 W
WThe Bristol Bloodhound is a British ramjet powered surface-to-air missile developed during the 1950s. It served as the UK's main air defence weapon into the 1990s and was in large-scale service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the forces of four other countries.
 W
WThe Shorts Blowpipe is a man-portable (MANPADS) surface-to-air missile that was in use with the British Army and Royal Marines from 1975. It also saw service in other military forces around the world. Most examples were retired by the mid-1990s. It is unique among MANPADS in that it is manually guided to its target with a small joystick, sending guidance corrections to the missile over a radio control link.
 W
WThe Common Anti-Air Modular Missile (CAMM) is a family of surface-to-air missiles developed by MBDA UK for the United Kingdom.[8] CAMM shares some common features and components with the ASRAAM air-to-air missile, but with updated electronics and an active radar homing seeker. CAMM is replacing the Sea Wolf missile on Type 23 frigates of the Royal Navy since 2018, will replace the Rapier missile in British Army service and is contributing to the updating of MBDA's ASRAAM in service with the Royal Air Force. [1][9]
 W
WThe Fairey Aviation Stooge was a command guided surface-to-air missile (SAM) development project carried out in the United Kingdom starting in World War II. Development dates to a British Army request from 1944, but the work was taken over by the Royal Navy as a potential counter to the Kamikaze threat. Development was not complete when the war ended, but the Ministry of Supply funded further development and numerous test launches into 1947, assisting in the development of more advanced successor missiles.
 W
WJavelin is a British man-portable surface-to-air missile, formerly used by the British Army and Canadian Army. It can be fired from the shoulder, or from a dedicated launcher known as Javelin LML: Lightweight Multiple Launcher. Capable of being vehicle mounted, the LML carries three rounds.
 W
WRapier is a surface-to-air missile developed for the British Army to replace their towed Bofors 40/L70 anti-aircraft guns. The system is unusual as it uses a manual optical guidance system, sending guidance commands to the missile in flight over a radio link. This results in a high level of accuracy, therefore a large warhead is not required.
 W
WSea Dart or GWS30 was a Royal Navy surface-to-air missile system designed in the 1960s and entering service in 1973. It was fitted to the Type 42 destroyers, Type 82 destroyer and Invincible-class aircraft carriers of the Royal Navy. Originally developed by Hawker Siddeley, the missile was built by British Aerospace after 1977. It was withdrawn from service in 2012.
 W
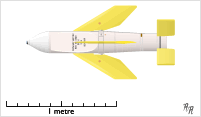
WSea Wolf is a naval surface-to-air missile system designed and built by BAC, later to become British Aerospace (BAe) Dynamics, and now MBDA. It is an automated point-defence weapon system designed as a short-range defence against both sea-skimming and high angle anti-ship missiles and aircraft. The Royal Navy has fielded two versions, the GWS-25 Conventionally Launched Sea Wolf (CLSW) and the GWS-26 Vertically Launched Sea Wolf (VLSW) forms. In Royal Navy service Sea Wolf is being replaced by Sea Ceptor.
 W
WSeacat was a British short-range surface-to-air missile system intended to replace the ubiquitous Bofors 40 mm gun aboard warships of all sizes. It was the world's first operational shipboard point-defence missile system, and was designed so that the Bofors guns could be replaced with minimum modification to the recipient vessel and (originally) using existing fire-control systems. A mobile land-based version of the system was known as Tigercat.
 W
WSeaslug was a first-generation surface-to-air missile designed by Armstrong Whitworth for use by the Royal Navy. Tracing its history as far back as 1943's LOPGAP design, it came into operational service in 1961 and was still in use at the time of the Falklands War in 1982.
 W
WSeacat was a British short-range surface-to-air missile system intended to replace the ubiquitous Bofors 40 mm gun aboard warships of all sizes. It was the world's first operational shipboard point-defence missile system, and was designed so that the Bofors guns could be replaced with minimum modification to the recipient vessel and (originally) using existing fire-control systems. A mobile land-based version of the system was known as Tigercat.
 W
WStarburst is a British man-portable surface-to-air missile produced by Shorts Missile Systems of Belfast. It was used by the British Army, Malaysian Armed Forces, and in the Canadian Army as the Javelin until 2005. It can be fired from the shoulder or from a launcher known as Starburst LML – Lightweight Multiple Launcher.
 W
WStarstreak is a British short range man-portable air-defence system (MANPADS) manufactured by Thales Air Defence, in Belfast. It is also known as Starstreak HVM. After launch, the missile accelerates to more than Mach 4, making it the fastest short-range surface-to-air missile in the world. It then launches three laser beam riding submunitions, increasing the likelihood of a successful hit on the target. Starstreak has been in service with the British Army since 1997. In 2012, Thales rebranded the system under the ForceSHIELD banner.
 W
WThe English Electric Thunderbird was a British surface-to-air missile produced for the British Army. Thunderbird was primarily intended to attack higher altitude targets at ranges up to approximately 30 miles (48 km), providing wide-area air defence for the Army in the field. AA guns were still used for lower altitude threats. Thunderbird entered service in 1959 and underwent a major mid-life upgrade to Thunderbird 2 in 1966, before being slowly phased out by 1977. Ex-Army Thunderbirds were also operated by the Royal Saudi Air Force after 1967.
 W
WViolet Friend was the Ministry of Supply rainbow code for an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system developed in the United Kingdom. The project began in 1954 with study contracts for an early warning radar system, which was followed by the February 1955 release of Air Staff Target 1135 (AST.1135) calling for a system to counter intermediate range ballistic missiles (IRBMs) being fired at the UK from eastern Europe. AST.1135 required the system to be able to attack six targets at once and be ready for initial deployment in 1963.