 W
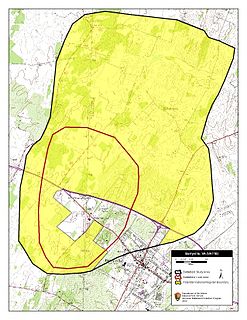
WThe Battle of Berryville was fought September 3 and September 4, 1864, in Clarke County, Virginia. It took place toward the end of the American Civil War.
 W
WThe Battle of Cedar Creek, or Battle of Belle Grove, fought October 19, 1864, was the culminating battle of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 during the American Civil War. Confederate Lt. Gen. Jubal Early launched a surprise attack against the encamped army of Union Maj. Gen. Philip Sheridan, across Cedar Creek, northeast of Strasburg, Virginia. During the morning fighting, seven Union infantry divisions were forced to fall back and lost numerous prisoners and cannons. Early failed to continue his attack north of Middletown, and Sheridan, dramatically riding to the battlefield from Winchester, was able to rally his troops to hold a new defensive line. A Union counterattack that afternoon routed Early's army.
 W
WThe Battle of Cool Spring, also known as Castleman's Ferry, Island Ford, Parker's Ford, and Snicker's Ferry, was a battle in the American Civil War fought July 17–18, 1864, in Clarke County, Virginia, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864. The battle was a Confederate victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Fisher's Hill was fought September 21–22, 1864, near Strasburg, Virginia, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 during the American Civil War. Despite its strong defensive position, the Confederate army of Lt. Gen. Jubal Early was defeated by the Union Army of the Shenandoah, commanded by Maj. Gen. Philip Sheridan.
 W
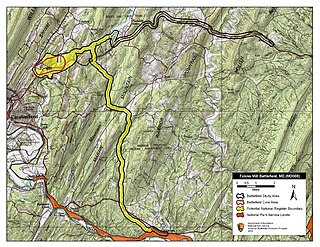
WThe Battle of Folck's Mill, also known as the Battle of Cumberland, was a small cavalry engagement, fought August 1, 1864, in northern Maryland, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 during the American Civil War.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Stevens was an American Civil War battle fought July 11–12, 1864 in what is now Northwest Washington, DC, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 between forces under Confederate Lieutenant General Jubal Early and Union Major General Alexander McDowell McCook. Although Early caused consternation in the Union government, reinforcements under Maj. Gen. Horatio G. Wright and the strong defenses of Fort Stevens minimized the military threat, and Early withdrew after two days of skirmishing and had attempted no serious assaults. The battle is noted for stories that US President Abraham Lincoln observed the fighting.
 W
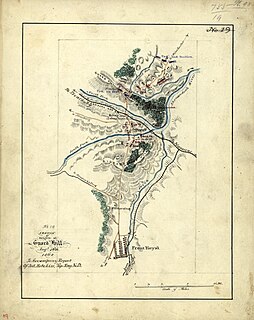
WThe Battle of Guard Hill, Battle of Crooked Run, or the Battle of Front Royal took place on August 16, 1864, in Warren County, Virginia as part of Philip H. Sheridan's Shenandoah Valley Campaign of the American Civil War. According to Pachan, the Union's superior numbers and quality leadership routed the Confederate infantry, and the battle proved a watershed event in the Shenandoah Valley campaign.
 W
WHeaton's Crossroads, also known as the Purcellville Wagon Raid, was an American Civil War skirmish that took place between Federal cavalry under Brig. Gen. Alfred N. Duffié and Confederate infantry under Maj. Gen. John C. Breckinridge on July 16, 1864, near present-day Purcellville, Virginia in Loudoun County as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864. The action was tactically inconclusive.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Kernstown was fought on July 24, 1864, at Kernstown, Virginia, outside Winchester, Virginia, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 in the American Civil War. The Confederate Army of the Valley under Lt. Gen. Jubal A. Early soundly defeated the Union Army of West Virginia under Brig. Gen. George Crook and drove it from the Shenandoah Valley back over the Potomac River into Maryland. As a result, Early was able to launch the Confederacy's last major raid into northern Union territory, attacking the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in Maryland and West Virginia and burning Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, in retaliation for the burning of civilian houses and farms earlier in the campaign.
