. The Battle of Al-Anbar is often remembered as the "Action of the Eye" since Muslim archers used in the battle were told to aim at the "eyes" of the Persian garrison.
 W
WThe Battle of al-Qadisiyyah also spelled Qadisiyah, Qadisiyya, Ghadesiyeh or Kadisiya, fought in 636, was a decisive battle between the Arab Muslim army and the army of the Sasanian Empire of Persia during the first period of Muslim conquests.
 W
WThe Bajīla was an Arab tribe that inhabited the mountains south of Mecca in the pre-Islamic era and later dispersed to different parts of Arabia and then Iraq under the Muslims. The tribe, under one of its chieftains Jarir ibn Abd Allah, played a major role in the Muslim army that conquered Iraq in the mid-7th century.
 W
WBattle of Saniyy was between the Muslim Arab army and the Sasanian Empire. When Khalid ibn Walid gone from Ayn al-Tamr to Dumat Al-Jandal for the help of Iyad ibn Ghanm, The Persian court believed that Khalid had returned to Arabia with a large part of his army, Persians decided to throw the Muslims back into the desert and regain the territories and the prestige which the Empire had lost. The Persians had resolved not to fight Khalid again, but they were quite prepared to fight the Muslims without Khalid ibn al-Walid. Khalid ibn al-Walid first defeated them at the battle of Muzayyah and then advanced towards Saniyy.
 W
WThe Battle of Ullais was fought between the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sassanid Persian Empire in the middle of May 633 AD in Iraq, and is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Blood River since, as a result of the battle, there were enormous amounts of Persian Sassanian and Arab Christian casualties.
 W
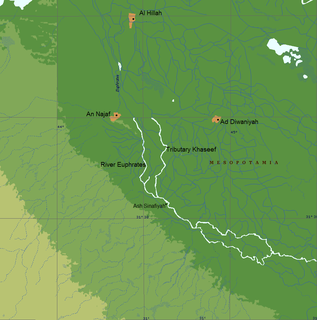
WThe Battle of the Bridge or the Battle of al-Jisr was a battle at the bank of the Euphrates river between Arab Muslims led by Abu Ubaid al-Thaqafi, and the Persian Sasanian forces led by Bahman Jaduya. It is traditionally dated to the year 634, and was the only major Sassanian victory over the Rashidun Caliphate army.
 W
WThe Battle of Sallasil or the Battle of Chains was the first battle fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Persian Empire. The battle was fought in Kazima soon after the Ridda Wars were over and Eastern Arabia was united under the authority of Caliph Abu Bakr. It was also the first battle of the Rashidun Caliphate in which the Muslim army sought to extend its frontiers.
 W
WThe Battle of Firaz was the last battle of the Muslim Arab commander Khalid ibn al-Walid in Mesopotamia (Iraq) against the combined forces of the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
 W
WThe Battle of Hira was fought between the Sasanian Empire and the Rashidun Caliphate in 633. It was one of the early battles of the Muslim conquest of Persia, and the loss of the frontier city on the Euphrates River opened the way to the Sasanian capital at Ctesiphon on the Tigris River.
 W
WBattle of Muzayyah was between the Muslim Arab army and the Sasanian Empire. When Khalid ibn Walid left from Ayn al-Tamr to Dumat Al-Jandal for the help of Iyad ibn Ghanm, the Persian court believed that Khalid had returned to Arabia with a large part of his army. The Persians decided to throw the Muslims back into the desert and regain the territories and the prestige which the Persian Empire had lost. The Persians had resolved not to fight Khalid again, but they were quite prepared to fight the Muslims without Khalid ibn al-Walid.
 W
WThe Battle of Walaja was a battle fought in Mesopotamia (Iraq) in May 633 between the Rashidun Caliphate army under Khalid ibn al-Walid and Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha against the Sassanid Empire and its Arab allies. In this battle the Sassanid army is said to have been two times the size of the Muslim army.
 W
WThe battle of Zumail was fought in 633 CE in Mesopotamia. It was a major Muslim victory in their conquest of that area. Under cover of night the Arab Muslims attacked the Christian-Arab forces, loyal to the Sasanian Empire, from three different sides. The Christian-Arab forces were unable to withstand the Muslim's surprise attack and soon dispersed but failed to escape from the battlefield and became the victims of a three sided attack by Khalid ibn al-Walid's army. At Zumail nearly the whole Christian Arab army was slaughtered by Khalid's Corps.