 W
WThe Battle of Byram's Ford was fought on October 22 and 23, 1864, in Missouri during Price's Raid, a campaign of the American Civil War. With the Confederate States of America collapsing, Major General Sterling Price of the Confederate States Army conducted an invasion of the state of Missouri in late 1864. Union forces led Price to abandon goals of capturing the cities of St. Louis and Jefferson City, and he turned west with his army towards Kansas City.
 W
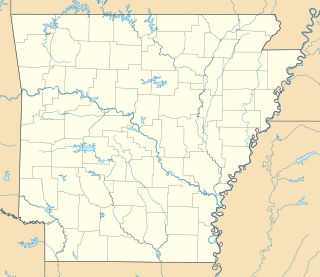
WThe Camden Expedition was the final campaign conducted by the United States Army against the Confederate States Army in Arkansas, during the American Civil War. The offensive was designed to cooperate with Maj. Gen. Banks' movement against Shreveport.
 W
WThe Battle of Cove Mountain occurred in Wythe County, Virginia, on May 10, 1864, during the American Civil War. A small Union division commanded by Brigadier General William W. Averell was prevented from moving to Wytheville by Confederate forces commanded by Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan and a detachment of a brigade of cavalry belonging to William E. "Grumble" Jones. Morgan stopped Averell at Cove Gap, which is adjacent to Crockett's Cove and Cove Mountain. Averell and a larger force commanded by Brigadier General George Crook were part of a Union plan to damage the Virginia and Tennessee Railroad. The railroad was used by the Confederacy to transport soldiers and supplies, and served important lead and salt mines in southwestern Virginia. It was part of a rail network that connected the Confederate capital in Richmond, Virginia, to Tennessee, and had telegraph wires along its line.
 W
WThe town of Dedham, Massachusetts participated in the American Civil War primarily through the 630 men who served in the United States Armed Forces during the war. A total of 46 men would die in the war, including in battle, from disease, from wounds sustained in battle, and in prisoner of war camps. The Town of Dedham supported the soldiers and their families both through appropriations raised by taxes, and through donations of supplies sent to the front lines.
 W
WThe Battle of Egypt Station was an engagement in Mississippi that took place during a successful Union cavalry raid during the American Civil War. A 3,500-man Union cavalry division under Brigadier General Benjamin Grierson defeated Confederate troops led by Franklin Gardner and Samuel J. Gholson. Grierson's raiding cavalry left Memphis, Tennessee on 21 December and first demolished a Confederate supply depot at Verona. Moving south while wrecking bridges and track along the Mobile and Ohio Railroad, the Union raiders encountered the Confederate defenders at Egypt Station. After their victory, Grierson's cavalry headed southwest to Vicksburg which it reached on January 5, 1865. The raiders destroyed a large amount of Confederate supplies and also damaged the Mississippi Central Railroad. Some of the men captured by Grierson's raiders proved to be former Union soldiers who volunteered to fight for the Confederacy rather than languish in prison camps. When John Bell Hood's army retreated into northern Mississippi after the Battle of Nashville, it was unable to obtain supplies because Grierson's raiders had damaged the railroad so badly.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Pillow, also known as the Fort Pillow massacre, was fought on April 12, 1864, at Fort Pillow on the Mississippi River in Henning, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. The battle ended with a massacre of Union soldiers attempting to surrender, by soldiers under the command of Confederate Major General Nathan Bedford Forrest. Military historian David J. Eicher concluded: "Fort Pillow marked one of the bleakest, saddest events of American military history."
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Pillow, also known as the Fort Pillow massacre, was fought on April 12, 1864, at Fort Pillow on the Mississippi River in Henning, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. The battle ended with a massacre of Union soldiers attempting to surrender, by soldiers under the command of Confederate Major General Nathan Bedford Forrest. Military historian David J. Eicher concluded: "Fort Pillow marked one of the bleakest, saddest events of American military history."
