 W
WThe siege of Bellegarde commenced on 23 May 1793 and ended on 24 June 1793 when Colonel Boisbrulé's French garrison surrendered the Fort de Bellegarde to a Spanish army under the command of Antonio Ricardos. The capture of the fort gave Spain control of an important road through the Pyrenees. The siege took place during the War of the Pyrenees, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Fort de Bellegarde is on a height overlooking the border town of Le Perthus, which lies on the modern A9 autoroute and Autovía A-7.
 W
WThe Siege of Breda took place from 21 to 27 February 1793 in the course of the Flanders Campaign during the War of the First Coalition.
 W
WThe Siege of Collioure saw a Republican French army led by Jacques François Dugommier invest a French port held by a Spanish garrison commanded by Eugenio Navarro. The actual siege work was carried out by Pierre François Sauret's reinforced division. After the three-and-a-half-week War of the Pyrenees siege the Spanish fleet sent to evacuate the garrison was blown off station by a storm. Navarro surrendered the town on the promise to exchange the paroled garrison with an equal number of French prisoners. After the defenders were released, the Spanish army commander Luis Firmín de Carvajal, Conde de la Unión refused to authorize the agreement or return any French captives. The infuriated French government afterward passed a decree ordering death to all Spanish prisoners and some units carried out the brutal order.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort-Louis saw a force composed of Habsburg Austrians, Hessians and Bavarians led by Franz von Lauer lay siege to Fort-Louis which was held by a Republican French garrison under Michel Durand. The French capitulated after a defense lasting exactly one month. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. In 1793 the fortress was sited on an island in the Rhine River, but today Fort-Louis is a village in the Bas-Rhin department in France.
 W
WIn the Siege of Hüningen, the Austrians captured the city from the French. Hüningen is in the present-day Department of Haut-Rhin, France. Its fortress lay approximately 2.5 miles (4.0 km) north of the Swiss city of Basel and .5 miles (0.80 km) north of the spot where the present-day borders of Germany, France and Switzerland meet. During the time of this siege, the village was part of the Canton of Basel City and the fortress lay in area contested between the German states and the First French Republic.
 W
WThe siege of Kehl lasted from 26 October 1796 to 9 January 1797. Habsburg and Württemberg regulars numbering 40,000, under the command of Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour, besieged and captured the French-controlled fortifications at the village of Kehl in the German state of Baden-Durlach. The fortifications at Kehl represented important bridgehead crossing the Rhine to Strasbourg, an Alsatian city, a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition.
 W
WThe siege of Le Quesnoy saw a force made up of Habsburg Austrians and French Royalists led by François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt lay siege to a Republican French garrison commanded by François Goullus. After two and a half week siege, the French capitulated after suffering heavy losses. The War of the First Coalition operation was fought at Le Quesnoy, located near the border with Belgium about 27 kilometres (17 mi) west of Maubeuge.
 W
WThe Siege of Lille saw a Republican French garrison under Jean-Baptiste André Ruault de La Bonnerie hold Lille against an assault by a Habsburg army commanded by Duke Albert of Saxe-Teschen. Though the city was fiercely bombarded, the French successfully withstood the Austrian attack in the action. Because the Austrians were unable to completely encircle the city, the French were able to continuously send in reinforcements. After news of the French victory over the Prussians at Valmy, Albert withdrew his troops and siege cannons. The next battle was at Jemappes in November. The Column of the Goddess monument was completed in 1845 to commemorate the siege.
 W
WThe siege of Luxembourg was a siege by France of the Habsburg-held Fortress of Luxembourg that lasted from 1794 until 7 June 1795, during the French Revolutionary Wars. Although the French army failed to breach the walls of the city, which were renowned as amongst the best in the world, the fortress was forced to surrender after more than seven months.
 W
WThe Siege of Maastricht was a failed siege of the city of Maastricht by the forces of the French First Republic from 6 February to 2 March 1793, marking the final action of the 1793 campaign of the War of the First Coalition. The city was successfully defended by the Dutch garrison with the assistance of a small band of French Royalists.
 W
WThe siege of Mainz was a short engagement at the beginning of the War of the First Coalition. The victorious French army of Custine seized the town on October 21, 1792, after three days of siege. The French occupied Mainz, and tried to install the Republic of Mainz there.
