 W
WAkagi (赤城) was a steel-hulled, steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. She was the fourth and final vessel to be completed in the four-vessel Maya class and was named after Mount Akagi in Gunma Prefecture.
 W
WAmagi was a screw sloop in the early Imperial Japanese Navy, and was the third vessel built by the Yokosuka Naval Arsenal after its acquisition by the Meiji government. When built, Amagi was the largest warship yet produced domestically in Japan. Amagi was named after the Mount Amagi, in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan.
 W
WAtago (愛宕) was a composite hulled, steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. She was the third vessel to be completed in the four vessel Maya class, and was named after Mount Atago in Kyoto.
 W
WBanjō was a steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. The ship was named after a mountain in Shizuoka prefecture
 W
WChōkai (鳥海) was an iron-hulled, steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. She was the second vessel to be completed in the four vessel Maya class, and was named after Mount Chōkai in between Yamagata and Akita Prefectures.
 W
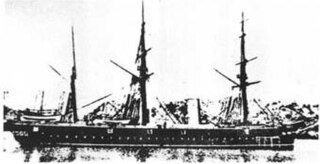
WHeien , originally known as Pingyuan, built by the Mawei Navy Yard near Foochow (Fuzhou), was an ironclad coastal battleship serving with the Imperial Chinese Beiyang Fleet and later the Imperial Japanese Navy. Previous transliterations of its Chinese name include Ping Yuen and Ping Yuan, also of its Japanese name Heiyen.
 W
WHiei was the second and last vessel of the Kongō-class ironclad corvettes built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the 1870s. They were built in the United Kingdom because the Japanese were unable to build ironclad warships in Japan. She became a training ship in 1887 and made training cruises to the Mediterranean and to countries on the edge of the Pacific Ocean. The ship returned to active duty during the First Sino-Japanese War of 1894–1895 where she was damaged during the Battle of the Yalu River. Hiei also participated in the Battle of Weihaiwei and the invasion of Formosa in 1895. The ship resumed her training duties after the war, although she played a minor role in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. She was reclassified as a survey ship in 1906 and was sold for scrap in 1912.
 W
WHōshō was a screw sloop, originally built in the United Kingdom for Chōshū Domain in western Japan, and subsequently served in the early Imperial Japanese Navy.
 W
WKaimon was a sail-and-steam corvette of the early Imperial Japanese Navy. Although the name Kaimon translates to "sea gate", the ship was named for Mount Kaimon, although written with different kanji, located in Kagoshima prefecture.
 W
WKatsuragi (葛城) was the lead ship in the Katsuragi class of three composite hulled, sail-and-steam corvettes of the early Imperial Japanese Navy. The ship was named for a mountain located between Osaka and Nara prefectures.
 W
WKongō was the lead ship of the Kongō-class ironclad corvettes built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the 1870s. The class was built in the United Kingdom because such ships could not yet be constructed in Japan. Completed in 1878, Kongō briefly served with the Small Standing Fleet before becoming a training ship in 1887, thereafter making training cruises to the Mediterranean and to countries on the edge of the Pacific Ocean. The ship returned to active duty during the First Sino-Japanese War of 1894–95 where she participated in the Battle of Weihaiwei. Kongō resumed her training duties after the war, though she also played a minor role in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05. The ship was reclassified as a survey ship in 1906 and was sold for scrap in 1910.
 W
WMaya (摩耶) was an iron-hulled, steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. She was the lead vessel in the four vessel Maya class, and was named after Mount Maya in Kobe.
 W
WMusashi (武蔵) was the third and final vessel in the Katsuragi class of composite hulled, sail-and-steam corvettes of the early Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named for Musashi province, a former province of Japan located in the Kantō region. The name was used again for the more famous World War II battleship Musashi.
 W
WŌshima (大島) was a steam gunboat, serving in the early Imperial Japanese Navy. She was named after the island of Ōshima off Shizuoka prefecture.
 W
WSaikyō Maru (西京丸) was a Japanese cargo and transport ship involved in the Battle of the Yalu River (1894) during the First Sino-Japanese War, carrying Viscount Admiral Kabayama Sukenori, and commanded by John Wilson.
 W
WTenryū was a sail-and-steam corvette of the early Imperial Japanese Navy. Tenryū was named after the Tenryū River in Shizuoka and Nagano Prefectures.
 W
WTsao Kiang was a 640-ton wooden gunboat, launched in 1869 by Jiangnan Shipyard, Shanghai, for the Nanyang Fleet. Acquired in 1872 for Zhili Province by Li Hongzhang the ship served with Beiyang Fleet as a governor's yacht.
 W
WTsukushi (筑紫) was an early unprotected cruiser, serving in the fledgling Imperial Japanese Navy. Its name is a traditional name for Kyūshū island. Its sister ships Chaoyong and Yangwei were acquired by the Chinese Beiyang Fleet.
 W
WYamato was the second vessel in the Katsuragi class of three composite hulled, sail-and-steam corvettes of the early Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named for Yamato province, the old name for Nara prefecture and the historic heartland of Japan. The name was used again for the World War II battleship Yamato, commissioned in 1941.