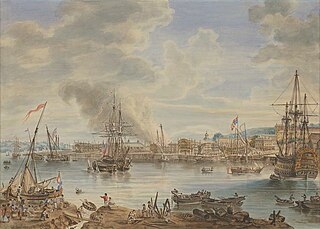 W
WChatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham.
 W
WThe Defence Fire Training and Development Centre was the site of the Ministry of Defence's firefighter training. It occupied part of a former Royal Air Force base near the village of Manston in the southeast corner of England. The remainder of the former RAF Manston was part of Kent International Airport, a civilian airfield, until the site was closed on the 15 May 2014.
 W
WThe Dover Barrage was an underwater blockade of German submarines attempting to use the English Channel during World War I. The barrier consisted of minefields laid between Belgium and Dover at the outbreak of war, followed in February 1915 by steel netting anchored to the sea bed. The first stage of the barrage was completed in April 1915 and it was patrolled by ships of the Dover patrol.
 W
WThe Dover Patrol and later known as the Dover Patrol Force was a Royal Navy command of the First World War, notable for its involvement in the Zeebrugge Raid on 22 April 1918. The Dover Patrol formed a discrete unit of the Royal Navy based at Dover and Dunkirk for the duration of the First World War. Its primary task was to prevent enemy German shipping—chiefly submarines—from entering the English Channel en route to the Atlantic Ocean, thereby obliging the Imperial German Navy to travel via the much longer route around Scotland which was itself covered by the Northern Patrol.
 W
WThe Dover Strait coastal guns were long-range coastal artillery batteries that were sited on both sides of the English Channel during the Second World War. The British built several gun position along the coast of Kent, England while the Germans fortified the Pas-de-Calais in occupied France. The Strait of Dover was strategically important because it is the narrowest part of the English channel. Batteries on both sides attacked shipping as well as bombarding the coastal towns and military installations. The German fortifications would be incorporated into the Atlantic Wall which was built between 1942 and 1944.
 W
WFan Bay Deep Shelter is a series of tunnels constructed during World War II as accommodation for Fan Bay Battery artillery battery, 23 metres down in the White Cliffs of Dover at Fan Bay near the Port of Dover. The tunnels and gun battery were built by the Royal Engineers between 20 November 1940 and 28 February 1941. The site is maintained by the National Trust.
 W
WFaversham, in Kent, England, has claims to be the cradle of the UK's explosives industry: it was also to become one of its main centres. The first gunpowder plant in the UK was established in the 16th century, possibly at the instigation of the abbey at Faversham. With their estates and endowments, monasteries were keen to invest in promising technology.
 W
WThe Governor of Rochester Castle commanded the important castle at Rochester in Kent, England which dominated the Medway estuary and Watling Street. After being badly damaged during the Barons' Wars the castle was completely renovated by King Henry III and put under the control of a series of Governors responsible for its upkeep and security.
 W
WThe Battle of Graveney Marsh, on the night of 27 September 1940 in Kent, England, was the last ground engagement involving a foreign force to take place on the mainland of Great Britain. The fighting took place between the crew of a shot-down German Junkers Ju 88A-1 bomber from KG 77 and a detachment of soldiers from the 1st Battalion, London Irish Rifles (1 LIR) in Seasalter on the north Kent coast. The Ju 88, W.Nr 088 8099, 3Z+EL, and nicknamed Eule ("Owl") by its crew, was a new model and had only entered service two weeks earlier. The British forces were aware of the new model, and had issued orders to capture one intact if at all possible. It was crewed by Unteroffizier (Uffz) Fritz Ruhlandt (pilot), Feldwebel Gotthard Richter ; Uffz Erwin Richter ; and Flieger (Private) Jakob Reiner (gunner).
 W
WThe history of Folkestone stretches back to prehistoric times, with evidence of human habitation dating to the Mesolithic and Paleolithic ages over 12,000 years ago. Its close proximity to the Continent means that it has often been a point of transit for migrating people groups. The area has alternatively been occupied by groups of Britons, Romans and Saxons. During the Iron Age, a large oppidum and quern-stone workshop were situated on the eastern headlands of the bay. By the Roman era, it had been transformed into a large Roman Villa overlooking the sea.
 W
WHMS Kent is a Type 23 Duke class frigate of the Royal Navy, and the twelfth ship to bear the name, although technically she is named after the dukedom rather than the county. Sponsored by Princess Alexandra, The Hon. Lady Ogilvy, Kent was launched on 28 May 1998 and commissioned on 8 June 2000. She was the first ship to enter Royal Navy service in the 21st Century.
 W
WThe Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of Allied soldiers during World War II from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the north of France, between 26 May and 4 June 1940. The operation commenced after large numbers of Belgian, British, and French troops were cut off and surrounded by German troops during the six-week Battle of France. In a speech to the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this "a colossal military disaster", saying "the whole root and core and brain of the British Army" had been stranded at Dunkirk and seemed about to perish or be captured. In his "We shall fight on the beaches" speech on 4 June, he hailed their rescue as a "miracle of deliverance".
 W
WThe Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment Cenotaph is a First World War memorial dedicated to members of the Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment and located in Maidstone in Kent, south-eastern England. Unveiled in 1921, the memorial was designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens following his design for the Cenotaph on Whitehall in London and is today a grade II* listed building.
 W
WRolvenden War Memorial is a First World War memorial in the village of Rolvenden, Kent, in south-eastern England. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, the memorial was unveiled in 1922 and is today a grade II listed building.
 W
WSandhurst War Memorial is a First World War memorial in the village of Sandhurst in Kent, south-eastern England, close to the border with East Sussex. The memorial is one of fifteen War Crosses by Sir Edwin Lutyens and arguably the one with the most elaborate setting. It was unveiled in 1923 and is today a grade II listed building.
 W
WSheerness Dockyard also known as the Sheerness Station was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the Sheerness peninsula, at the mouth of the River Medway in Kent. It was opened in the 1660s and closed in 1960.
 W
WShorncliffe Redoubt is a British Napoleonic earthwork fort. The site is approximately 300 feet by 300 feet and is situated on the Kentish Coast in Sandgate, Kent.