 W
WAt the outbreak of the American Civil War in April 1861, Kansas was the newest U.S. state, admitted just months earlier in January. The state had formally rejected slavery by popular vote and vowed to fight on the side of the Union, though ideological divisions with neighboring Missouri, a slave state, had led to violent conflict in previous years and persisted for the duration of the war.
 W
WBleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the legality of slavery in the proposed state of Kansas.
 W
WBushwhacking was a form of guerrilla warfare common during the American Revolutionary War, War of 1812, American Civil War and other conflicts in which there were large areas of contested land and few governmental resources to control these tracts. This was particularly prevalent in rural areas during the Civil War where there were sharp divisions between those favoring the Union and Confederacy in the conflict. The perpetrators of the attacks were called bushwhackers. The term "bushwhacking" is still in use today to describe ambushes done with the aim of attrition.
 W
WRichard Cordley was a Protestant minister and abolitionist associated with the Jayhawkers of Kansas. Known primarily as the pastor of Plymouth Congregational Church in Lawrence, Kansas in the 19th and early 20th century, Cordley was an early settler of Lawrence and a survivor of both the Sacking of Lawrence and the Lawrence Massacre in 1863. Cordley wrote about the history of Lawrence and the state of Kansas later in his lifetime and was also the recipient of the first degree awarded by the University of Kansas.
 W
WFort Leavenworth is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, roughly 20 miles northwest of Kansas City. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., and the oldest permanent settlement in Kansas. Fort Leavenworth has been historically known as the "Intellectual Center of the Army."
 W
WFort Scott National Cemetery is a United States National Cemetery located in Fort Scott, in Bourbon County, Kansas. Administered by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, it encompasses 21.8 acres (8.8 ha), and as of 2021, had more than 8,000 interments. It is one of three national cemeteries in Kansas.
 W
WFort Scott National Historic Site is a historical area under the control of the United States National Park Service in Bourbon County, Kansas, United States. Named after General Winfield Scott, who achieved renown during the Mexican–American War, during the middle of the 19th century the fort served as a military base for US Army action in what was the edge of settlement in 1850. For the next quarter century, it was used as a supply base and to provide security in turbulent areas during the opening of the West to settlement, a period which included Bleeding Kansas and the American Civil War.
 W
WGeneral Order No. 11 is the title of a Union Army directive issued during the American Civil War on August 25, 1863, forcing the evacuation of rural areas in four counties in western Missouri. The order, issued by Union General Thomas Ewing, Jr., affected all rural residents regardless of their allegiance. Those who could prove their loyalty to the Union were permitted to stay in the affected area, but had to leave their farms and move to communities near military outposts. Those who could not do so had to vacate the area altogether.
 W
WJayhawkers and red legs are terms that came to prominence in Kansas Territory, during the Bleeding Kansas period of the 1850s; they were adopted by militant bands affiliated with the free-state cause during the American Civil War. These gangs were guerrillas who often clashed with pro-slavery groups from Missouri, known at the time in Kansas Territory as "Border Ruffians" or "Bushwhackers." After the Civil War, the word "Jayhawker" became synonymous with the people of Kansas, or anybody born in Kansas. Today a modified version of the term, Jayhawk, is used as a nickname for a native-born Kansan, but more typically for a student, fan, or alumnus of the University of Kansas.
 W
WList of military units raised by the state of Kansas during the American Civil War (1861–1865).
 W
WMount Oread is a hill in Lawrence, Kansas upon which the University of Kansas, and parts of the city of Lawrence, Kansas is located. It sits on the water divide between the Kansas River and the Wakarusa River rivers. It was named after the long defunct Oread Institute in Worcester, Massachusetts, where many of the settlers of Lawrence moved from prior to the American Civil War. The hill was originally called Hogback Ridge by many Lawrence residents until the Oread name was adopted in 1864, two years after the university was founded.
 W
WThe Osage Battalion was a Native American unit of the Confederate States Army. Recruited from among the Osage tribe, whose loyalties were split between the Union and Confederacy, it did not meet its 500-man establishment. From early 1863 a four-company battalion of 200 men served under Brigadier General Douglas H. Cooper in the Trans-Mississippi Department. In 1864 the unit was transferred to the First Indian Brigade under Native American Brigadier General Stand Watie and fought under his command at the Second Battle of Cabin Creek on September 19, 1864. The battalion surrendered to Union forces on June 23, 1865, one of the last Confederate units to lay down its arms.
 W
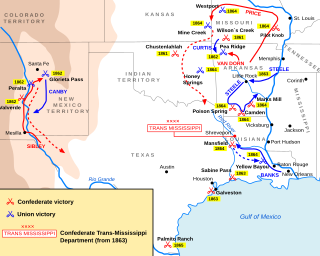
WPrice's Missouri Expedition, also known as Price's Raid or Price's Missouri Raid, was an unsuccessful Confederate cavalry raid through Arkansas, Missouri, and Kansas in the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. Led by Confederate Major-General Sterling Price, the campaign's intention was to recapture Missouri and renew the Confederate initiative in the larger conflict.
 W
WQuantrill's Raiders were the best-known of the pro-Confederate partisan guerrillas who fought in the American Civil War. Their leader was William Quantrill and they included Jesse James and his brother Frank.
 W
WRide with the Devil is a 1999 American revisionist Western film directed by Ang Lee, and starring Tobey Maguire, Skeet Ulrich, Jeffrey Wright, and Jewel in her feature film debut. Based on the novel Woe to Live On, by Daniel Woodrell, the film, set during the American Civil War, follows a group of men who join the First Missouri Irregulars, also known as the Bushwhackers—guerrilla units loyal to pro-Confederacy units of the state—and their attempt to disrupt and marginalize the political activities of Northern Jayhawkers allied with Union soldiers. Simon Baker, Jonathan Rhys Meyers, Jonathan Brandis, Jim Caviezel, Mark Ruffalo, and Celia Weston are featured in supporting performances.
 W
WThe Texas Road, also known as the Shawnee Trail, Sedalia Trail, or Kansas Trail, was a major trade and emigrant route to Texas across Indian Territory. Established during the Mexican War by emigrants rushing to Texas, it remained an important route across Indian Territory until Oklahoma statehood. The Shawnee Trail was the earliest and easternmost route by which Texas Longhorn cattle were taken to the north. It played a significant role in the history of Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, and Kansas in the early and mid-1800s.
 W
WThe Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War consists of the major military operations west of the Mississippi River. The area is often thought of as excluding the states and territories bordering the Pacific Ocean, which formed the Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War (1861–1865).