 W
WA rotary cannon, rotary autocannon, rotary gun or Gatling cannon, is any large-caliber multiple-barreled automatic firearm that uses in a Gatling-type rotating barrel assembly to deliver a sustained saturational direct fire at much greater rates of fire than single-barreled autocannons of the same caliber. The loading, firing and ejection functions are performed simultaneously in different barrels as the whole assembly rotates, and the rotation also permits the barrels some time to cool. The rotating barrels on nearly all modern Gatling-type guns are powered by an external force such as an electric motor, although internally powered gas-operated versions have also been developed.
 W
WThe AK-630 is a Soviet and Russian fully automatic naval close-in weapon system based on a six-barreled 30 mm rotary cannon. In "630", "6" means 6 barrels and "30" means 30 mm. It is mounted in an enclosed automatic turret and directed by MR-123 radar and television detection and tracking. The system's primary purpose is defense against anti-ship missiles and other precision guided weapons. However it can also be employed against fixed or rotary wing aircraft, ships and other small craft, coastal targets, and floating mines. Once operational, this weapon system was rapidly adopted, with up to 8 units installed in every new Soviet warship, and hundreds produced in total.
 W
WThe flaming onion was a 37 mm Hotchkiss revolving-barrel anti-aircraft gun used by the German army at the beginning of World War I, the name referring to both the gun, and especially the flare or tracer ammunition it fired. The American "balloon-buster" ace, Frank Luke, was a prominent victim of later versions of this device, and it was mentioned in Eddie Rickenbacker's book Fighting the Flying Circus and in many "Biggles" stories. Later in the war the term was also applied to any sort of anti-aircraft fire that used a visible tracer, appearing in reports of combat from the Battle of Taranto, for instance.
 W
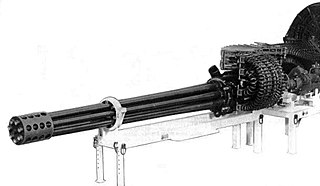
WThe Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
 W
WThe General Electric GAU-8/A Avenger is a 30 mm hydraulically driven seven-barrel Gatling-style autocannon that is typically mounted in the United States Air Force's Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II. Designed specifically for the anti-tank role, the Avenger delivers very powerful rounds at a high rate of fire. The GAU-8/A is also used in the Goalkeeper CIWS ship weapon system, which provides defense against short-range threats such as highly maneuverable missiles, aircraft, and fast maneuvering surface vessels. The GAU-8/A is currently produced by General Dynamics.
 W
WThe General Electric GAU-13/A is a 30 mm electric Gatling-type rotary cannon derived from the GAU-8 Avenger cannon.
 W
WGoalkeeper is a Dutch close-in weapon system (CIWS) introduced in 1979. It is an autonomous and completely automatic weapon system for short-range defence of ships against highly manoeuvrable missiles, aircraft and fast-manoeuvering surface vessels. Once activated the system automatically undertakes the entire air defence process from surveillance and detection to destruction, including the selection of the next priority target.
 W
WThe Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-23 is a six-barreled 23 mm rotary cannon used by some modern Soviet/Russian military aircraft.
 W
WThe Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-30 is a Russian 30 mm rotary cannon aircraft-mounted and naval autocannon used by Soviet and later CIS military aircraft. The GSh-6-30 fires a 30×165mm, 390 g projectile.
 W
WThe Glagolev-Shipunov-Gryazev GShG-7.62 is a four-barreled rotary machine gun designed in the Soviet Union, similar to firearms such as the M134 Minigun. It is a gas operated, self-powered weapon, which is in contrast with most other rotary guns. It was developed in 1968–1970 for the Mi-24 helicopter together with YakB 12.7mm machine gun, and is currently used in GUV-8700 gun pods, and flexible mounts on Kamov Ka-29.
 W
WThe Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch (42 mm) light mountain gun; there were also a navy (47 mm) and a 3-inch (76 mm) Hotchkiss guns. The 42 mm gun was intended to be mounted on a light carriage or packed on two mules to accompany a troop of cavalry or an army travelling in rough country.
 W
WThe Kortik close-in weapon system (CIWS) is a modern naval air defence gun-missile system deployed by the Russian Navy. Its export version is known as Kashtan, with the NATO designation CADS-N-1 Kashtan.
 W
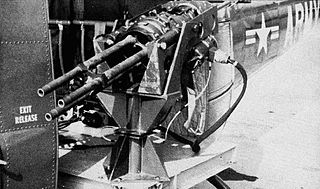
WThe M61 Vulcan is a hydraulically, electrically or pneumatically driven, six-barrel, air-cooled, electrically fired Gatling-style rotary cannon which fires 20 mm rounds at an extremely high rate. The M61 and its derivatives have been the principal cannon armament of United States military fixed-wing aircraft for sixty years.
 W
WThe M197 electric cannon is a 20 mm three-barreled electric Gatling-type rotary cannon used by the United States military.
 W
WPantsir-M is a Russian jamming-resistant naval close-in weapon system (CIWS) which entered service in 2018. Pantsir-M is equipped with friend or foe identification system and armed with naval version of the Pantsir's 57E6 missiles and Hermes-K missiles. Its secondary armament are two six-barreled 30×165mm GSh-6-30K/AO-18KD rotary cannons. Same as on Kashtan-M. Pantsir-M is fully automated and can engage up to four targets simultaneously at a range of up to 20 km and can operate as a battery of up to four modules. Pantsir-M can intercept sea skimming missiles flying as low as two meters above the surface. If a target isn't sufficiently destroyed by Pantsir's missile attack it can automatically direct its cannons against it. Pantsir-M's phased array radar, electro-optical/infrared targeting and identification system are based on that of Pantsir's 1RS2-1.
 W
WThe Phalanx CIWS is a close-in weapon system for defense against incoming threats such as small boats, surface torpedoes, anti-ship missiles and helicopters. It was designed and manufactured by the General Dynamics Corporation, Pomona Division, later a part of Raytheon. Consisting of a radar-guided 20 mm (0.8 in) Vulcan cannon mounted on a swiveling base, the Phalanx has been used by the United States Navy and the naval forces of 15 other countries. The US Navy deploys it on every class of surface combat ship, except the Zumwalt-class destroyer and San Antonio-class amphibious transport dock. Other users include the British Royal Navy, the Royal Australian Navy, the Royal Canadian Navy and the US Coast Guard .
 W
WThe T249 Vigilante was a prototype 37 mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) designed as a replacement for the Bofors 40 mm gun and M42 Duster in US Army service. The system consisted of a 37 mm T250 six-barrel Gatling gun mounted on a lengthened M113 armored personnel carrier platform.
 W
WThe Type 730 is a Chinese seven-barrelled 30 mm Gatling gun CIWS. It has a PLA Navy designation H/PJ12. It is mounted in an enclosed automatic turret and directed by radar, and electro-optical tracking systems. The maximum rate of fire is 5800 rd/m, and the effective range is up to 3 km.