 W
WThe Amiriyah shelter bombing was an aerial attack that killed at least 408 civilians on 13 February 1991 during the Persian Gulf War, when an air-raid shelter in the Amiriyah neighborhood of Baghdad, Iraq was destroyed by the U.S. Air Force with two GBU-27 Paveway III laser-guided "smart bombs".
 W
WThe July 12, 2007, Baghdad airstrikes were a series of air-to-ground attacks conducted by a team of two U.S. AH-64 Apache helicopters in Al-Amin al-Thaniyah, New Baghdad during the Iraqi insurgency which followed the Iraq War. On April 5, 2010, the attacks received worldwide coverage and controversy following the release of 39 minutes of gunsight footage by the Internet whistleblower website WikiLeaks. The footage was portrayed as classified, but the individual who leaked it, U.S. Army soldier Chelsea Manning, testified in 2013 that the video was not classified. The video, which WikiLeaks titled Collateral Murder, showed the crew firing on a group of men and killing several of them, then laughing at some of the casualties, all of whom were civilians, including two Reuters journalists. An anonymous U.S. military official confirmed the authenticity of the footage, which provoked global discussion on the legality and morality of the attacks.
 W
WThe air campaign of the Gulf War, also known as the 1991 bombing of Iraq, was an extensive aerial bombing campaign from 17 January 1991 to 23 February 1991. The Coalition of the Gulf War flew over 100,000 sorties, dropping 88,500 tons of bombs, widely destroying military and civilian infrastructure. The air campaign was commanded by USAF Lieutenant General Chuck Horner, who briefly served as Commander-in-Chief—Forward of U.S. Central Command while General Schwarzkopf was still in the United States. The British air commanders were Air Vice-Marshal Andrew Wilson and Air Vice-Marshal Bill Wratten. The air campaign had largely finished by 23 February 1991 when the coalition invasion of Kuwait took place.
 W
WThe H-3 airstrike was a surprise air attack by the Iranian Air Force during the Iran–Iraq War on 4 April 1981 against the airbases of the Iraqi Air Force at the H-3 Air Base in western Iraq. The Iranians destroyed at least 48 Iraqi aircraft on the ground with no losses of their own. Based on the results achieved, it is considered one of the most successful raids in the history of aerial warfare.
 W
WThe 1998 bombing of Iraq was a major four-day bombing campaign on Iraqi targets from 16 to 19 December 1998, by the United States and the United Kingdom. The contemporaneous justification for the strikes was Iraq's failure to comply with United Nations Security Council resolutions and its interference with United Nations Special Commission inspectors who were looking for weapons of mass destruction.
 W
WOperation Opera, also known as Operation Babylon, was a surprise airstrike conducted by the Israeli Air Force on 7 June 1981, which destroyed an unfinished Iraqi nuclear reactor located 17 kilometres southeast of Baghdad, Iraq. The Israeli operation came after Iran's partially-successful Operation Scorch Sword had caused minor damage to the same nuclear facility a year prior, with the damage having been subsequently repaired by French technicians. Operation Opera, and related Israeli government statements following it, established the Begin Doctrine, which explicitly stated the strike was not an anomaly, but instead "a precedent for every future government in Israel". Israel's counter-proliferation preventive strike added another dimension to its existing policy of deliberate ambiguity, as it related to the nuclear weapons capability of other states in the region.
 W
WOperation Instant Thunder was the preliminary name given to a planned air strike by the United States during the Gulf War. Designed by Colonel John A. Warden III, it was planned to be an overwhelming strike which would devastate the Iraqi military with a minimum loss of civilian as well as American life.
 W
WOperation Alborz, more commonly known by the code-name Operation Kaman 99, was an operation launched by the Iranian Air Force in retaliation to Iraqi surprise aerial attacks on Iran the day before which marked the beginning of the 8-year-long Iran–Iraq War. Involving nearly 200 aircraft, it is considered the largest operation carried out by the IRIAF. The outcome was clearly successful, as the Iranians achieved Air superiority for the first years of the conflict.
 W
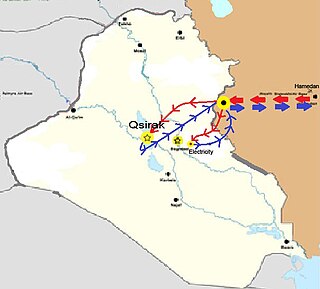
WOperation Scorch Sword was a surprise airstrike carried out by the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force on 30 September 1980, that damaged an almost-complete nuclear reactor located 17 kilometres southeast of Baghdad, Iraq. The operation was carried out eight days into the Iran–Iraq War. At dawn on 30 September 1980, four Iranian F-4E Phantom jets refuelled mid-air near the Iran–Iraq border. After crossing into Iraq, the fighters climbed to a high altitude in order to stay undetected by Iraqi airspace radar systems. Moments later, two of the Phantoms peeled off and dropped to a low altitude again to avoid internal radar detection and proceeded to fly stealthily to the Tuwaitha Nuclear Research Centre just southeast of the capital city of Baghdad, and home to the Osirak nuclear reactor.
 W
WOperation Senior Surprise, also known as Secret Squirrel, was a long range B-52G Stratofortress cruise missile strike against Iraqi targets that initiated the bombing campaign during the Gulf War in 1991. But was given the unofficial nickname Operation Secret Squirrel by the B-52 crews. The mission took place from January 16 1991 and ended January 17 1991. Lt. Col John "Jay" Beard, was the mission commander and Barksdale AFB's 596th Bomb Squadron's commanding officer.
 W
WOperation Sultan 10 was an operation of the Iranian Air Force on 29 October 1980, the beginning of the Iran–Iraq War. In this operation six F-4E Phantom IIs from IRIAF's 31st and 3rd Squadrons took part in an attack on the Al-Hurriah Airbase near Mosul in Saddam Hussein's Iraq.
 W
WThe Package Q Airstrike was the largest airstrike of the Persian Gulf War and the largest strike of F-16s in military history. Many aircraft including the F-117 were used to attack targets in Baghdad, which was the most heavily defended area of Iraq. The same target was hit several times by F-117s, and the last package consisted of seventeen F-111F on the 19th day of the war.
 W
WThe War of the Cities was five series of air raids, missile attacks and artillery shellings on major cities and urban areas initiated by Saddam Hussein's Iraqi Air Force, with the aim of disrupting the morale of Iran during the Iran–Iraq War. The first phase of air strikes were undertaken by the Iraqi Air Force, which normally was followed by retaliation by Iranian Armed Forces.