 W
WThe siege of Acre took place in 1291 and resulted in the Crusaders losing control of Acre to the Mamluks. It is considered one of the most important battles of the period. Although the crusading movement continued for several more centuries, the capture of the city marked the end of further crusades to the Levant. When Acre fell, the Crusaders lost their last major stronghold of the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem. They still maintained a fortress at the northern city of Tartus, engaged in some coastal raids, and attempted an incursion from the tiny island of Ruad, but when they lost that as well in 1302 in the siege of Ruad, the Crusaders no longer controlled any part of the Holy Land.
 W
WThe first Battle of Homs was fought in Homs, Syria, on December 10, 1260, between the Ilkhanates of Persia and the forces of Egypt.
 W
WThe Battle of Ain Jalut, also spelled Ayn Jalut, was fought between the Bahri Mamluks of Egypt and the Mongol Empire on 3 September 1260 in southeastern Galilee in the Jezreel Valley near what is known today as the Spring of Harod. The battle marked the height of the extent of Mongol conquests, and was the first time a Mongol advance had ever been permanently beaten back in direct combat on the battlefield.
 W
WOn April 15, 1277, the Mamluk Sultan Baibars marched from Syria into the Mongol-dominated Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm and attacked the Mongol occupation force in the Battle of Elbistan (Abulustayn). Upon reaching Elbistan with at least 10,000 horseman, Baibars made ready for battle with the Mongols, expecting them to be around 30,000. However, although the Mongol forces were smaller than the Mamluk army, there were the Georgians and Rum Seljuks that bolstered their numbers.
 W
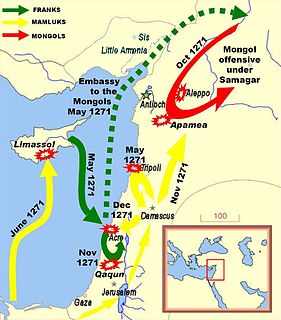
WThe Crusader fortress of Krak des Chevaliers fell to the Mamluk sultan Baibars in 1271. Baibars went north to deal with Krak des Chevaliers after the death of Louis IX of France on 29 November 1270.
 W
WThe Fall of Tripoli was the capture and destruction of the Crusader state, the County of Tripoli, by the Muslim Mamluks. The battle occurred in 1289 and was an important event in the Crusades, as it marked the capture of one of the few remaining major possessions of the Crusaders. The event is represented in a rare surviving illustration from a now fragmentary manuscript known as the 'Cocharelli Codex', thought to have been created in Genoa in the 1330s. The image shows the countess Lucia, Countess of Tripoli and Bartholomew, Bishop of Tortosa sitting in state in the centre of the fortified city, and Qalawun's assault in 1289, with his army depicted massacring the inhabitants fleeing to boats in the harbour and to the nearby island of St Thomas.
 W
WLord Edward's crusade, sometimes called the Ninth Crusade, was a military expedition to the Holy Land under the command of Lord Edward, Duke of Gascony in 1271–1272. It was an extension of the Eighth Crusade and was the last of the Crusades to reach the Holy Land before the fall of Acre in 1291 brought an end to the permanent crusader presence there.
 W
WThe Battle of Mari, also called the Disaster of Mari, was a battle between the Mamluks of Egypt and the Armenians of Cilician Armenia on 24 August 1266.
 W
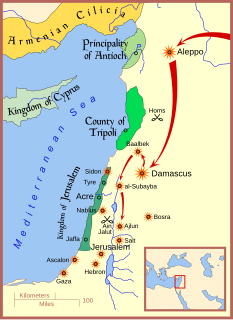
WStarting in the 1240s, the Mongols made repeated invasions of Syria or attempts thereof. Most failed, but they did have some success in 1260 and 1300, capturing Aleppo and Damascus and destroying the Ayyubid dynasty. The Mongols were forced to retreat within months each time by other forces in the area, primarily the Egyptian Mamluks. Since 1260, it had been described as the Mamluk-Ilkhanid War.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Homs was fought in western Syria on 29 October 1281, between the armies of the Mamluk dynasty of Egypt and the Ilkhanate, a division of the Mongol Empire centered on Iran. The battle was part of Abaqa Khan's attempt at taking Syria from the Mamluks.
 W
WThe Seventh Crusade was a crusade led by Louis IX of France from 1248 to 1254. Louis' Christian army was defeated by the Ayyubid army led by Fakhr ad-Din ibn as-Shaikh and their allies, the Bahriyya Mamluks, led by Faris ad-Din Aktai, Baibars al-Bunduqdari, Qutuz, Aybak and Qalawun. Fakhr ad-Din was killed in the war, and Louis was captured. Approximately 800,000 bezants were paid in ransom for his return.
 W
WThe 1271 siege of Tripoli was initiated by the Mamluk ruler Baibars against the Frankish ruler of the Principality of Antioch and the County of Tripoli, Bohemond VI. It followed the dramatic fall of Antioch in 1268, and was an attempt by the Mamluks to completely destroy the Crusader states of Antioch and Tripoli.
 W
WThe Battle of Wadi al-Khaznadar, also known as the Third Battle of Homs, was a Mongol victory over the Mamluks in 1299.