 W
WMilford Battlefield is situated in Overall, Virginia in Warren County and Page County, Virginia. It was the site of a battle on September 22–24 during the Valley campaigns of 1864 in the American Civil War. The site is located on property now privately owned.
 W
WThe Battle of Monocacy was fought on July 9, 1864, approximately 6 miles (9.7 km) from Frederick, Maryland, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 during the American Civil War. Confederate forces under Lt. Gen. Jubal A. Early defeated Union forces under Maj. Gen. Lew Wallace. The battle was part of Early's raid through the Shenandoah Valley and into Maryland in an attempt to divert Union forces away from Gen. Robert E. Lee's army under siege at Petersburg, Virginia. The battle was the northernmost Confederate victory of the war. While the Union troops retreated to Baltimore, Maryland, the Confederates continued toward Washington, D.C., but the battle at Monocacy delayed Early's march for a day, allowing time for Union reinforcements to arrive in the Union capital. The Confederates launched an attack on Washington on July 12 at the Battle of Fort Stevens, but were unsuccessful and retreated to Virginia.
 W
WThe Battle of Moorefield was a cavalry battle in the American Civil War, which took place on August 7, 1864. The fighting occurred along the South Branch of the Potomac River, north of Moorefield, West Virginia, in Hardy County. The National Park Service groups this battle with Early's Washington Raid and operations against the B&O Railroad, and it was the last major battle in the region before General Philip Sheridan took command of Union troops in the Shenandoah Valley. This Union triumph was the third of three major victories for Brigadier General William W. Averell, who performed best when operating on his own.
 W
WThe Battle of New Market was fought on May 15, 1864, in Virginia during the Valley Campaigns of 1864 in the American Civil War. A makeshift Confederate army of 4,100 men, which included cadets from the Virginia Military Institute (VMI), defeated Union Major General Franz Sigel and his Army of the Shenandoah. The cadets were integral to the Confederate victory at New Market and this event marks the only time in U.S. history wherein the student body of a functioning and operating college fought as an organized unit in pitched combat in battle. This event and battle was the 14th time VMI cadets were called into action during the Civil War. As a result of this defeat, Sigel was relieved of his command and replaced by Maj. Gen. David Hunter, who later burned VMI in retaliation for New Market.
 W
WThe Battle of Piedmont was fought June 5, 1864, in the village of Piedmont, Augusta County, Virginia. Union Maj. Gen. David Hunter engaged Confederates under Brig. Gen. William E. "Grumble" Jones north of Piedmont. After severe fighting, Jones was killed and the Confederates were routed. Hunter occupied Staunton on June 6 and soon began to advance on Lynchburg, destroying military stores and public property in his wake.
 W
WThe Battle of Rutherford's Farm, also known as Carter's Farm and Stephenson's Depot, was a small engagement between Confederate forces under Maj. Gen. Stephen D. Ramseur and Union forces under Brig. Gen. William W. Averell on July 20, 1864, in Frederick County, Virginia, during the American Civil War, as part of Confederate Lt. Gen. Jubal Early's Valley Campaign, resulting in a Union victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Summit Point, also known as Flowing Springs or Cameron's Depot, was an inconclusive battle of the American Civil War fought on August 21, 1864, near Summit Point, West Virginia.
 W
WThe Third Battle of Winchester, also known as the Battle of Opequon or Battle of Opequon Creek, was an American Civil War battle fought near Winchester, Virginia, on September 19, 1864. Union Army Major General Philip Sheridan defeated Confederate Army Lieutenant General Jubal Early in one of the largest, bloodiest, and most important battles in the Shenandoah Valley. Among the 5,000 Union casualties were one general killed and three wounded. The casualty rate for the Confederates was high: about 4,000 of 15,500. Two Confederate generals were killed and four were wounded. Participants in the battle included two future presidents of the United States, two future governors of Virginia, a former vice president of the United States, and a colonel whose grandson became a famous general in World War II.