 W
WThe Battle of al-Babein took place on March 18, 1167, during the third Crusader invasion of Egypt. King Amalric I of Jerusalem, and a Zengid army under Shirkuh, both hoped to take the control of Egypt over from the Fatimid Caliphate. Saladin served as Shirkuh’s highest-ranking officer in the battle. The result was a tactical draw between the forces, however the Crusaders failed to gain access to Egypt.
 W
WIn the Battle of al-Buqaia in 1163, the Crusaders and their allies inflicted a rare defeat on Nur ad-Din Zangi, the Emir of Aleppo and Damascus. King Amalric I led the army of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, together with contingents from the northern Latin states, a substantial body of pilgrims who had just arrived from France, and a force brought by the Byzantine governor of Cilicia. For the Christian forces, this victory only gave a brief respite from the sustained Muslim offensive.
 W
WThe siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusader's way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, lasted from 20 October 1097 to 3 June 1098. The second siege, of the crusader-held city by a Seljuk relieving army, lasted three weeks in June 1098. On that day was the Battle of Antioch, in which the crusaders defeated the relieving army led by Kerbogha. The crusaders then established the Principality of Antioch, ruled by Bohemond of Taranto.
 W
WThe Battle of Artah was fought in 1105 between Crusader forces and the Seljuk Turks at the town of Artah near Antioch. The Turks were led by Fakhr al-Mulk Radwan of Aleppo, while the Crusaders were led by Tancred, Prince of Galilee, regent of the Principality of Antioch. The Crusaders were victorious and proceeded to threaten Aleppo itself.
 W
WIn the Battle of Azaz forces of the Crusader States commanded by King Baldwin II of Jerusalem defeated Aq-Sunqur al-Bursuqi's army of Seljuk Turks on 11 June 1125 and raised the siege of the town.
 W
WThe Siege of Baghdad in 1157 was the last Seljuq attempt to capture Baghdad from the Abbasids. Caliph al-Muqtafi successfully defended his capital against the coalition armies of Seljuq Sultan Muhammad of Hamadan and Qutb ad-Din of Mosul.
 W
WBattle of Kerj Abu Dulaf was fought in 1073 between the Seljuk Army of Malik-Shah I and KermanSeljuk army of Qavurt and his son, Sultan-shah. It took place approximately near Kerj Abu Dulaf, the present-day between Hamadan and Arak, and was a decisive Malik-Shah I victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Dandanaqan was fought in AD 1040 between the Seljuq Turkmens and the Ghaznavid Empire near the city of Merv. The battle ended with a decisive Seljuq victory, which subsequently brought down the Ghaznavid domination in Khorasan.
 W
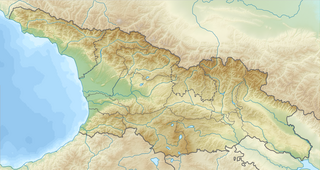
WThe Battle of Didgori was fought between the armies of the Kingdom of Georgia and the Great Seljuq Empire at the narrow place of Didgori, 40 km west of Tbilisi, on August 12, 1121. The large Muslim army, under the command of Ilghazi, was unable to maneuver, and suffered a devastating defeat due to King David IV of Georgia’s effective military tactics.
 W
WThe Battle of Harran took place on May 7, 1104 between the Crusader states of the Principality of Antioch and the County of Edessa, and the Seljuk Turks. It was the first major battle against the newfound Crusader states in the aftermath of the First Crusade, marking a key turning point against Frankish expansion. The battle had a disastrous effect on the Principality of Antioch as the Turks regained territory earlier lost.
 W
WThe Battle of Inab, also called Battle of Ard al-Hâtim or Fons Muratus, was fought on 29 June 1149, during the Second Crusade. The Zengid army of Atabeg Nur ad-Din Zangi destroyed the combined army of Prince Raymond of Poitiers and the Assassins of Ali ibn-Wafa. The Principality of Antioch was subsequently pillaged and reduced in size as its eastern border was pushed west.
 W
WThe Battle of Partskhisi was fought between the armies of Kingdom of Georgia and Seljuk Empire. After hours of intense fighting, Georgians won a decisive victory over the Turks.
 W
WThe Battle of Qatwan was fought in September 1141 between the Qara Khitai and the Seljuq Empire and its vassal-state the Kara-Khanids. The Seljuqs were decisively defeated, which signalled the beginning of the end of the Great Seljuk Empire.
 W
WThe Battle of Sarmin, also known as the Battle of Tell Danith, took place on September 14, 1115 with Roger of Salerno's Crusader army surprising and routing the Seljuk Turkish army of Bursuq ibn Bursuq of Hamadan. It is also known as the First Battle of Tell Danith, distinguishing it from the Battle of Hab of 1119, the Second Battle of Tell Danith.
 W
WDizkuh or Shahdiz (شاهدز) was a fortress near Isfahan, Iran, notably held by the Nizari Ismailis. It was captured and destroyed in Seljuk sultan Muhammad Tapar's anti-Nizari campaign. Its conspicuous, picturesque ruins lie about 8 km south of Isfahan on a subpeak of Mount Soffeh.