 W
WThe militarisation of space involves the placement and development of weaponry and military technology in outer space. The early exploration of space in the mid-20th century had, in part, a military motivation, as the United States and the Soviet Union used it as an opportunity to demonstrate ballistic-missile technology and other technologies having the potential for military application. Outer space has since been used as an operating location for military spacecraft such as imaging and communications satellites, and some ballistic missiles pass through outer space during their flight. As of 2019 known deployments of weapons stationed in space include only the Almaz space-station armament and pistols such as the TP-82 Cosmonaut survival pistol.
 W
WThe Almaz program was a highly secret Soviet military space station program, begun in the early 1960s.
 W
WAsteroid impact avoidance comprises the methods by which near-Earth objects (NEO) on a potential collision course with Earth could be diverted away, preventing destructive impact events. An impact by a sufficiently large asteroid or other NEOs would cause, depending on its impact location, massive tsunamis or multiple firestorms, and an impact winter caused by the sunlight-blocking effect of large quantities of pulverized rock dust and other debris placed into the stratosphere.
 W
WThe Ballistic Missile Defense Organization (BMDO) was an agency of the United States Department of Defense that began on 20 May 1974 with the responsibility for all U.S. ballistic missile defense efforts.
 W
WThe Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar was a United States Air Force (USAF) program to develop a spaceplane that could be used for a variety of military missions, including aerial reconnaissance, bombing, space rescue, satellite maintenance, and as a space interceptor to sabotage enemy satellites. The program ran from October 24, 1957, to December 10, 1963, cost US$660 million, and was cancelled just after spacecraft construction had begun.
 W
WBoost-glide trajectories are a class of spacecraft guidance and reentry trajectories that extend the range of suborbital spaceplanes and reentry vehicles by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. In most examples, boost-glide roughly doubles the range over the purely ballistic trajectory. In others, a series of skips allows range to be further extended, and leads to the alternate terms skip-glide and skip reentry.
 W
WProject Casaba-Howitzer was a 1960s-era study into the use of nuclear weapons as the drivers for intense beams of plasma for use in space warfare. The basic concept grew out of work on the Project Orion spaceship concept, which studied nuclear shaped charges.
 W
WThe Exoatmospheric Kill Vehicle (EKV) is the Raytheon-manufactured interceptor component with subcontractor Aerojet of the U.S. Ground-Based Midcourse Defense (GMD), part of the larger National Missile Defense system.
 W
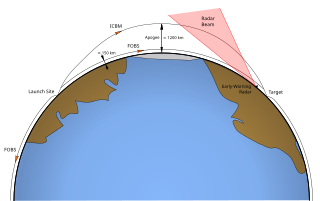
WThe Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS) was a nuclear-weapons delivery system developed in the 1960s by the Soviet Union. One of the first Soviet efforts to use space to deliver weapons, FOBS envisioned launching nuclear warheads into low Earth orbit before bringing them down on their targets.
 W
WA Hypervelocity Asteroid Intercept Vehicle (HAIV) is a spacecraft being developed by NASA to deflect dangerous Near Earth objects (NEOs) such as comets and asteroids that threaten colliding with Earth. HAIVs focus on utilizing powerful explosives, such as nuclear bombs, to achieve deflection by detonating on the surface of the NEO to change its trajectory away from Earth. This method of asteroid impact avoidance is intended to be used on dangerous NEOs detected within a short time frame before a possible impact event with Earth. The idea came about when asteroid detection improved. Since then, scientists and engineers have made a well thought out design for an HAIV.
 W
WThe Near Field Infrared Experiment (NFIRE) is a satellite which was proposed and developed by the Missile Defense Agency, a division of the United States Department of Defense. It was launched atop a Minotaur rocket, from Wallops Island, at 06:48 GMT on 24 April 2007. Though primarily designed to gather data on exhaust plumes from rockets, the satellite was also intended to contain a kill vehicle similar to kinds intended for the Strategic Defense Initiative. A missile was then to be fired at and nearly miss the instrumented kill vehicle. This feature was later removed.
 W
WThe Outer Space Treaty, formally the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, is a treaty that forms the basis of international space law. The treaty was opened for signature in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union on 27 January 1967, and entered into force on 10 October 1967. As of February 2021, 111 countries are parties to the treaty, while another 23 have signed the treaty but have not completed ratification. In addition, the Republic of China in Taiwan, which is currently recognized by 14 UN member states, ratified the treaty prior to the United Nations General Assembly's vote to transfer China's seat to the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1971.
 W
WPax Americana and the Weaponization of Space is a documentary film by Denis Delestrac with a music score by Amon Tobin. The film deals with the issue of space weapons and their politics, featuring interviews with several key United States military personnel, academics such as Noam Chomsky and others, including Martin Sheen. The film won the Best Documentary award at the 2009 Whistler Film Festival and has been selected in a number of international film festivals.
 W
WThe Safeguard Program was a U.S. Army anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system designed to protect the U.S. Air Force's Minuteman ICBM silos from attack, thus preserving the US's nuclear deterrent fleet. It was intended primarily to protect against the very small Chinese ICBM fleet, limited Soviet attacks and various other limited-launch scenarios. A full-scale attack by the Soviets would easily overwhelm it. It was designed to allow gradual upgrades to provide similar lightweight coverage over the entire United States over time.
 W
WSalyut 3 was a Soviet space station launched on 25 June 1974. It was the second Almaz military space station, and the first such station to be launched successfully. It was included in the Salyut program to disguise its true military nature. Due to the military nature of the station, the Soviet Union was reluctant to release information about its design, and about the missions relating to the station.
 W
WStarfire Optical Range is a United States Air Force research laboratory on the Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Its primary duty, according to the official website, is to "develop and demonstrate optical wavefront control technologies." The range is a secure lab facility and is a division of the Directed Energy Directorate of the Air Force Research Laboratory.
 W
WThe Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), nicknamed the "Star Wars program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons. The concept was announced on March 23, 1983 by President Ronald Reagan, a vocal critic of the doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD), which he described as a "suicide pact". Reagan called upon American scientists and engineers to develop a system that would render nuclear weapons obsolete.
 W
WTerra-3 was a Soviet laser testing centre, located on the Sary Shagan anti-ballistic missile (ABM) testing range in the Karaganda Region of Kazakhstan. It was originally built to test missile defense concepts, but these attempts were dropped after the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty was signed. The site later hosted two modest devices used primarily for experiments in space tracking. Several other laser test sites were also active during this period. During the 1980s, officials within the United States Department of Defense (DoD) suggested it was the site of a prototypical anti-satellite weapon system. The site was abandoned and is now partially disassembled.
 W
WThe TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station.