 W
WIn the siege of Mainz, from 14 April to 23 July 1793, a coalition of Prussia, Austria, and other German states led by the Holy Roman Empire besieged and captured Mainz from revolutionary French forces. The allies, especially the Prussians, first tried negotiations, but this failed, and the bombardment of the city began on the night of 17 June.
 W
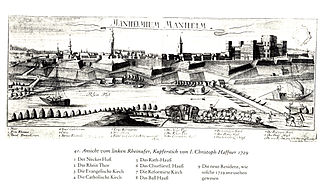
WThe action at Mannheim began in April 1795 when two French armies crossed the Rhine and converged on the confluence of the Main and the Rhine. Initial action at Mannheim resulted in a minor skirmish, but the Bavarian commander negotiated a quick truce with the French and withdrew. On 17 October 1795, 17,000 Habsburg Austrian troops under the command of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser engaged 12,000 soldiers, led by Jean-Charles Pichegru in the grounds outside the city of Mannheim. In a combination of maneuvers, the Habsburg army forced 10,000 of the French forces to withdraw into the city itself; other French troops fled to join neighboring Republican armies. First Coalition forces then laid siege to Mannheim. Subsequent action at neighboring cities forced the French to withdraw further westward toward France; after a month's siege, the 10,000-strong Republican French garrison now commanded by Anne Charles Basset Montaigu surrendered to 25,000 Austrians commanded by Wurmser. This surrender brought the 1795 campaign in Germany to an end. The battle and siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Situated on the Rhine River at its confluence with the Neckar River, Mannheim lies in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in modern-day Germany.
 W
WDuring the siege of Mantua, which lasted from 4 July 1796 to 2 February 1797 with a short break, French forces under the overall command of Napoleon Bonaparte besieged and blockaded a large Austrian garrison at Mantua for many months until it surrendered. This eventual surrender, together with the heavy losses incurred during four unsuccessful relief attempts, led indirectly to the Austrians suing for peace in 1797. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which is part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mantua, a city in the Lombardy region of Italy, lies on the Mincio River.
 W
WThe Siege of Nijmegen occurred from 27 October to 8 November 1794 during the Flanders campaign of the War of the First Coalition. It was the last major military confrontation between the forces of the Revolutionary French First Republic and the reactionary First Coalition of European monarchs including William V, Prince of Orange, before the fall of the Dutch Republic in January 1795, which William had ruled as hereditary stadtholder since 1751. As commander-in-chief of the Dutch States Army, his indecision, several changes of mind and lack of coordination with his Anglo-Hanoverian, Hessian, Prussian and Austrian allies contributed to the eventual surrender of Nijmegen to the French revolutionaries.
 W
WThe siege of Pondicherry was a colonial military operation in the early stages of the French Revolutionary Wars. Britain and France both controlled colonies on the Indian Subcontinent and when the French National Convention declared war on Britain on 1 February 1793, both sides were prepared for conflict in India. British India was centred on the principal ports of Bombay, Madras and Calcutta, administered by the East India Company. French India was governed from Pondicherry on the Coromandel Coast. British forces in India were considerably stronger than the French, with the British Indian Army supported by British Army detachments and a Royal Navy squadron under Rear-Admiral William Cornwallis. Pondicherry's defenses were strong, but the garrison was too small to effectively man the walls, and although a French frigate squadron was stationed at the distant Île de France, it was unable to effectively protect the French Indian coast.
 W
WThe siege of Valenciennes took place between 13 June and 28 July 1793, during the Flanders Campaign of the War of the First Coalition. The French garrison under Jean Henri Becays Ferrand was blockaded by part of the army of Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, commanded by the Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany. Valenciennes fell on 28 July, resulting in an Allied victory.
 W
WThe Siege of Ypres saw a Republican French army commanded by Jean-Charles Pichegru invest the fortress of Ypres and its 7,000-man garrison composed of Habsburg Austrians under Paul von Salis and Hessians led by Heinrich von Borcke and Georg von Lengerke. French troops under Joseph Souham fended off three relief attempts by the corps of François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt. Meanwhile, the French besiegers led by Jean Victor Marie Moreau compelled the Coalition defenders to surrender the city. The fighting occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the Wars of the French Revolution. In 1794 Ypres was part of the Austrian Netherlands, but today it is a municipality in Belgium, located about 120 kilometres (75 mi) west of Brussels.