 W
WThe Bastarnae and Peucini were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman frontier on the Lower Danube. The Bastarnae lived in the region between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dnieper, to the north and east of ancient Dacia. The Peucini occupied the region north of the Danube Delta.
 W
WThe Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi, a small but militarily powerful Germanic tribe that inhabited Batavia, on the delta of the river Rhine. They were soon joined by the Celtic tribes from Gallia Belgica and some Germanic tribes.
 W
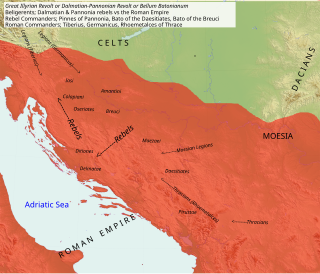
WThe Bellum Batonianum was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Romans. The rebellion began among native peoples who had been recruited as auxiliary troops for the Roman army. They were led by Bato the Daesitiate, a chieftain of the Daesitiatae in the central part of present-day Bosnia, and were later joined by the Breuci, a tribe in Pannonia led by Bato the Breucian. Many other tribes in Illyria also joined the revolt.
 W
WThe Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by the native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60-61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Roman failure to honor an agreement they had made with her husband, Prasutagus, regarding the succession of his kingdom upon his death. The revolt ended unsuccessfully, after a decisive Roman victory at the Defeat of Boudica.
 W
WThe Carpi or Carpiani were an ancient people that resided in the eastern parts of modern Romania in the historical region of Moldavia from no later than c. AD 140 and until at least AD 318.
 W
WThe First Roman–Dacian War took place from 101 to 102 AD. The Kingdom of Dacia, under King Decebalus, had become a threat to the Roman Empire, and defeated several of Rome's armies during Domitian's reign (81–96). The Emperor Trajan was set on ridding this threat to Rome's power and in 101 set out determined to defeat Dacia. After a year of heavy fighting, King Decebalus came to terms and accepted an unfavourable peace. When he broke these terms in 105, the Second Dacian War began.
 W
WThe German and Sarmatian campaigns of Constantine were fought by the Roman Emperor Constantine I against the neighbouring Germanic peoples, including the Franks, Alemanni and Goths, as well as the Sarmatian Iazyges, along the whole Roman northern defensive system to protect the empire's borders, between 306 and 336.
 W
WThe Great Conspiracy was a year-long state of war and disorder that occurred in Roman Britain near the end of the Roman rule of the island. The historian Ammianus Marcellinus described it as a barbarica conspiratio that capitalized on a depleted military force in the province brought about by Magnentius' losses at the Battle of Mursa Major in Pannonia, after his unsuccessful bid to become emperor.
 W
WThe Marcomannic Wars were a series of wars lasting from about 166 AD until 180. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts with several other Germanic, Sarmatian and Gothic peoples along both sides of the whole length of the Roman Empire's northeastern European border, the river Danube. The struggle against the Germans and Sarmatians occupied the major part of the reign of Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius, and it was during his campaigns against them that he started writing his philosophical work Meditations.
 W
WTrajan's Parthian campaign was engaged by Roman Emperor Trajan in 115 against the Parthian Empire in Mesopotamia. The war was initially successful for the Romans, but a series of setbacks, including wide-scale rebellions in the Eastern Mediterranean and North Africa and Trajan's death in 117, ended in a Roman withdrawal.
 W
WThe Parthian war of Caracalla was an unsuccessful campaign by the Roman Empire under Caracalla against the Parthian Empire in 216–17 AD. It was the climax of a four-year period, starting in 213, when Caracalla pursued a lengthy campaign in central and eastern Europe and the Near East. After intervening to overthrow rulers in client kingdoms adjoining Parthia, he invaded in 216 using an abortive wedding proposal to the Parthian king's daughter as a casus belli. His forces carried out a campaign of massacres in the northern regions of the Parthian Empire before withdrawing to Asia Minor, where he was assassinated in April 217. The war was ended the following year after Parthian victory at a battle at Nisibis, with the Romans paying a huge sum of war reparations to the Parthians.
 W
WThe Roman conquest of Britain was a process that consisted of the conquest of territory located on the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed by 87 when the Stanegate was established.
 W
WThe Roman invasion of Caledonia was launched in 208 by the Roman emperor Septimius Severus. The invasion lasted until late 210 when the emperor became ill and died at Eboracum (York) on 4 February 211. The war started well for the Romans with Severus managing to quickly reach the Antonine Wall, but when Severus pushed north into the highlands he became bogged down in a guerrilla war and he was never able to fully subjugate Caledonia. He reoccupied many forts built by Agricola over 100 years earlier, following the Battle of Mons Graupius, and crippled the ability of the Caledonians to raid Roman Britain.
 W
WThe Roman–Bosporan War was a lengthy war of succession that took place in the Cimmerian Bosporus, probably from 45 to 49. It was fought between the Roman client-king Tiberius Julius Cotys I and his allies King Eunones of the Aorsi and the Roman commander Gaius Julius Aquila against the former king Tiberius Julius Mithridates and his ally King Zorsines of the Siraces.
 W
WTacfarinas was a Numidian Berber deserter from the Roman army who led his own Musulamii tribe and a loose and changing coalition of other Berber tribes in a war against the Romans in North Africa during the rule of the emperor Tiberius. Though Tacfarinas' personal motivation is unknown, it is likely that the Roman occupation under Augustus of the traditional grazing grounds of the Musulamii was the determining factor.
 W
WThe Dacian Wars were two military campaigns fought between the Roman Empire and Dacia during Emperor Trajan's rule. The conflicts were triggered by the constant Dacian threat on the Danubian province of Moesia and also by the increasing need for resources of the economy of the Empire.
 W
WThe war between the kingdoms of Iberia and Armenia is known chiefly through its description in Tacitus' Annals.
 W
WThe wars of Augustus are the military campaigns undertaken by the Roman government during the sole rule of the founder-emperor Augustus. This was a period of 45 years when almost every year saw major campaigning, in some cases on a scale comparable to the Second Punic War, when Roman manpower resources were stretched to the limit. The result of these wars was a major expansion of the empire that Augustus inherited from the Roman Republic, although the attempted conquest of Germania ended in defeat despite the enormous deployment of resources involved. As a result of these campaigns, the Roman Empire assumed the borders it would hold, with a few modifications, for its entire history.