 W
WThe Aggregat series was a set of ballistic missile designs developed in 1933–45 by a research program of Nazi Germany's Armed Forces (Wehrmacht). Its greatest success was the A4, more commonly known as the V-2.
 W
WThe Angara rocket family is a family of space-launch vehicles being developed by the Moscow-based Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. The rockets are to put between 3,800 and 24,500 kg into low Earth orbit and are intended, along with Soyuz-2 variants, to replace several existing launch vehicles.
 W
WAntares, known during early development as Taurus II, is an expendable launch system developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation and the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau to launch the Cygnus spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of NASA's COTS and CRS programs. Able to launch payloads heavier than 8,000 kg (18,000 lb) into low-Earth orbit, Antares is currently the largest rocket operated by Northrop Grumman. Antares launches from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport and made its inaugural flight on April 21, 2013.
 W
WAriane is a series of a European civilian expendable launch vehicles for space launch use. The name comes from the French spelling of the mythological character Ariadne. France first proposed the Ariane project and it was officially agreed upon at the end of 1973 after discussions between France, Germany and the UK. The project was Western Europe's second attempt to develop its own launcher following the unsuccessful Europa project. The Ariane project was code-named L3S.
 W
WAtlas is a family of US missiles and space launch vehicles that originated with the SM-65 Atlas. The Atlas intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) program was initiated in the late 1950s under the Convair Division of General Dynamics. Atlas was a liquid propellant rocket burning RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen in three engines configured in an unusual "stage-and-a-half" or "parallel staging" design: two outboard booster engines were jettisoned along with supporting structures during ascent, while the center sustainer engine, propellant tanks and other structural elements remained connected through propellant depletion and engine shutdown.
 W
WDelta is an American versatile family of expendable launch systems that has provided space launch capability in the United States since 1960. More than 300 Delta rockets have been launched with a 95% success rate. Only the Delta IV Heavy rocket remains in use as of November 2020. Delta rockets are currently manufactured and launched by the United Launch Alliance.
 W
WLambda is the name of a series of Japanese carrier rockets. It consisted of the types Lambda 2, LS-A, LSC-3, Lambda 3, Lambda 4 and LS-C, developed jointly by Institute of Industrial Science of University of Tokyo, Institute of Space and Astronautical Science of Tokyo University, and Prince Motor Company, which merged with Nissan in 1966.
 W
WThe Minotaur is a family of United States solid fuel launch vehicles derived from converted Minuteman and Peacekeeper intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM). They are built by Northrop Grumman via contract with the Air Force Space and Missile Systems Center's Space Development and Test Directorate (SMC/SD) as part of the Air Force's Rocket Systems Launch Program which converts retired Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles into space and test launch systems for U.S. government agencies.
 W
WThe Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese solid-fueled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006. Originally developed by Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Mu rockets were later operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency following ISAS becoming part of it.
 W
WAndøya Space, formerly named Andøya Space Center and Andøya Rocket Range, is a rocket launch site, rocket range, and spaceport on Andøya island in Andøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. Since 1962, over 1,200 sounding and sub-orbital rockets of various configurations have been launched from the site.
 W
WProton is an expendable launch system used for both commercial and Russian government space launches. The first Proton rocket was launched in 1965. Modern versions of the launch system are still in use as of 2021, making it one of the most successful heavy boosters in the history of spaceflight. All Protons are built at the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center factory in Moscow and Chemical Automatics Design Bureau in Voronezh, transported to the Baikonur Cosmodrome, brought to the launch pad horizontally by rail, and raised into vertical position for launch.
 W
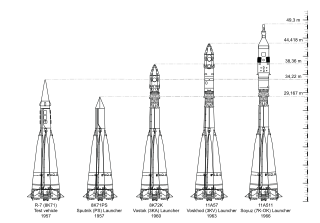
WThe R-7 family of rockets is a series of rockets, derived from the Soviet R-7 Semyorka, the world's first ICBM. More R-7 rockets have been launched than any other family of large rockets.
 W
WThe Saturn family of American rockets was developed by a team of mostly German rocket scientists led by Wernher von Braun to launch heavy payloads to Earth orbit and beyond. The Saturn family used liquid hydrogen as fuel in the upper stages. Originally proposed as a military satellite launcher, they were adopted as the launch vehicles for the Apollo Moon program. Three versions were built and flown: the medium-lift Saturn I, the heavy-lift Saturn IB, and the super heavy-lift Saturn V.
 W
WThe Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages. It was also the only vehicle of that type until the successful launch of the Japanese Lambda 4S in 1970.
 W
WThor was a US space launch vehicle derived from the PGM-17 Thor intermediate-range ballistic missile. The Thor rocket was the first member of the Delta rocket family of space launch vehicles. The last launch of a direct derivative of the Thor missile occurred in 2018 as the first stage of the final Delta II.
 W
WTitan was a family of United States expendable rockets used between 1959 and 2005. The Titan I and Titan II were part of the US Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile fleet until 1987. The space launch vehicle versions contributed the majority of the 368 Titan launches, including all the Project Gemini crewed flights of the mid-1960s. Titan vehicles were also used to lift US military payloads as well as civilian agency reconnaissance satellites and to send interplanetary scientific probes throughout the Solar System.
 W
WZenit is a family of space launch vehicles designed by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau in Dnipro, Ukraine, which was then part of the Soviet Union. Zenit was originally built in the 1980s for two purposes: as a liquid rocket booster for the Energia rocket and, equipped with a second stage, as a stand-alone middle-weight launcher with a payload greater than the 7 tonnes of the Soyuz but smaller than the 20 tonnes payload of the Proton. The last rocket family developed in the USSR, the Zenit was intended as an eventual replacement for the dated Soyuz and Proton families, and it would employ propellants which were safer and less toxic than the Proton's nitrogen tetroxide/UDMH mix. Zenit was planned to take over crewed spaceship launches from Soyuz, but these plans were abandoned after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.