 W
WTomography is imaging by sections or sectioning through the use of any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word tomography is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος tomos, "slice, section" and γράφω graphō, "to write" or, in this context as well, " to describe." A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram.
 W
WThe computed tomography imaging spectrometer (CTIS) is a snapshot imaging spectrometer conceived separately by Takayuki Okamoto and Ichirou Yamaguchi at Riken (Japan), and by F. Bulygin and G. Vishnakov in Moscow (Russia). The concept was subsequently further developed by Michael Descour, at the time a PhD student at the University of Arizona, under the direction of Prof. Eustace Dereniak.
 W
WIn radiography, focal plane tomography is tomography by simultaneously moving the X-ray generator and X-ray detector so as to keep a consistent exposure of only the plane of interest during image acquisition. This was the main method of obtaining tomographs in medical imaging until the late-1970s. It has since been largely replaced by more advanced imaging techniques such as CT and MRI. It remains in use today in a few specialized applications, such as for acquiring orthopantomographs of the jaw in dental radiography.
 W
WIndustrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography and computed tomographic radiography.
 W
WLaboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery is a system used for virtual surgical planning. Starting with 1998, LUCAS was developed at the University of Regensburg, Germany, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. The resulting surgical planning is then reproduced onto the patient by using a navigation system. In fact, LUCAS is integrated into the same platform together with the Surgical Segment Navigator (SSN), the Surgical Tool Navigator (STN), the Surgical Microscope Navigator (SMN) and the 6DOF Manipulator, also from the Carl Zeiss Company.
 W
WNeutron tomography is a form of computed tomography involving the production of three-dimensional images by the detection of the absorbance of neutrons produced by a neutron source. It created a three-dimensional image of an object by combining multiple planar images with a known separation. It has a resolution of down to 25 μm. Whilst its resolution is lower than that of X-ray tomography, it can be useful for specimens containing low contrast between the matrix and object of interest; for instance, fossils with a high carbon content, such as plants or vertebrate remains.
 W
WOcean acoustic tomography is a technique used to measure temperatures and currents over large regions of the ocean. On ocean basin scales, this technique is also known as acoustic thermometry. The technique relies on precisely measuring the time it takes sound signals to travel between two instruments, one an acoustic source and one a receiver, separated by ranges of 100–5000 km. If the locations of the instruments are known precisely, the measurement of time-of-flight can be used to infer the speed of sound, averaged over the acoustic path. Changes in the speed of sound are primarily caused by changes in the temperature of the ocean, hence the measurement of the travel times is equivalent to a measurement of temperature. A 1 °C change in temperature corresponds to about 4 m/s change in sound speed. An oceanographic experiment employing tomography typically uses several source-receiver pairs in a moored array that measures an area of ocean.
 W
WOptical projection tomography is a form of tomography involving optical microscopy. The OPT technique is sometimes referred to as Optical Computed Tomography (optical-CT) and Optical Emission Computed Tomography (optical-ECT) in the literature, to address the fact that the technique bears similarity to X-ray computed tomography (CT) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
Quantum tomography or quantum state tomography is the process by which a quantum state is reconstructed using measurements on an ensemble of identical quantum states. The source of these states may be any device or system which prepares quantum states either consistently into quantum pure states or otherwise into general mixed states. To be able to uniquely identify the state, the measurements must be tomographically complete. That is, the measured operators must form an operator basis on the Hilbert space of the system, providing all the information about the state. Such a set of observations is sometimes called a quorum.
 W
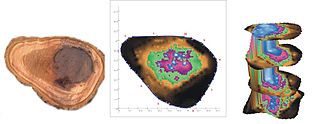
WAcoustic or stress wave tomography is a non-destructive measurement method for the visualization of the structural integrity of a solid object. It is being used to test the preservation of wood or concrete, for example. The term acoustic tomography refers to the perceptible sounds that are caused by the mechanical impulses used for measuring. The term stress wave tomography describes the measurement method more accurately.
 W
WThe surgical planning is the preoperative method of pre-visualising a surgical intervention, in order to predefine the surgical steps and furthermore the bone segment navigation in the context of computer-assisted surgery. The surgical planning is most important in neurosurgery and oral and maxillofacial surgery. The transfer of the surgical planning to the patient is generally made using a medical navigation system.
 W
WTomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann Radon. A notable example of applications is the reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) where cross-sectional images of patients are obtained in non-invasive manner. Recent developments have seen the Radon transform and its inverse used for tasks related to realistic object insertion required for testing and evaluating computed tomography use in airport security.
 W
WTomoPy is an open-sourced Python toolbox to perform tomographic data processing and image reconstruction.