 W
WThe Battle of New Market was fought on May 15, 1864, in Virginia during the Valley Campaigns of 1864 in the American Civil War. A makeshift Confederate army of 4,100 men defeated the larger Army of the Shenandoah under Major General Franz Sigel, delaying the capture of Staunton by several weeks.
 W
WPrice's Missouri Expedition, also known as Price's Raid or Price's Missouri Raid, was an unsuccessful Confederate cavalry raid through Arkansas, Missouri, and Kansas in the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. Led by Confederate Major-General Sterling Price, the campaign's intention was to recapture Missouri and renew the Confederate initiative in the larger conflict.
 W
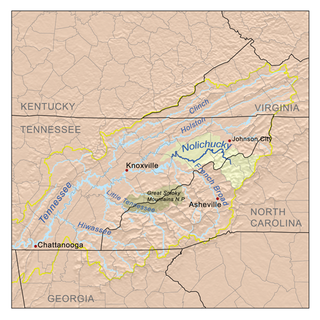
WThe Battle of Red Banks was an American Civil War battle that took place on December 29, 1864, between Union and Confederate forces. It took place at the Red Banks of the Nolichucky River in Unicoi County, Tennessee near the North Carolina border. Southern soldiers referred to the conflict as the Battle of the Bloody Chucky.
 W
WThe Red River campaign or Red River expedition comprised a series of battles fought along the Red River in Louisiana during the American Civil War from March 10 to May 22, 1864. The campaign was a Union initiative, fought between approximately 30,000 Union troops under the command of Major General Nathaniel P. Banks, and Confederate troops under the command of Lieutenant General Richard Taylor, whose strength varied from 6,000 to 15,000.
 W
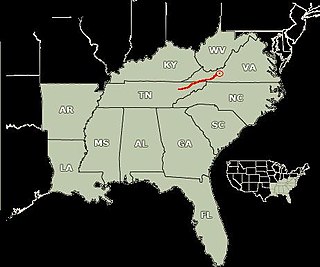
WSherman's March to the Sea was a military campaign of the American Civil War conducted through Georgia from November 15 until December 21, 1864, by William Tecumseh Sherman, major general of the Union Army. The campaign began with Sherman's troops leaving the captured city of Atlanta on November 15 and ended with the capture of the port of Savannah on December 21. His forces followed a "scorched earth" policy, destroying military targets as well as industry, infrastructure, and civilian property, disrupting the Confederacy's economy and transportation networks. The operation broke the back of the Confederacy and helped lead to its eventual surrender. Sherman's decision to operate deep within enemy territory and without supply lines is considered to be one of the major campaigns of the war, and is taught by some historians as an early example of modern warfare or total war.
 W
WStoneman's 1864 raid also known as Stoneman's raid into Southwest Virginia was an American Civil War expedition into southwest Virginia by Cavalry and Infantry regiments, including the 3rd North Carolina Mounted Infantry, under Union Maj. Gen. George Stoneman, designed to disrupt infrastructure beneficial to the Confederate war effort. This expedition resulted in the Battle of Marion and the Second Battle of Saltville against a Confederate force under the command of John C. Breckinridge and accomplished the destruction of the saltworks at Saltville, Virginia.
 W
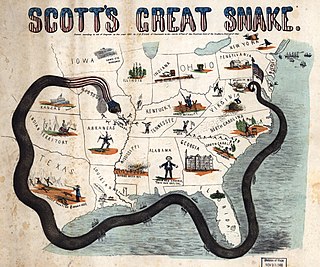
WThe Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
 W
WThe Battle of Yazoo City was an engagement in Mississippi during a month-long Union expedition up the Yazoo River in the American Civil War. The Union force commanded by Colonel James Henry Coates repulsed an attack led by Confederate Brigadier General Lawrence Sullivan Ross. The Union force suffered greater losses and withdrew down the river the next day with a large amount of cotton seized or bought from plantations along the river. The expedition was undertaken in cooperation with Major General William Tecumseh Sherman's Meridian campaign.